- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄385408 > HTG2150 (Holtek Semiconductor Inc.) 8-Bit 320 Pixel LCD Microcontroller PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | HTG2150 |
| 廠商: | Holtek Semiconductor Inc. |
| 英文描述: | 8-Bit 320 Pixel LCD Microcontroller |
| 中文描述: | 8位微控制器320像素LCD |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 17/49頁 |
| 文件大小: | 316K |
| 代理商: | HTG2150 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁當(dāng)前第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁
HTG2150
17
July 24, 2000
Preliminary
All I/O ports maintain their original status.
The PD flag is set and the TO flag is cleared.
The system can leave the HALT mode by means
of an external reset, an interrupt, an external
falling edge signal on port Aor a WDT overflow.
An external reset causes a device initialization
and the WDT overflow performs a warm reset .
ByexaminingtheTOandPDflags,thereasonfor
chip reset can be determined. The PD flag is
cleared when the system powers up or upon exe-
cuting the CLR WDT instruction and is set when
the HALT instruction is executed. The TO flag is
set if the WDT time-out occurs, and causes a
wake-up that only resets the PC and SP, the oth-
ers maintain their original status.
The port Awake-up and interrupt methods can
be considered as a continuation of normal exe-
cution. Each bit in port A can be independently
selected to wake up the device by mask option.
Awakening from an I/O port stimulus, the pro-
gram will resume execution of the next instruc-
tion. If awakening from an interrupt, two
sequences may happen. If the related interrupt
is disabled or the interrupt is enabled but the
stack is full, the program will resume execution
at the next instruction. If the interrupt is en-
abledandthestackisnotfull,theregularinter-
rupt response takes place.
Once a wake-up event occurs, it takes 1024 t
SYS
(system clock period) to resume normal opera-
tion. In other words, a dummy cycle period will
be inserted after the wake-up. If the wake-up
results from an interrupt acknowledge, the ac-
tual interrupt subroutine will be delayed by one
more cycle. If the wake-up results in the next
instruction execution, this will be executed im-
mediately after a dummy period has finished. If
an interrupt request flag is set to 1 before en-
tering the HALT mode, the wake-up function of
the related interrupt will be disabled.
To minimize power consumption, all I/O pins
should be carefully managed before entering
the HALT status.
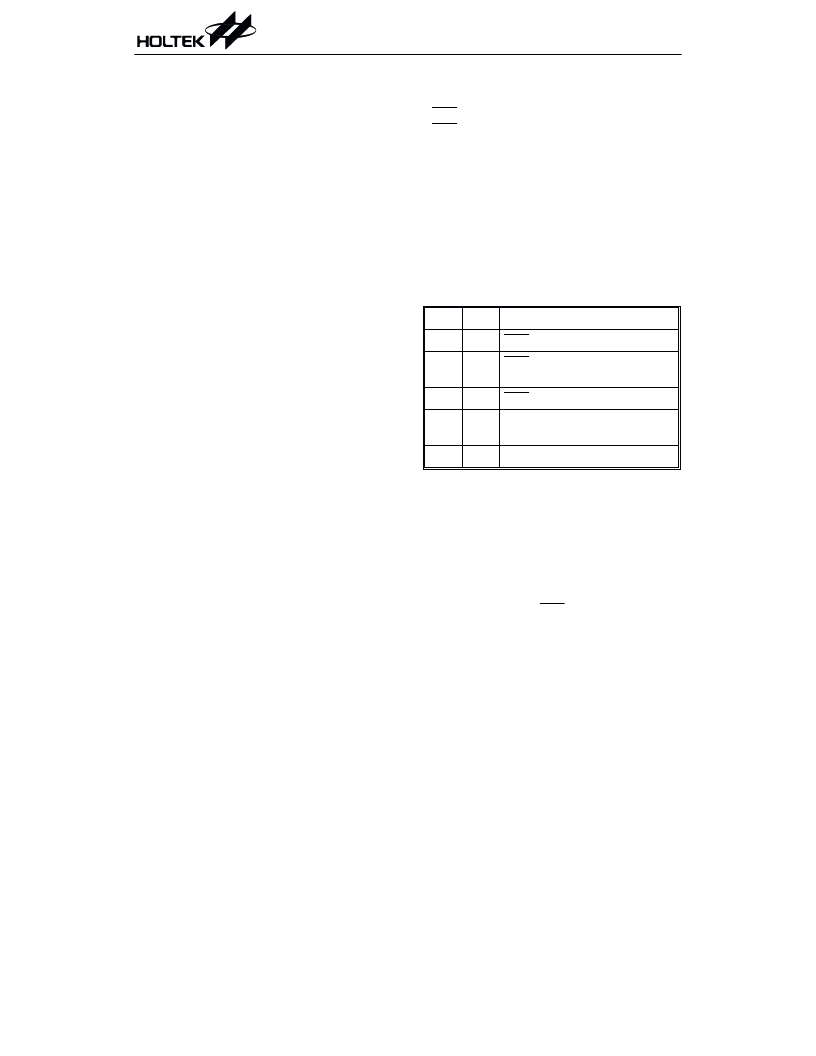
Reset
Therearethreewaysinwhicharesetcanoccur:
RES reset during normal operation
RES reset during HALT
WDT time-out reset during normal operation
The WDT time-out during HALT is different
from other chip reset conditions, since it can
perform a warm reset
and SP, leaving the other circuits in their origi-
nal state. Some registers remain unchanged
during other reset conditions. Most registers
are reset to the initial condition when the re-
set conditions are met. By examining the PD
and TO flags, the program can distinguish be-
tween different chip resets .
that just resets the PC
TO
PD
RESET Conditions
0
0
RES reset during power-up
u
u
RES reset during normal
operation
0
1
RES wake-up HALT
1
u
WDT time-out during normal
operation
1
1
WDT wake-up HALT
Note: u means unchanged
To guarantee that the system oscillator has
started and stabilized, the SST (System
Start-upTimer)providesanextra-delayof1024
system clock pulses when the system powers up
or awakes from the HALT state.
When a system power-up occurs, the SST delay
is added during the reset period. But when the
reset comes from the RES pin, the SST delay is
disabled. Any wake-up from HALT will enable
the SST delay.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| HTG2190 | 8-Bit 1024 Pixel LCD Microcontroller |
| HTIP117D | PNP EPITAXIAL PLANAR TRANSISTOR |
| HTM1505 | RELATIVE HUMIDITY AND TEMPERATURE MODULE |
| HTM2500 | RELATIVE HUMIDITY/ TEMPERATURE MODULE |
| HTS2010SMD | TEMPERATURE AND RELATIVE HUMIDITY SENSOR |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| HTG2150_02 | 制造商:HOLTEK 制造商全稱:Holtek Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:8-Bit 320 Pixel Dot Matrix LCD MCU Series |
| HTG2170 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:8-Bit Microcontroller |
| HTG2190 | 制造商:HOLTEK 制造商全稱:Holtek Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:8-Bit 1024 Pixel Dot Matrix LCD MCU Series |
| HTG2190_02 | 制造商:HOLTEK 制造商全稱:Holtek Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:8-Bit 1024 Pixel Dot Matrix LCD MCU Series |
| HTG3110 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Speech Synthesizer |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。