- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄383876 > T7698 (Lineage Power) Quad T1/E1 Line Interface and Octal T1/E1 Monitor(四T1/E1線接口和八T1/E1監(jiān)控器) PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | T7698 |
| 廠商: | Lineage Power |
| 英文描述: | Quad T1/E1 Line Interface and Octal T1/E1 Monitor(四T1/E1線接口和八T1/E1監(jiān)控器) |
| 中文描述: | 四T1/E1線路接口和八路的T1/E1監(jiān)視器(四個T1/E1線接口和八T1/E1的監(jiān)控器) |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 31/112頁 |
| 文件大小: | 1359K |
| 代理商: | T7698 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁當(dāng)前第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁
Data Sheet
January 1999
T7698 Quad T1/E1 Line Interface and Octal T1/E1 Monitor
31
Lucent Technologies Inc.
Line Interface Units: Transmit
(continued)
Transmitter Configuration Modes
Zero Substitution Encoding (CODE)
Zero substitution B8ZS/HDB3 encoding can be acti-
vated only in the single-rail system interface mode
(DUAL = 0). CODE = 1 selects the B8ZS/HDB3 encod-
ing operation in all four channels, regardless of the
state of the CODE[1—4] bits. The B8ZS/HDB3 encod-
ing operation can be selected for individual channels
independently by setting CODE = 0 and programming
CODE[1—4] bits for the respective channels.
Note:
Encoding and decoding are not independent.
Selecting B8ZS/HDB3 encoding in the transmit-
ter selects B8ZS/HDB3 decoding in the receiver.
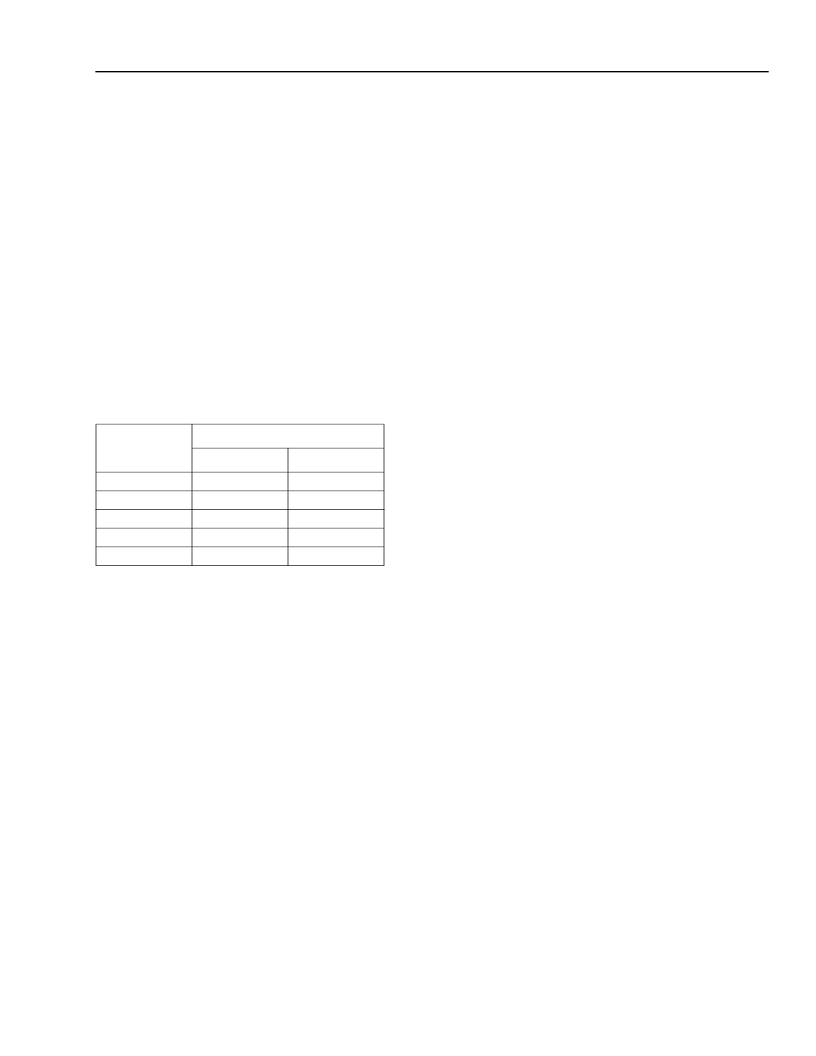
Table 13. Register Map for CODE Bits
When coding is selected for a given channel, data
transmitted from the system interface on TDATA (pins
17, 35, 67, 85) will be B8ZS/HDB3 encoded before
appearing on TTIP and TRING at the line interface.
