- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄384797 > OR4E6 (Lineage Power) Field-Programmable Gate Arrays(現(xiàn)場可編程門陣列) PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | OR4E6 |
| 廠商: | Lineage Power |
| 英文描述: | Field-Programmable Gate Arrays(現(xiàn)場可編程門陣列) |
| 中文描述: | 現(xiàn)場可編程門陣列(現(xiàn)場可編程門陣列) |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 66/132頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 2667K |
| 代理商: | OR4E6 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁當前第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁
66
Lucent Technologies Inc.
Preliminary Data Sheet
August 2000
ORCA Series 4 FPGAs
FPGA Configuration Modes
(continued)
5-9739(F)
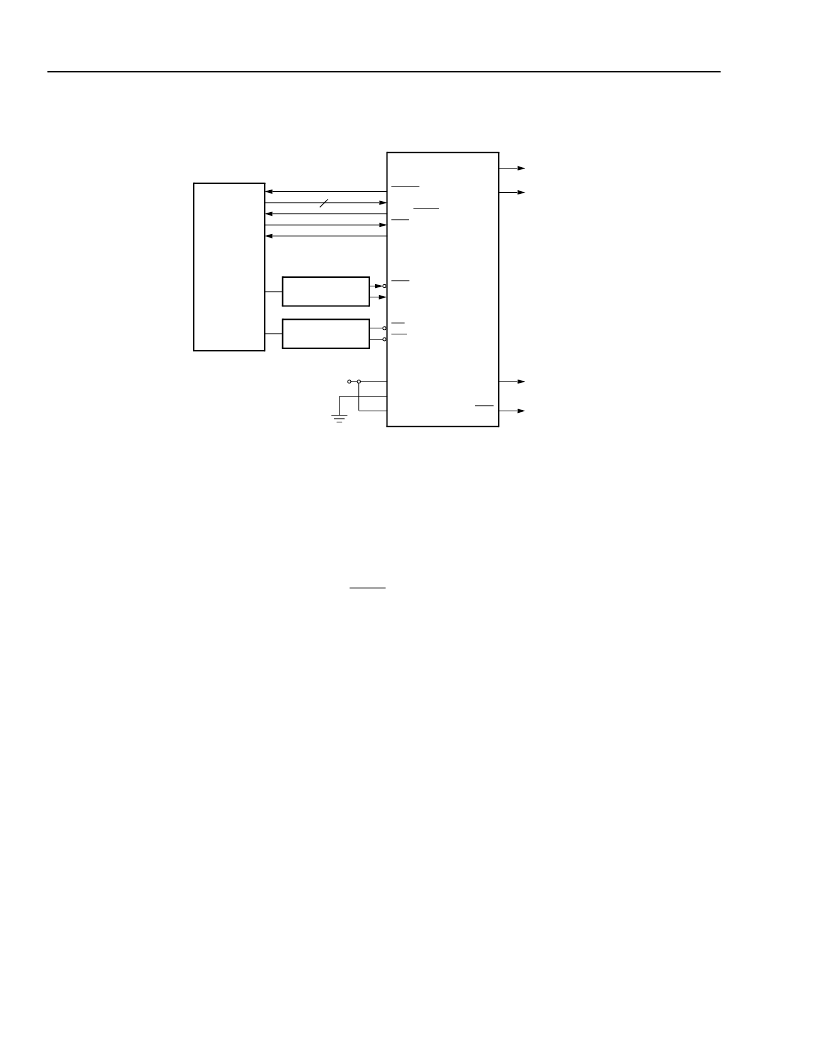
Figure 40. Asynchronous Peripheral Configuration
Microprocessor Interface Mode
The built-in
MPI
in Series 4 FPGAs is designed for use in configuring the FPGA.
Figure 41 show the glueless inter-
face for FPGA configuration and readback from the PowerPCprocessor. When enabled by the mode pins, the
MPI
handles all configuration/readback control and handshaking with the host processor. For single FPGA configura-
tion, the host sets the configuration control register
PRGM
bit to zero then back to a one and, after reading that the
configuration write data acknowledge register is high, transfers data 8, 16, or 32 bits at a time to the FPGA’s D[#:0]
input pins. If configuring multiple FPGAs through daisy-chain operation is desired, the SYS_DAISY bit must be set
in the configuration control register of the
MPI
.
There are two options for using the host interrupt request in configuration mode. The configuration control register
offers control bits to enable the interrupt on either a bit stream error or to notify the host processor when the FPGA
is ready for more configuration data. The
MPI
status register may be used in conjunction with, or in place of, the
interrupt request options. The status register contains a 2-bit field to indicate the bit stream error status. As previ-
ously mentioned, there is also a bit to indicate the
MPI
’s readiness to receive another byte of configuration data. A
flow chart of the
MPI
configuration process is shown in Figure 42.
MICRO-
PROCESSOR
PRGM
D[7:0]
RDY/BUSY
INIT
DONE
ORCA
SERIES
FPGA
DOUT
CCLK
HDC
LDC
M2
M1
M0
V
DD
TO DAISY-
CHAINED
DEVICES
ADDRESS
DECODE LOGIC
BUS
CONTROLLER
8
CS0
CS1
RD
WR
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| ORT4622 | Field-Programmable System Chip (FPSC) Four Channel x 622 Mbits/s Backplane Transceiver(現(xiàn)場可編程系統(tǒng)芯片(四通道x 622 M位/秒背板收發(fā)器)) |
| ORT8850 | Field-Programmable System Chip(現(xiàn)場可編程系統(tǒng)芯片) |
| OS8740230 | Si Optical Receiver, 40 - 870MHz, 225mA max. @ 24VDC |
| OSC-1A0 | Ultra Miniature TCXO |
| OSC-1A1 | Ultra Miniature TCXO |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| OR4E6-1BA352 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:FPGA |
| OR4E6-1BC432 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:FPGA |
| OR4E6-1BM680 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:FPGA |
| OR4E6-2BA352 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:FPGA |
| OR4E6-2BC432 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:FPGA |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。