- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄382378 > PCA9500 (NXP Semiconductors N.V.) The CAT24FC02 is a 2-kb Serial CMOS EEPROM internally organized as 256 words of 8 bits each PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | PCA9500 |
| 廠商: | NXP Semiconductors N.V. |
| 元件分類: | DRAM |
| 英文描述: | The CAT24FC02 is a 2-kb Serial CMOS EEPROM internally organized as 256 words of 8 bits each |
| 中文描述: | 該CAT24FC02是一個2 KB的EEPROM的國內(nèi)256個8位每字舉辦的串行CMOS |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 8/23頁 |
| 文件大小: | 169K |
| 代理商: | PCA9500 |
Philips Semiconductors
Product data sheet
PCA9500
8-bit I
2
C and SMBus I/O port with 2-kbit EEPROM
2004 Sep 30
8
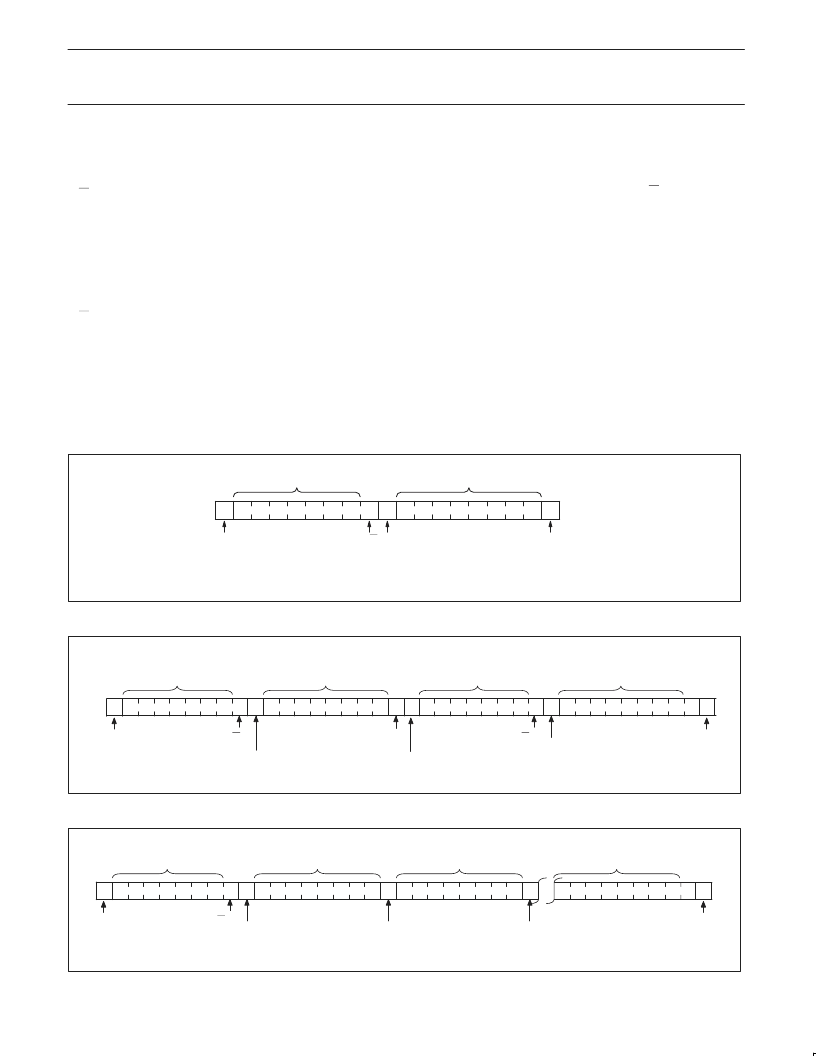
Read operations
PCA9500 read operations are initiated in an identical manner to
write operations with the exception that the memory slave address’
R/W bit is set to a one. There are three types of read operations;
current address, random and sequential.
Current Address Read (see Figure 11)
The PCA9500 contains an internal address counter that increments
after each read or write access, as a result if the last word accessed
was at address n then the address counter contains the address
n+1.
When the PCA9500 receives its memory slave address with the
R/W bit set to one it issues an acknowledge and uses the next eight
clocks to transmit the data contained at the address stored in the
address counter. The master ceases the transmission by issuing the
stop condition after the eighth bit. There is no ninth clock cycle for
the acknowledge.
