- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄299576 > OR3T125-4B432 FPGA, 784 CLBS, 92000 GATES, PBGA432 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | OR3T125-4B432 |
| 元件分類: | FPGA |
| 英文描述: | FPGA, 784 CLBS, 92000 GATES, PBGA432 |
| 封裝: | BGA-432 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 128/210頁 |
| 文件大小: | 2138K |
| 代理商: | OR3T125-4B432 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁當前第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁第155頁第156頁第157頁第158頁第159頁第160頁第161頁第162頁第163頁第164頁第165頁第166頁第167頁第168頁第169頁第170頁第171頁第172頁第173頁第174頁第175頁第176頁第177頁第178頁第179頁第180頁第181頁第182頁第183頁第184頁第185頁第186頁第187頁第188頁第189頁第190頁第191頁第192頁第193頁第194頁第195頁第196頁第197頁第198頁第199頁第200頁第201頁第202頁第203頁第204頁第205頁第206頁第207頁第208頁第209頁第210頁
24
Lucent Technologies Inc.
Preliminary Data Sheet, Rev. 1
ORCA Series 3 FPGAs
September 1998
Programmable Logic Cells (continued)
PLC Routing Resources
Generally, the
ORCA Foundry Development System is
used to automatically route interconnections. Interac-
tive routing with the
ORCA Foundry design editor
(EPIC) is also available for design optimization. To use
EPIC for interactive layout, an understanding of the
routing resources is needed and is provided in this sec-
tion.
The routing resources consist of switching circuitry and
metal interconnect segments. Generally, the metal
lines which carry the signals are designated as routing
segments. The switching circuitry connects the routing
segments, providing one or more of three basic func-
tions: signal switching, amplification, and isolation. A
net running from a PFU or PIC output (source) to a
PLC or PIC input (destination) consists of one or more
routing segments, connected by switching circuitry
called configurable interconnect points (CIPs).
The following sections discuss PLC, PIC, and inter-
quad routing resources. This section discusses the
PLC switching circuitry, intra-PLC routing, inter-PLC
routing, and clock distribution.
Configurable Interconnect Points
The process of connecting routing segments uses
three basic types of switching circuits: two types of
