- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄383682 > OMAP5910(DSP) Dual-Core Processor PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | OMAP5910(DSP) |
| 英文描述: | Dual-Core Processor |
| 中文描述: | 雙核處理器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 41/160頁 |
| 文件大小: | 1997K |
| 代理商: | OMAP5910(DSP) |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁當(dāng)前第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁第155頁第156頁第157頁第158頁第159頁第160頁
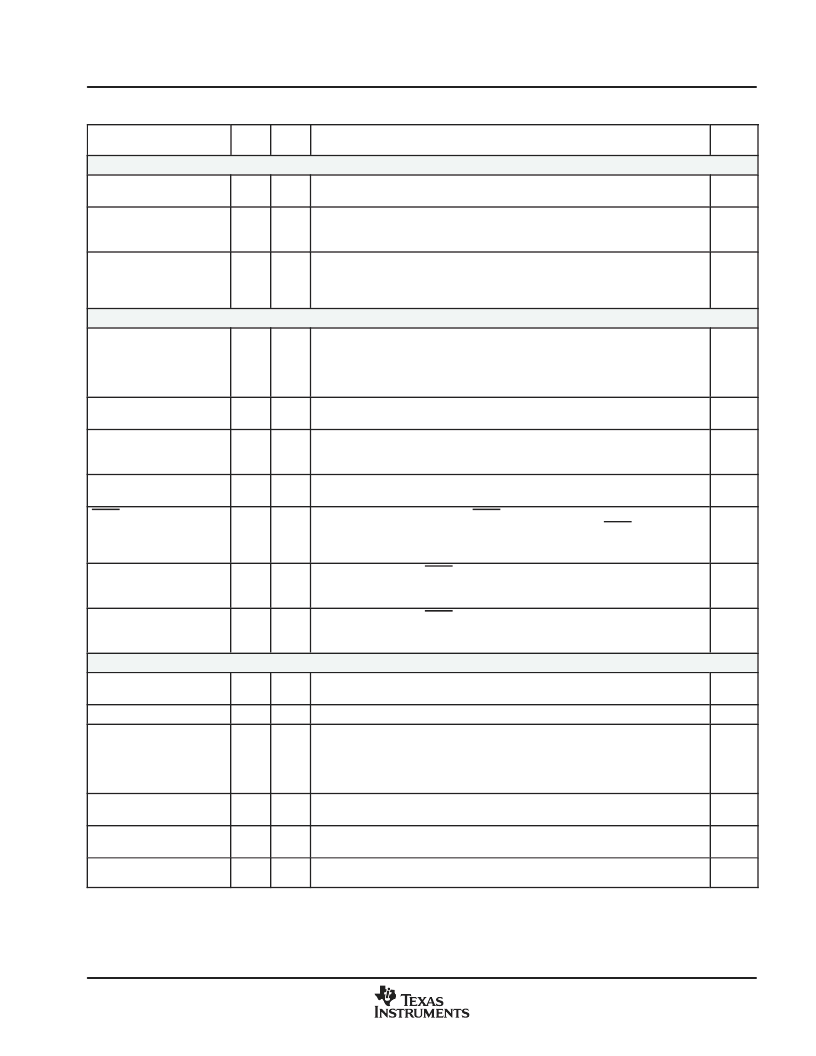
Introduction
29
August 2002 Revised August 2003
SPRS197B
Table 24. Signal Description (Continued)
GDY
BALL
SIGNAL
TYPE
DESCRIPTION
GZG
BALL
USB Miscellaneous Signals
USB.CLKO
W4
T3
USB clock output. 6-MHz divided clock output of the internal USB DPLL provided
for reference. Common for all USB host and Function peripherals.
O
USB.PUEN
W4
T3
USB pullup enable. Control output used in conjunction with an external pullup
resistor to implement USB device connect and disconnect via software.
USB.PUEN is used with the USB Function peripheral.
O
USB.VBUS
R18
M16
USB voltage bus enable. USB.VBUS is used to provide a logic-high voltage level
which may be used to enable pullup resistors on the USB bus to indicate
connection or disconnection status of the OMAP5910 device as a USB Function
device.
I
JTAG/Emulation Interface
TCK
W18
T14
IEEE Standard 1149.1 test clock. TCK is normally a free-running clock signal with
a 50% duty cycle. The changes on the test access port (TAP) of input signals TDI
and TMS are clocked into the TAP controller, instruction register, or selected test
data register on the rising edge of TCK. Changes at the TAP output signal TDO
occur on the falling edge of TCK.