Random Read (see Figure 12)
The PCA9500’s random read mode allows the address to be read
from to be specified by the master. This is done by performing a
dummy write to set the address counter to the location to be read.
The master must perform a byte write to the address location to be
read, but instead of transmitting the data after receiving the
acknowledge from the PCA9500 the master reissues the start
condition and memory slave address with the R/W bit set to one.
The PCA9500 will then transmit an acknowledge and use the next
eight clock cycles to transmit the data contained in the addressed
location. The master ceases the transmission by issuing the stop
condition after the eighth bit, omitting the ninth clock cycle
acknowledge.
Sequential Read (see Figure 13)
The PCA9500 sequential read is an extension of either the current
address read or random read. If the master doesn’t issue a stop
condition after it has received the eighth data bit, but instead issues
an acknowledge, the PCA9500 will increment the address counter
and use the next eight cycles to transmit the data from that location.
The master can continue this process to read the contents of the
entire memory. Upon reaching address 255 the counter will return to
address 0 and continue transmitting data until a stop condition is
received. The master ceases the transmission by issuing the stop
condition after the eighth bit, omitting the ninth clock cycle
acknowledge.
SW00556
S
1
0
1
0
A2
A1
A0
1
A
P
SDA
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM SLAVE
R/W
START CONDITION
STOP
CONDITION
SLAVE ADDRESS (MEMORY)
DATA FROM MEMORY
Figure 11. Current Address Read
S
P
SDA
SW00557
1
0
1
0
A2 A1 A0
A
A
0
START
CONDITION
R/W
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM SLAVE
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM SLAVE
A
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM SLAVE
DATA FROM MEMORY
STOP
CONDITION
S
START
CONDITION
1
0
1
0
A2 A1 A0
1
R/W
SLAVE ADDRESS (MEMORY)
WORD ADDRESS
SLAVE ADDRESS (MEMORY)
Figure 12. Random Read
S
P
SDA
SW00558
SLAVE ADDRESS (MEMORY)
DATA FROM MEMORY
DATA FROM MEMORY
1
0
1
0
A2 A1 A0
A
A
1
START CONDITION
R/W
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM SLAVE
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM MASTER
DATA n
A
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM MASTER
DATA n+X
STOP
CONDITION
DATA n+1
DATA FROM MEMORY
Figure 13. Sequential Read
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PCA9501 | 8-bit I2C and SMBus I/O port with interrupt, 2-kbit EEPROM and 6 address pins |
| PCA9513DP | Hot swappable IC and SMBus bus buffer |
| PCA9514D | Hot swappable IC and SMBus bus buffer |
| PCA9514DP | Hot swappable IC and SMBus bus buffer |
| PCA9513 | Hot swappable IC and SMBus bus buffer |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| PCA9500BS | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:8-bit I2C-bus and SMBus I/O port with 2-kbit EEPROM |
| PCA9500BS,118 | 功能描述:接口-I/O擴(kuò)展器 8BIT I2C FMQB GPIO PU2K EEPROM RoHS:否 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 邏輯系列: 輸入/輸出端數(shù)量: 最大工作頻率:100 kHz 工作電源電壓:1.65 V to 5.5 V 工作溫度范圍:- 40 C to + 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:HVQFN-16 封裝:Reel |
| PCA9500BSHP | 功能描述:接口-I/O擴(kuò)展器 RoHS:否 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 邏輯系列: 輸入/輸出端數(shù)量: 最大工作頻率:100 kHz 工作電源電壓:1.65 V to 5.5 V 工作溫度范圍:- 40 C to + 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:HVQFN-16 封裝:Reel |
| PCA9500D | 功能描述:接口-I/O擴(kuò)展器 I/O EXPANDER W/2K EE RoHS:否 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 邏輯系列: 輸入/輸出端數(shù)量: 最大工作頻率:100 kHz 工作電源電壓:1.65 V to 5.5 V 工作溫度范圍:- 40 C to + 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:HVQFN-16 封裝:Reel |
| PCA9500D,112 | 功能描述:接口-I/O擴(kuò)展器 I/O EXPANDER W/2K EE RoHS:否 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 邏輯系列: 輸入/輸出端數(shù)量: 最大工作頻率:100 kHz 工作電源電壓:1.65 V to 5.5 V 工作溫度范圍:- 40 C to + 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:HVQFN-16 封裝:Reel |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。