- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄385376 > HFA3861BIN96 (INTERSIL CORP) Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Baseband Processor PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | HFA3861BIN96 |
| 廠商: | INTERSIL CORP |
| 元件分類: | 無(wú)繩電話/電話 |
| 英文描述: | Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Baseband Processor |
| 中文描述: | TELECOM, CELLULAR, BASEBAND CIRCUIT, PQFP64 |
| 封裝: | 10 X 10 MM, PLASTIC, MS-026ACD, TQFP-64 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 9/36頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 733K |
| 代理商: | HFA3861BIN96 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)當(dāng)前第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)
9
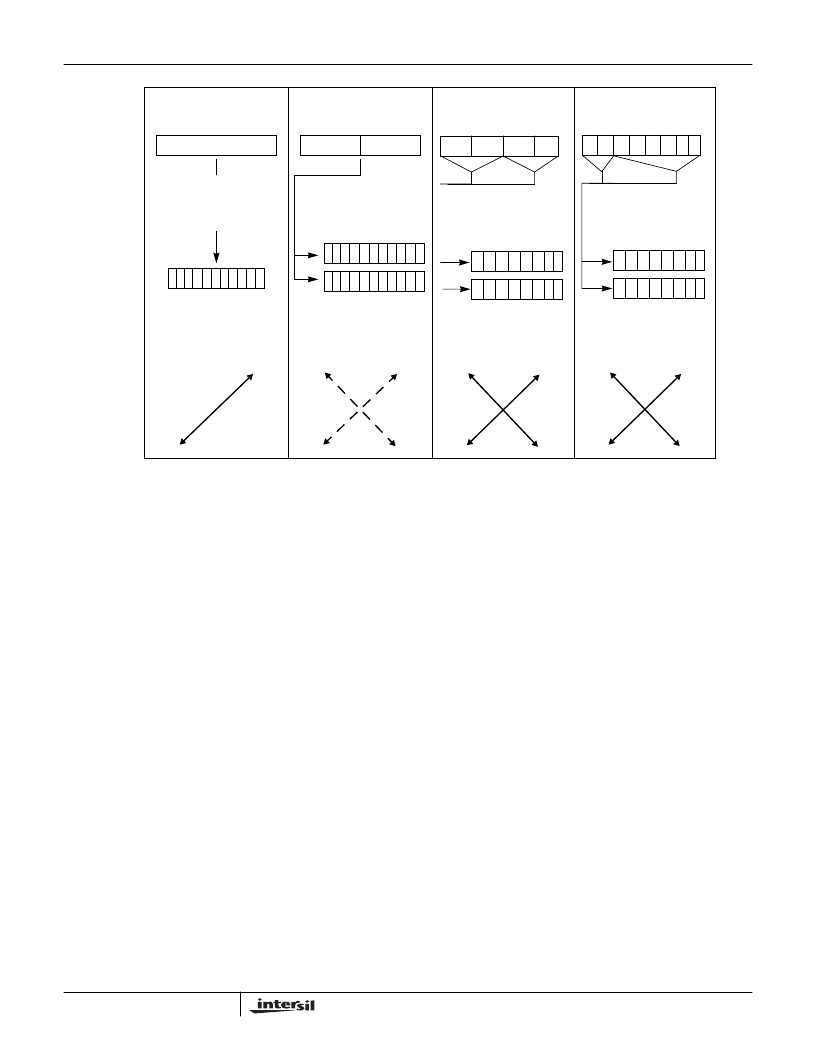
For the 1 and 2Mbps modes, the transmitter accepts data
from the external source, scrambles it, differentially encodes
it as either DBPSK or DQPSK, and spreads it with the BPSK
PN sequence. The baseband digital signals are then output
to the external IF modulator.
For the CCK modes, the transmitter inputs the data and
partitions it into nibbles (4 bits) or bytes (8 bits). At 5.5Mbps,
it uses two of those bits to select one of 4 complex spread
sequences from a table of CCK sequences and then QPSK
modulates that symbol with the remaining 2 bits. Thus, there
are 4 possible spread sequences to send at four possible
carrier phases, but only one is sent. This sequence is then
modulated on the I and Q outputs. The initial phase
reference for the data portion of the packet is the phase of
the last bit of the header. At 11Mbps, one byte is used as
above where 6 bits are used to select one of 64 spread
sequences for a symbol and the other 2 are used to QPSK
modulate that symbol. Thus, the total possible number of
combinations of sequence and carrier phases is 256. Of
these only one is sent.
