- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄383960 > TMX32C6411AGLZ (Texas Instruments, Inc.) FIXED POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | TMX32C6411AGLZ |
| 廠商: | Texas Instruments, Inc. |
| 元件分類: | 數(shù)字信號處理 |
| 英文描述: | FIXED POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR |
| 中文描述: | 定點數(shù)字信號處理器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 73/119頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 1742K |
| 代理商: | TMX32C6411AGLZ |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁當(dāng)前第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁
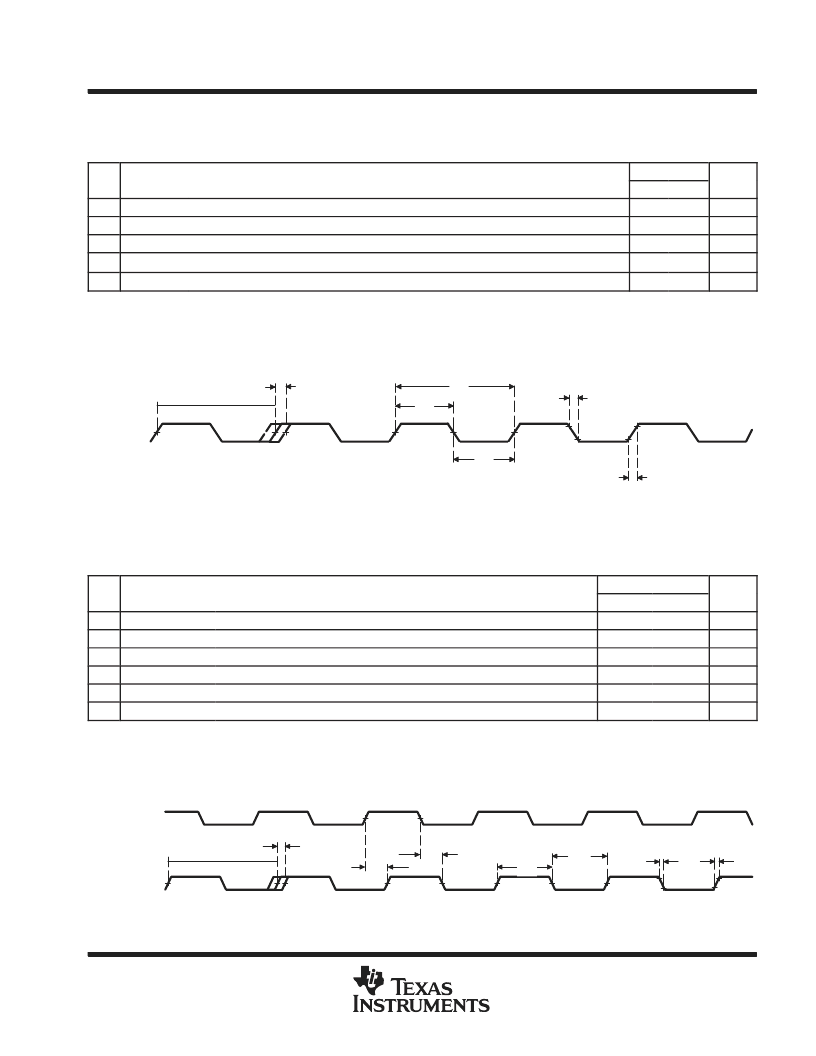
SPRS196H MARCH 2002 REVISED JULY 2004
73
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
HOUSTON, TEXAS 772511443
INPUT AND OUTPUT CLOCKS (CONTINUED)
timing requirements for ECLKIN
§
(see Figure 19)
NO.
300
UNIT
MIN
7.5
MAX
1
tc(EKI)
tw(EKIH)
tw(EKIL)
tt(EKI)
tJ(EKI)
Cycle time, ECLKIN
16P
ns
2
Pulse duration, ECLKIN high
3.38
ns
3
Pulse duration, ECLKIN low
3.38
ns
4
Transition time, ECLKIN
2
ns
5
Period jitter, ECLKIN
0.02E
ns
P = 1/CPU clock frequency in ns. For example, when running parts at 300 MHz, use P = 3.33 ns.
The reference points for the rise and fall transitions are measured at VIL MAX and VIH MIN.
§E = the EMIF input clock (ECLKIN, CPU/4 clock, or CPU/6 clock) period in ns for EMIFA or EMIFB.
Minimum ECLKIN times are based on internal logic speed; the maximum useable speed of the EMIF may be lower due to AC timing requirements.
On the -300 device, 75-MHz operation is achievable if the requirements of the EMIF Device Speed section are met. Minimum ECLKIN cycle times
must
be met, even when ECLKIN is generated by an internal clock source.
ECLKIN
2
3
4
4
5
1
Figure 19. ECLKIN Timing
switching characteristics over recommended operating conditions for ECLKOUT1
§#||
(see Figure 20)
NO.
PARAMETER
300
UNIT
MIN
MAX
±
175
EH + 0.7
1
tJ(EKO1)
tw(EKO1H)
tw(EKO1L)
tt(EKO1)
td(EKIH-EKO1H)
td(EKIL-EKO1L)
§E = the EMIF input clock (ECLKIN, CPU/4 clock, or CPU/6 clock) period in ns.
#The reference points for the rise and fall transitions are measured at VOL MAX and VOH MIN.
||EH is the high period of E (EMIF input clock period) in ns and EL is the low period of E (EMIF input clock period) in ns.
This cycle-to-cycle jitter specification was measured with CPU/4 or CPU/6 as the source of the EMIF input clock.
Period jitter, ECLKOUT1
0
ps
2
Pulse duration, ECLKOUT1 high
EH 0.7
ns
3
Pulse duration, ECLKOUT1 low
EL 0.7
EL + 0.7
ns
4
Transition time, ECLKOUT1
1
ns
5
Delay time, ECLKIN high to ECLKOUT1 high
1
8
ns
6
Delay time, ECLKIN low to ECLKOUT1 low
1
8
ns
1
5
6
2
3
ECLKIN
ECLKOUT1
4
4
Figure 20. ECLKOUT1 Timing
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| TMP32C6411AZLZ | FIXED POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR |
| TMP320C6411AZLZ | FIXED POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR |
| TMX32C6411AZLZ | ER 5C 2#6 3#4 SKT PLUG |
| TMP320C6411ZLZ | FIXED POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR |
| TMX32C6411ZLZ | FIXED POINT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| TMX32C6414EGLZ6E3 | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| TMX32C6415EGLZ5E0 | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:LAPLACE, REV. 2.0, 500 MHZ, 100 MHZ EMIF - Bulk |
| TMX32C6416EGLZ5E0 | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| TMX32TCI6482BZTZA2 | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述: |
| TMX32TCI6616BXCYPA | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。