- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄383645 > MT90812 (Mitel Networks Corporation) Integrated Digital Switch (IDX)(集成數(shù)字開關(guān)) PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | MT90812 |
| 廠商: | Mitel Networks Corporation |
| 英文描述: | Integrated Digital Switch (IDX)(集成數(shù)字開關(guān)) |
| 中文描述: | 綜合數(shù)字交換機(jī)(IDX的)(集成數(shù)字開關(guān)) |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 28/105頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 334K |
| 代理商: | MT90812 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)當(dāng)前第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)第77頁(yè)第78頁(yè)第79頁(yè)第80頁(yè)第81頁(yè)第82頁(yè)第83頁(yè)第84頁(yè)第85頁(yè)第86頁(yè)第87頁(yè)第88頁(yè)第89頁(yè)第90頁(yè)第91頁(yè)第92頁(yè)第93頁(yè)第94頁(yè)第95頁(yè)第96頁(yè)第97頁(yè)第98頁(yè)第99頁(yè)第100頁(yè)第101頁(yè)第102頁(yè)第103頁(yè)第104頁(yè)第105頁(yè)
MT90812
Advance Information
24
8.2
Constant Delay Mode (CST bit=1)
In Constant Delay mode, channel integrity is maintained by making use of a multiple Data Memory buffer
technique. The input channels written in any of the buffers during frame N will be read out during frame N+2.
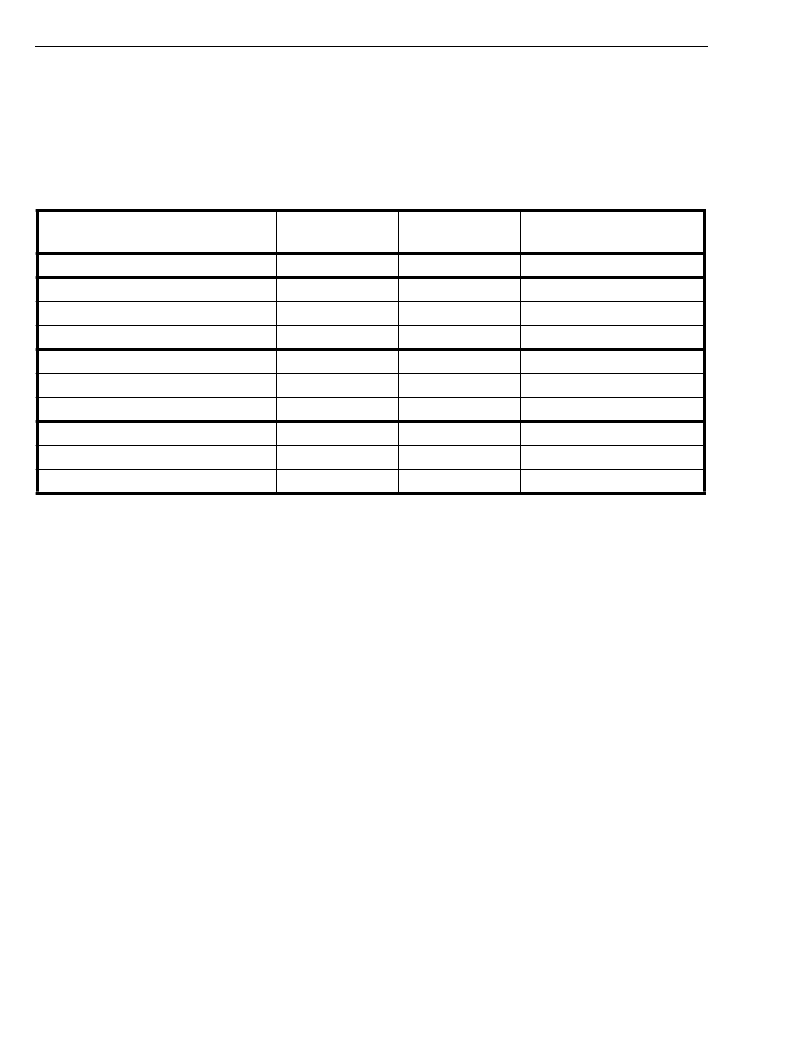
Table 8 lists the throughput delay for Constant Delay mode for all combinations of source and destination
streams.
Table 8 - Throughput Delay for Constant Delay Mode
Notes: t.s. = time-slot. t.s
. =2Mb/s t.s. = 3.9 us. t.s
. =4Mb/s t.s.=1.95 us. t.s
.=8Mb/s t.s.=0.975 us.
Delays are measured in timeslots and at the point in time from when the input channel is completely shifted in and when the output
channel is completely shifted out.
