- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄382377 > PCA5007H (NXP Semiconductors N.V.) Pager baseband controller PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | PCA5007H |
| 廠商: | NXP Semiconductors N.V. |
| 英文描述: | Pager baseband controller |
| 中文描述: | 傳呼機基帶控制器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 101/112頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 604K |
| 代理商: | PCA5007H |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁當前第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁
1998 Oct 07
101
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
Pager baseband controller
PCA5007
15.4
Address space
The PCA5007 has a 20 kbytes memory and therefore 15 address pins. Applying an address above 32 kbytes
(address<15> = 1) leads to the selection of the extra rows. The user should not apply these addresses during
programming.
15.5
Single byte programming
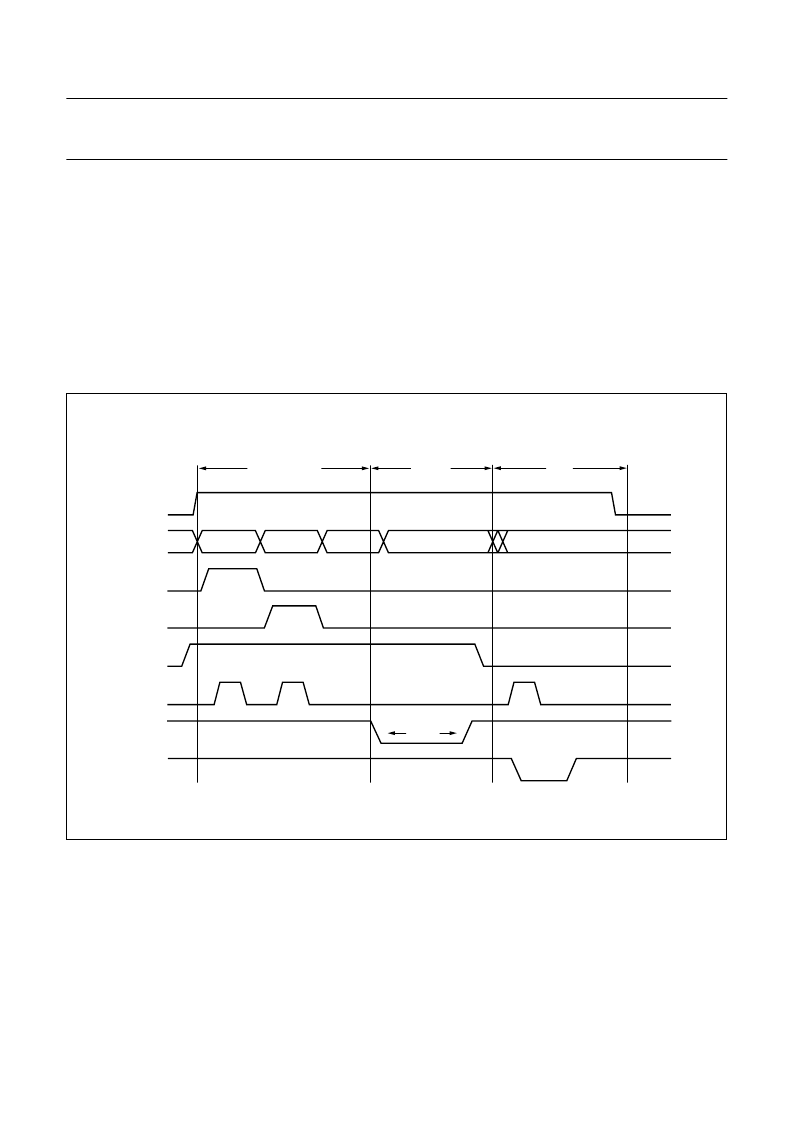
Programming and verifying is shown in Fig.65. The upper and lower address byte are loaded one after the other.
The address latch control signals select the proper latch and the RdStrb signal opens the latch (level sensitive).
The order of loading the latches is not important. The data is latched if write enable bar becomes active. After
programming a byte, this byte can be verified without reloading the addresses. If more bytes are programmed after each
other having the same upper address, it is not necessary to reload this upper address.
15.6
Multiple byte programming
A multiple byte programming mode has been implemented to increase programming speed. In this mode four bytes can
be programmed in parallel. The addresses of these four bytes have to be equal except for bit 0 and bit 1. Loading the
address and data latches is enabled by making PGM HIGH and GBMbpB LOW at the same time. Figure 66 shows the
address and data set-up and the program pulse. Loading the upper address is only necessary if it differs from the upper
address of the previous quadruple of bytes. In this mode the data latches are controlled by the RdStrb signal (level
sensitive). Figure 67 shows the verification in this mode. It should be noted that data 3 is verified before data 0. If this is
unwanted the lower address byte of data 0 has to be loaded before verifying data 0 and the lower address byte of data 1
before verifying data 1.
Fig.65 Single byte programming mode.
handbook, full pagewidth
MGR168
VPP
P0.0 to P0.7
P2.1/LS1
P2.0/LS0
P2.2/PGM
P2.3/RdStrb
P2.5/WEB
P2.4/GBMbpB
Addr high
Addr low
Data in
Data out
Addr/data set-up
program
100
μ
s
verify
VDD = 12.5 to 13 V
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PCA5010 | Pager baseband controller |
| PCA5010H | Pager baseband controller |
| PCA82C200 | STAND-ALONE CAN-CONTROLLER |
| PCA82C200P | STAND-ALONE CAN-CONTROLLER |
| PCA82C200T | STAND-ALONE CAN-CONTROLLER |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| PCA5007H/XXX | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:8-Bit Microcontroller |
| PCA5010 | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:Pager baseband controller |
| PCA5010H | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:Pager baseband controller |
| PCA5010H/XXX | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:MICROCONTROLLER|8-BIT|8051 CPU|CMOS|QFP|48PIN|PLASTIC |
| PCA503HL320 | 制造商:ADAM-TECH 制造商全稱:Adam Technologies, Inc. 功能描述:ZIF FLEX CIRCUIT CONNECTOR |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。