I
TDI
Y19
U17
IEEE Standard 1149.1 test data input. TDI is clocked into the selected register
(instruction or data) on the rising edge of TCK.
I
TDO
AA19
U16
IEEE Standard 1149.1 test data output. The contents of the selected register
(instruction or data) are shifted out of TDO on the falling edge of TCK. TDO is in
the high-impedance state except when the scanning of data is in progress.
O
TMS
V17
R13
IEEE Standard 1149.1 test mode select. This serial control input is clocked into
the TAP controller on the rising edge of TCK.
I
TRST
Y18
U15
IEEE Standard 1149.1 test reset. TRST, when high, gives the IEEE standard
1149.1 scan system control of the operations of the device. If TRST is not
connected, or driven low, the device operates in its functional mode, and the IEEE
standard 1149.1 signals are ignored.
I
EMU0
V16
R17
Emulation pin 0. When TRST is driven high, EMU0 is used as an interrupt to or
from the emulator system and is defined as input/output by way of the IEEE
standard 1149.1 scan system.
I/O
EMU1
W17
T13
Emulation pin 1. When TRST is driven high, EMU1 is used as an interrupt to or
from the emulator system and is defined as input/output by way of the IEEE
standard 1149.1 scan system.
I/O
Device Clock Pins
CLK32K_IN
P13
N9
32-kHz clock input. Digital CMOS 32-kHz clock input driven by an external
32-kHz oscillator if the internal 32-kHz oscillator is not used.
I
CLK32K_OUT
Y12
N10
32-kHz clock output. Clock output reflecting the internal 32-kHz clock.
O
CLK32K_CTRL
AA20
T15
32-kHz clock selection control input. CLK32K_CTRL selects whether or not the
internal 32-kHz oscillator is used or if the 32-kHz clock is to be provided externally
via the CLK32K_IN input. If CLK32K_CTRL is high, the 32-kHz internal oscillator
is used; if CLK32K_CTRL is low, the CMOS input CLK32K_IN is used as a 32-kHz
clock source.
I
OSC32K_IN
W12
T10
32-kHz crystal XI connection. Analog clock input to 32-kHz oscillator for use with
external crystal.
analog
OSC32K_OUT
R12
T9
32-kHz crystal XO connection. Analog output from 32-kHz oscillator for use with
external crystal.
analog
OSC1_IN
Y2
R2
Base crystal XI connection. Analog input to base oscillator for use with external
crystal or to be driven by external 12- or 13-MHz oscillator.
analog
I = Input, O = Output, Z = High-Impedance
All core voltage supplies should be tied to the same voltage level (within 0.3 V). During system prototyping phases, it may be useful to maintain
a capability for independent measurement of core supply currents to facilitate power optimization experiments.
§See Sections 5.6.1 and 5.6.2 for special VSS considerations with oscillator circuits.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| OMAP5910(RISC) | Dual-Core Processor |
| OMC506 | Closed Loop Speed Controller For 3-Phase Brushless DC Motor MP-3T Package |
| OMC507 | 5 Amp. Push-Pull 3-Phase Brushless DC Motor Controller Driver(5A,推挽三相無刷直流電機控制驅(qū)動器) |
| OMC510 | 36V Hi-Rel Three-Phase Brushless DC Motor Controller in a PCB-1 package |
| OMC510 | DSP-Based Three-Phase Brushless DC Motor Controller(基于DSP的三相無刷直流電機控制器) |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| OMAP5910GGZG1 | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| OMAP5910GGZG2 | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| OMAP5910JGDY1R | 功能描述:IC OMAP DUAL-CORE PROC 289-BGA RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 嵌入式 - 微處理器 系列:OMAP-59xx 標(biāo)準包裝:60 系列:SCC 處理器類型:Z380 特點:全靜電 Z380 CPU 速度:20MHz 電壓:5V 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:144-LQFP 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝:144-LQFP 包裝:托盤 |
| OMAP5910JGDY2 | 功能描述:數(shù)字信號處理器和控制器 - DSP, DSC Applications Proc RoHS:否 制造商:Microchip Technology 核心:dsPIC 數(shù)據(jù)總線寬度:16 bit 程序存儲器大小:16 KB 數(shù)據(jù) RAM 大小:2 KB 最大時鐘頻率:40 MHz 可編程輸入/輸出端數(shù)量:35 定時器數(shù)量:3 設(shè)備每秒兆指令數(shù):50 MIPs 工作電源電壓:3.3 V 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 封裝 / 箱體:TQFP-44 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT |
| OMAP5910JGZG1 | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。