- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄359236 > MTVX2602 (Zarlink Semiconductor Inc.) Managed 24 Port 10/100 Mbps Ethernet Switch PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | MTVX2602 |
| 廠商: | Zarlink Semiconductor Inc. |
| 英文描述: | Managed 24 Port 10/100 Mbps Ethernet Switch |
| 中文描述: | 管理的24端口10/100 Mbps以太網(wǎng)交換機(jī) |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 30/147頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 924K |
| 代理商: | MTVX2602 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)當(dāng)前第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)第77頁(yè)第78頁(yè)第79頁(yè)第80頁(yè)第81頁(yè)第82頁(yè)第83頁(yè)第84頁(yè)第85頁(yè)第86頁(yè)第87頁(yè)第88頁(yè)第89頁(yè)第90頁(yè)第91頁(yè)第92頁(yè)第93頁(yè)第94頁(yè)第95頁(yè)第96頁(yè)第97頁(yè)第98頁(yè)第99頁(yè)第100頁(yè)第101頁(yè)第102頁(yè)第103頁(yè)第104頁(yè)第105頁(yè)第106頁(yè)第107頁(yè)第108頁(yè)第109頁(yè)第110頁(yè)第111頁(yè)第112頁(yè)第113頁(yè)第114頁(yè)第115頁(yè)第116頁(yè)第117頁(yè)第118頁(yè)第119頁(yè)第120頁(yè)第121頁(yè)第122頁(yè)第123頁(yè)第124頁(yè)第125頁(yè)第126頁(yè)第127頁(yè)第128頁(yè)第129頁(yè)第130頁(yè)第131頁(yè)第132頁(yè)第133頁(yè)第134頁(yè)第135頁(yè)第136頁(yè)第137頁(yè)第138頁(yè)第139頁(yè)第140頁(yè)第141頁(yè)第142頁(yè)第143頁(yè)第144頁(yè)第145頁(yè)第146頁(yè)第147頁(yè)
MVTX2602
Data Sheet
30
Zarlink Semiconductor Inc.
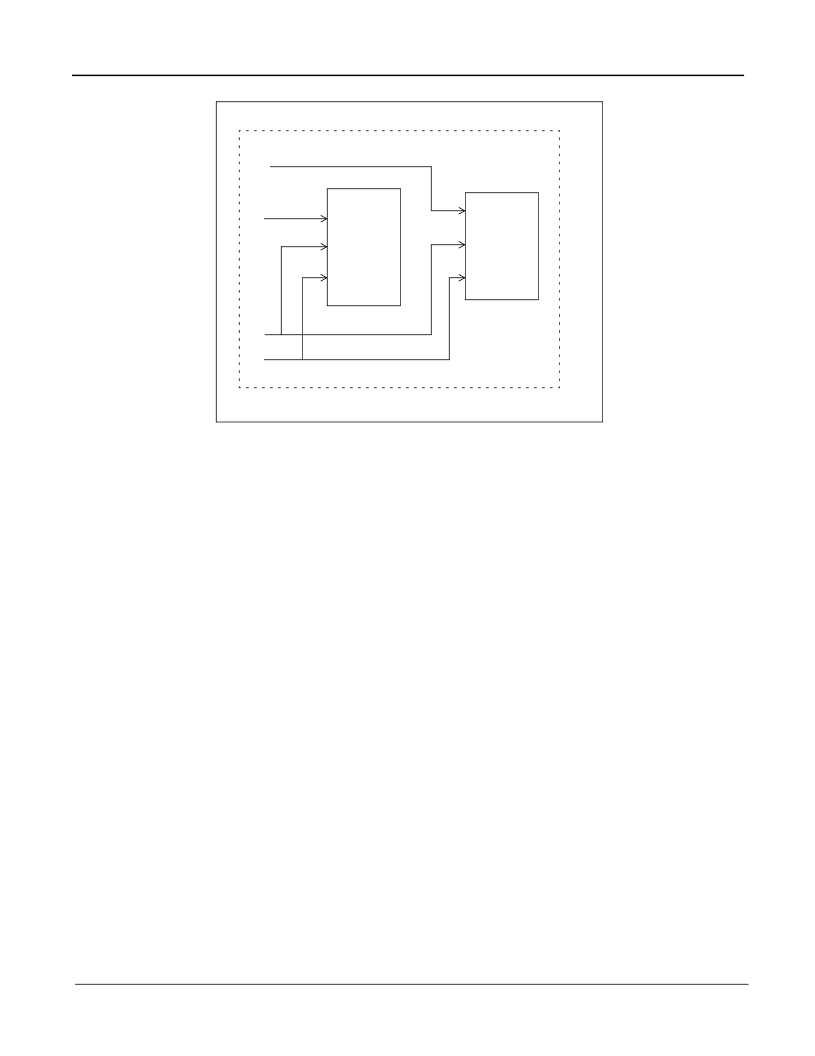
Figure 9 - Memory Configuration for 1 Bank, 1 Layer, 2 MB
6.0 Frame Engine
6.1
Data Forwarding Summary
When a frame enters the device at the RxMAC, the RxDMA will move the data from the MAC RxFIFO to the FDB.
Data is moved in 8-byte granules in conjunction with the scheme for the SRAM interface.
A switch request is sent to the Search Engine. The Search Engine processes the switch request.
A switch response is sent back to the Frame Engine and indicates whether the frame is unicast or multicast and its
destination port or ports. A VLAN table lookup is performed as well.
A Transmission Scheduling Request is sent in the form of a signal notifying the TxQ manager. Upon receiving a
Transmission Scheduling Request, the device will format an entry in the appropriate Transmission Scheduling
Queue (TxSch Q) or Queues. There are 4 TxSch Q for each 10/100, one for each priority. Creation of a queue
entry either involves linking a new job to the appropriate linked list if unicast or adding an entry to a physical queue
if multicast.
When the port is ready to accept the next frame, the TxQ manager will get the head-of-line (HOL) entry of one of
the TxSch Qs, according to the transmission scheduling algorithm (to ensure per-class quality of service). The
unicast linked list and the multicast queue for the same port-class pair are treated as one logical queue. The older
HOL between the two queues goes first. For 10/100 ports multicast queue 0 is associated with unicast queue 0 and
multicast queue 1 is associated with unicast queue 2.
The TxDMA will pull frame data from the memory and forward it granule-by-granule to the MAC TxFIFO of the
destination port.
Memory
256 K
32 bits
SRAM
Memory
256 K
32 bits
Data LA_D[63:32]
Data LA_D[31:0]
Address LA_A[20:3]
Bank A (2 M One Layer)
Bootstraps: TSTOUT7 = Open, TSTOUT13 = Open, TSTOUT4 = Open
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MU456FC-RD | SUPER RED 0.56 FOUR DIGIT NUMERIC DISPLAYS |
| MU9C1480A-90DC | Content Addressable Memory |
| MU9C1480A-90DI | Content Addressable Memory |
| MU9C1480B-50TAC | Content Addressable Memory |
| MU9C1480B-70TAC | Content Addressable Memory |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MTW 106 D | 制造商:KNITTER-SWITCH 功能描述:TOGGLE SWITCH SPST ON-ON |
| MTW 106 E | 制造商:KNITTER-SWITCH 功能描述:SWITCH SPST ON-OFF-ON |
| MTW 106 G | 制造商:knitter-switch 功能描述: |
| MTW 206 N | 制造商:KNITTER-SWITCH 功能描述:TOGGLE SWITCH DPDT ON-ON |
| MTW 206 P | 制造商:KNITTER-SWITCH 功能描述:SWITCH DPDT ON-OFF-ON |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。