- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄382386 > PDI1394P25BY (NXP SEMICONDUCTORS) 1-port 400 Mbps physical layer interface PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | PDI1394P25BY |
| 廠商: | NXP SEMICONDUCTORS |
| 元件分類: | 網絡接口 |
| 英文描述: | 1-port 400 Mbps physical layer interface |
| 中文描述: | DATACOM, INTERFACE CIRCUIT, PQFP48 |
| 封裝: | 7 X 7 MM, 1.40 MM HEIGHT, PLASTIC, MS-026, SOT-313-2, LQFP-48 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 25/42頁 |
| 文件大小: | 214K |
| 代理商: | PDI1394P25BY |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁當前第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁
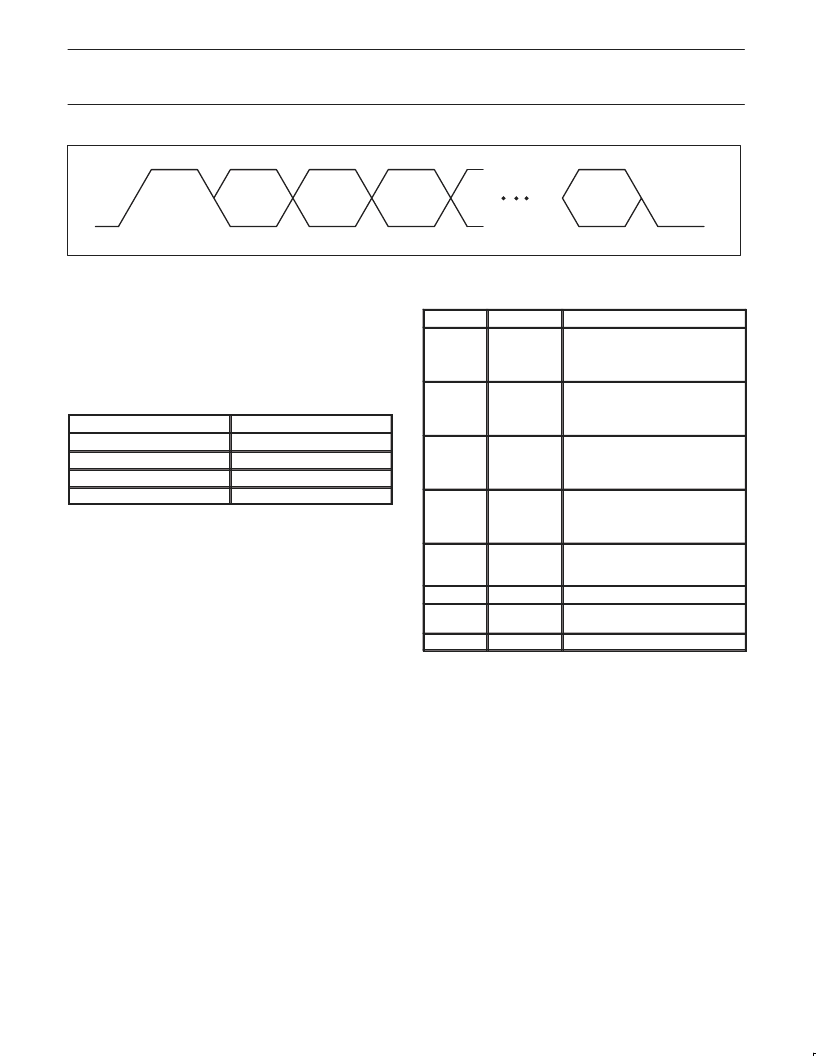
Philips Semiconductors
Product data
PDI1394P25BY
1-port 400 Mbps physical layer interface
2002 Oct 11
25
SV01758
LR0
LR1
LR2
LR3
LR(n–2)
LR(n–1)
Figure 14.
LREQ Request Stream
18.1
To request access to the bus, to read or write a PHY register, or to
control arbitration acceleration, the LLC sends a serial bit stream on
the LREQ terminal as shown in Figure 14.
LLC service request
The length of the stream will vary depending on the type of request
as shown in Table 11.
Table 11. Request Stream Bit Length
REQUEST TYPE
NUMBER OF BITS
Bus request
7 or 8
Read register request
9
Write register request
17
Acceleration control request
6
Regardless of the type of request, a start bit of 1 is required at the
beginning of the stream, and a stop bit of 0 is required at the end of
the stream. The second through fourth bits of the request stream
indicate the type of the request. In the descriptions below, bit 0 is the
most significant, and is transmitted first in the request bit stream.
The LREQ terminal is normally low.
Encoding for the request type is shown in Table 12.
Table 12. Request Type Encoding
LR1–LR3
NAME
DESCRIPTION
000
ImmReq
Immediate bus request. Upon
detection of idle, the PHY takes
control of the bus immediately
without arbitration
001
IsoReq
Isochronous bus request. Upon
detection of idle, the PHY arbitrates
for the bus without waiting for a
subaction gap.
010
PriReq
Priority bus request. The PHY
arbitrates for the bus after a
subaction gap, ignores the fair
protocol.
011
FairReq
Fair bus request. The PHY
arbitrates for the bus after a
subaction gap, follows the fair
protocol
100
RdReg
The PHY returns the specified
register contents through a status
transfer.
101
WrReg
Write to the specified register.
110
AccelCtl
Enable or disable asynchronous
arbitration acceleration.
Reserved.
111
Reserved
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PDI20AC1H0R | |
| PDI20AC1H0X | |
| PDI20AC1HR0 | |
| PDI20AC1HRX | |
| PDI20AC1L0R | |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| PDI1394P25EC | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:1-port 400 Mbps physical layer interface |
| PDI-15R | 制造商:Power Dynamics Inc 功能描述: |
| PDI-15RH-5 | 制造商:Power Dynamics Inc 功能描述: |
| PDI-15RH-5-R-G30 | 制造商:Power Dynamics Inc 功能描述:PDI Series 15 Position Right Angle Socket High Density D-Sub |
| PDI-15S | 制造商:POWER DYNAMICS 功能描述: 制造商:Power Dynamics Inc 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。