configurable interconnect points (CIPs) and bidirec-
tional buffers (BIDIs). The basic element in CIPs is one
or more pass transistors, each controlled by a configu-
ration RAM bit. The two types of CIPs are the mutually
exclusive (or multiplexed) CIP and the independent
CIP.
A mutually exclusive set of CIPs contains two or more
CIPs, only one of which can be on at a time. An inde-
pendent CIP has no such restrictions and can be on
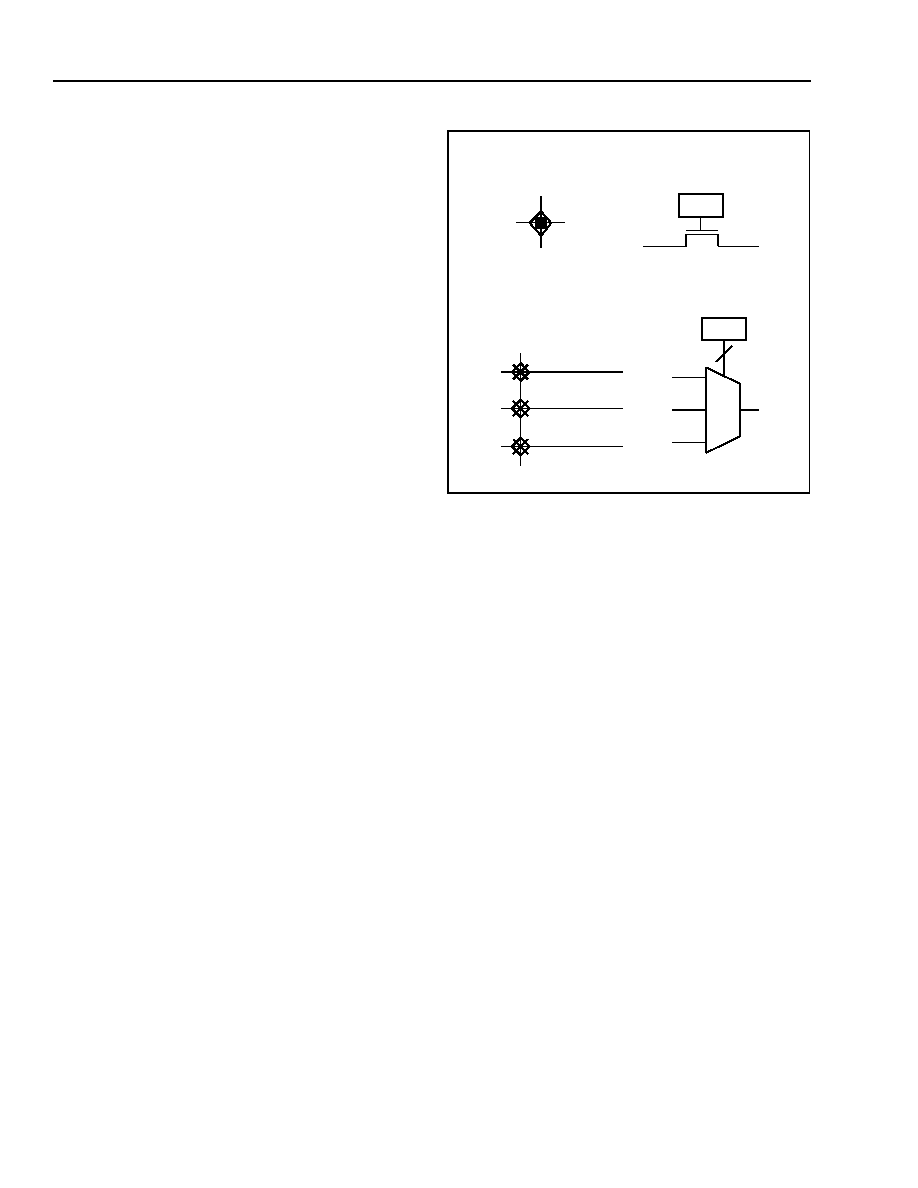
independent of the state of other CIPs. Figure 18
shows an example of both types of CIPs.
Key: C = configuration data.
5-5973(C)
Figure 18. Configurable Interconnect Point
3-Statable Bidirectional Buffers
Bidirectional buffers, previously described in the SLIC
section of the programmable logic cell discussion, pro-
vide isolation as well as amplification for signals routed
a long distance. Bidirectional buffers are also used to
route signals diagonally in the PLC (described later in
the subsection entitled Intra-PLC Routing), and BIDIs
can be used to indirectly route signals through the
switching routing (xSW) segments. Any number from
zero to ten BIDIs can be used in a given PLC.
MULTIPLEXED CIP
A
B
C
O
A
B
C
O
CD
INDEPENDENT CIP
A
B
CD
B
A
=
2
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| OR3T125-4B600 | FPGA, 784 CLBS, 92000 GATES, PBGA600 |
| OR3T125-4BA352I | FPGA, 784 CLBS, 92000 GATES, PBGA352 |
| OR3T125-4BA352 | FPGA, 784 CLBS, 92000 GATES, PBGA352 |
| OR3T125-5B432 | FPGA, 784 CLBS, 92000 GATES, PBGA432 |
| OR3T125-5B600 | FPGA, 784 CLBS, 92000 GATES, PBGA600 |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| OR3T125-4BC432I | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) |
| OR3T125-4BC600I | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) |
| OR3T125-4PS208I | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) |
| OR3T125-4PS240I | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) |
| OR3T125-5BA352 | 制造商:AGERE 制造商全稱:AGERE 功能描述:3C and 3T Field-Programmable Gate Arrays |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。