The bit rate Table 3 shows examples of the bit rates and the
symbol rates and Figure 7 shows the modulation schemes.
The modulator is completely independent from the
demodulator, allowing the PRISM baseband processor to be
used in full duplex operation.
Header/Packet Description
The HFA3861B is designed to handle packetized Direct
Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) data transmissions.
The HFA3861B generates its own preamble and header
information. It uses two packet preamble and header
configurations. The first is backwards compatible with the
existing IEEE 802.11-1997 1 and 2Mbps modes and the
second is the optional shortened mode which maximizes
throughput at the expense of compatibility with legacy
equipment.
In the long preamble mode, the device uses a
synchronization preamble of 128 symbols along with a
header that includes four fields. The preamble is all 1's
(before entering the scrambler) plus a start frame delimiter
(SFD). The actual transmitted pattern of the preamble is
randomized by the scrambler. The preamble is always
transmitted as a DBPSK waveform (1Mbps). The duration of
the long preamble and header is 192
μ
s.
In the short preamble mode, the modem uses a
synchronization field of 56 zero symbols along with an SFD
transmitted at 1Mbps. The short header is transmitted at
2Mbps. The synchronization preamble is all 0’s to distinguish
it from the long header mode and the short preamble SFD is
the time reverse of the long preamble SFD. The duration of
the short preamble and header is 96
μ
s.
802.11 DSSS BPSK
1Mbps
BARKER
802.11 DSSS QPSK
2Mbps
BARKER
DATA
I
OUT
Q
OUT
CHIP
RATE
1 BIT ENCODED TO
ONE OF 2 CODE
WORDS
(TRUE-INVERSE)
2 BITS ENCODED
TO ONE OF
4 CODE WORDS
SYMBOL
RATE
I vs Q
11 MC/S
11 MC/S
1 MS/S
1 MS/S
11 CHIPS
11 CHIPS
FIGURE 7. MODULATION MODES
5.5Mbps CCK
COMPLEX
SPREAD FUNCTIONS
4 BITS ENCODED
TO ONE OF 16
COMPLEX CCK
CODE WORDS
11 MC/S
1.375 MS/S
8 CHIPS
11Mbps CCK
COMPLEX
SPREAD FUNCTIONS
8 BITS ENCODED
TO ONE OF 256
COMPLEX CCK
CODE WORDS
11 MC/S
1.375 MS/S
8 CHIPS
HFA3861B
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| HFA3925IA | null2.4GHz - 2.5GHz 250mW Power Amplifier |
| HFA3925IA96 | null2.4GHz - 2.5GHz 250mW Power Amplifier |
| HFA50PA60C | RxxP2xx Series - Econoline Unregulated DC-DC Converters; Input Voltage (Vdc): 05V; Output Voltage (Vdc): 15V; Power: 2W; EN 60950 certified, rated for 250VAC; UL-60950-1 / CSA C22.2 certified; 5.2kVDC Isolation for 1 Minute; Optional Continuous Short Circuit Protected; Wide Operating Temperature Range atfull 2 Watts Load, ?40??C to +85??C; Twin Chamber Transformer System; UL94V-0 Package Material; Efficiency to 80% |
| HFB50PA60C | Ultrafast, Soft Recovery Diode |
| HFA5250 | 500MHz, Ultra High Speed Monolithic Pin Driver |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| HFA3861IV | 制造商:INTERSIL 制造商全稱:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Baseband Processor |
| HFA3861IV96 | 制造商:INTERSIL 制造商全稱:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Baseband Processor |
| HFA3863 | 制造商:INTERSIL 制造商全稱:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Baseband Processor |
| HFA3863IN | 制造商:INTERSIL 制造商全稱:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Baseband Processor |
| HFA3863IN96 | 制造商:INTERSIL 制造商全稱:Intersil Corporation 功能描述:Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Baseband Processor |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。