Alarm Indication Signal Generator (XAIS)
When the transmit alarm indication signal control is set
(XAIS = 1) for a given channel (registers 6 to 9, bit 2), a
continuous stream of bipolar 1s is transmitted to the
line interface. The TPD/TDATA and TND inputs are
ignored during this mode. The XAIS input is ignored
when a remote loopback (RLOOP) is selected using
loopback control bits (LOOPA and LOOPB; registers 6
to 9, bits 3 and 4). (See the Line Interface Units: Loop-
backs section.)
To maintain application flexibility, the clock source used
for the AIS signal is selected by configuring BCLK
(pin 30). If a data rate clock is input on the BCLK pin, it
will be used to transmit the AIS signal. If BCLK = 0,
then TCLK is used to transmit the AIS signal (the
smoothed clock from the jitter attenuator is used if
JAT = 1 is selected). If BCLK = 1, then the internal
XCLK (after being divided by a factor of 16) is used to
transmit the AIS signal.
After BCLK is established, a minimum of
16 μs is required for the device to properly select the
clock. For any of the above options, the clock tolerance
must meet the normal line transmission rates (DS1
1.544 MHz ± 32 ppm; CEPT 2.048 MHz ± 50 ppm).
Transmitter Alarms
Loss of Transmit Clock (LOTC) Alarm
A loss of transmit clock alarm (LOTC = 1; registers 0
and 1, bits 3 and 7) is indicated if any of the clocks in
the transmit path disappear. This includes loss of TCLK
input, loss of RCLK during remote loopback, loss of jit-
ter attenuator output clock (when enabled), or the loss
of clock from the pulse-width controller.
For all of these conditions, a core transmitter timing
clock is lost and no data can be driven onto the line.
Output drivers TTIP and TRING are placed in a high-
impedance state when this alarm condition is active.
The LOTC interrupt is asserted between 3 μs and
16 μs after the clock disappears, and deasserts imme-
diately after detecting the first clock edge. The LOTC
alarm status bit will latch the alarm and remain set until
being cleared by a read (clear on read). Upon the tran-
sition from LOTC = 0 to LOTC = 1 a microprocessor
interrupt will be generated if the LOTC interrupt mask
bit (MLOTC; registers 2 and 3, bits 3 and 7) is not set
and the GMASK bit (register 4, bit 0) is not set.
An LOTC alarm may occur when RLOOP is activated
and deactivated due to the phase transient that occurs
as TCLK switches its source to and from RCLK. Setting
the prevent RLOOP alarm bit, (PRLALM = 1; LIU regis-
ter 12, bit 3) prevents the LOTC alarm from occurring at
the activation and deactivation of RLOOP but allows
the alarm to operate normally during the RLOOP active
period.
Transmit Driver Monitor (TDM) Alarm
The transmit driver monitor detects two conditions: a
nonfunctional link due to a fault on the primary of the
transmit transformer, or periods of no data transmis-
sion. The transmit driver monitor alarm (TDM; registers
0 and 1, bits 2 and 6) is the ORed function of both
faults and provides information about the integrity of
the transmit signal path.
The first monitoring function is provided to detect non-
functional links and protect the device from damage.
The alarm is set (TDM = 1) when one of the transmit-
ter's line drivers (TTIP or TRING) is shorted to power
supply or ground, or TTIP and TRING are shorted
together.
Name
Location
Register
5
12
12
11
11
Bit
3
7
6
6
4
CODE
CODE1
CODE2
CODE3
CODE4
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| T7705A | SUPPLY-VOLTAGE SUPERVISORS |
| T8100A | H.100/H.110 Interface and Time-Slot Interchanger(H.100/H.110接口和干線時間段交換機(jī)) |
| T8100 | H.100/H.110 Interface and Time-Slot Interchanger(H.100/H.110接口和干線時隙交換機(jī)) |
| T8102 | H.100/H.110 Interface and Time-Slot Interchanger(H.100/H.110接口和干線時隙交換機(jī)) |
| T8105 | H.100/H.110 Interface and Time-Slot Interchanger(H.100/H.110接口和干線時隙交換機(jī)) |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| T77 | 制造商:Thomas & Betts 功能描述:2-1/2"CONDUIT BODY,IRON,T,F-7 制造商:Cooper Crouse-Hinds 功能描述: 制造商:Thomas & Betts 功能描述:Fittings T-Fitting 2.5inch Non-Thread Iron |
| T7700 | 制造商:INTEL 制造商全稱:Intel Corporation 功能描述:Core2 Duo Processors and Core2 Extreme Processors for Platforms Based on Mobile 965 Express Chipset Family |
| T77000150 | 制造商:Assembly Value Added 功能描述: |
| T7705102CA | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述: |
| T7705A | 制造商:TI 制造商全稱:Texas Instruments 功能描述:SUPPLY-VOLTAGE SUPERVISORS |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。