8.3
Delays in Conferencing
In a conference the data is read from Data Memory and transferred to the conference block as in constant
delay mode, with a 2 frame delay. If the incoming data is in frame N, then within the first half of frame N+2 the
conference output is calculated and stored in the conference output locations in Data Memory. The conference
output data is then switched to the outgoing data channel in Minimum Delay mode.
The minimum delay possible in a conference is one frame + two 2Mb/s-timeslots = 34 2Mb/s-timeslots. The
maximum delay possible is approximately 2 frames + 1.5 frames + two 2Mb/s-timeslots = 82 2Mb/s-timeslots.
9.0
Timing and Clock Control
The MT90812 clock control circuitry selects one of five possible input clock and frame pulse references. The
input clock can be either 4.092, 8.192, or 16.384 MHz as described in Section 9.1, “Input Timing Reference”.
Fig. 16 shows the Clock Control Functional diagram. The clock control circuitry provides an internal master
clock of 8.192 MHz, generates 2.048, 4.096, 8.192, and 10.24 MHz output clocks, F4 and F8 frame pulse
signals, as well as the serial interface timing for STi/o0, STi/o1 and EST0/1 serial streams. These signals are
either generated directly from the input clock source or from an on-chip analog PLL.
The on-chip analog PLL may be used to generate 2.048, 4.096, 8.192, and 10.24 MHz clocks. The PLL
operates in Master and Slave modes. Master mode provides more jitter attenuation while Slave mode
minimizes Phase delay. The PLL can provide the required 4.096 and 10.24 MHz clocks (C4 and C10) to be
supplied to the MT9171/72 DNIC devices. The C4 and C10 clocks meet the requirement that they be frequency
locked and maintain a jitter of less than or equal to 15ns with respect to each other, while maintaining at least
40/60 duty cycle for C10o. Refer to Section 9.3.1, “Master and Slave PLL Modes”.
Source and Destination streams
Input channel, n,
range
Output channel,
m, range
Throughput Delay
Sti0/1 -> Sto0/1
0-31
0-31
2x32-(n-m) t.s
2
.
2x32-(n-m) t.s
2
.
2x64-(n-m) t.s
4
.
2x128-(n-m) t.s
8
.
2x32-(n-m) t.s
2
.
2x64-(2n-m) t.s
4
.
2x128-(4n-m) t.s
8
.
2x32-(n-m) t.s
2
.
2x64-(n-2m) t.s
4
.
2x128-(n-4m) t.s
8
.
Est0/1 -> Est0/1 2.048 Mb/s
0-31
0-31
Est0/1 -> Est0/1 4.096 Mb/s
0-64
0-64
Est0/1 -> Est0/1 8.192 Mb/s
0-127
0-127
Sti0/1 -> Est0/1 2.048 Mb/s
0-31
0-31
Sti0/1 -> Est0/1 4.096 Mb/s
0-31
0-64
Sti0/1 -> Est0/1 8.192 Mb/s
0-31
0-127
Est0/1 2.048 Mb/s -> Sti0/1
0-31
0-31
Est0/1 4.096 Mb/s -> Sti0/1
0-64
0-31
Est0/1 8.192 Mb/s -> Sti0/1
0-127
0-31
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MT90840AK | Distributed Hyperchannel Switch |
| MT90840AP | Distributed Hyperchannel Switch |
| MT9085B | PAC - Parallel Access Circuit(并行存取電路) |
| MT9092 | Digital Telephone with HDLC(數(shù)字電話(帶高階數(shù)據(jù)鏈路控制HDLC)) |
| MT9092 | ISO2-CMOS ST-BUS⑩ FAMILY Digital Telephone with HDLC (HPhone-II) |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MT90812AL | 制造商:Microsemi Corporation 功能描述:SWIT FABRIC 192 X 192 16.384MBPS 5V 64MQFP - Trays 制造商:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:SWIT FABRIC 192 X 192 16.384MBPS 5V 64MQFP - Trays |
| MT90812AL1 | 制造商:Microsemi Corporation 功能描述:SWIT FABRIC 192 X 192 16.384MBPS 5V 64MQFP - Trays 制造商:Microsemi Corporation 功能描述:PB FREE INTEGRATED DIGITAL SWITCH |
| MT90812AP | 制造商:MITEL 制造商全稱:Mitel Networks Corporation 功能描述:Integrated Digital Switch (IDX) |
| MT90812AP1 | 制造商:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:SWIT FABRIC 192 X 192 16.384MBPS 5V 68PLCC /BAKE/DRYPACK - Rail/Tube 制造商:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:INTEGRATED DIGITAL SWCH |
| MT90812APR | 制造商:Microsemi Corporation 功能描述:SWIT FABRIC 192 X 192/64 X 64 1.048GBPS 5V 68PLCC - Tape and Reel |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。