- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄382304 > MC33887 (Motorola, Inc.) 5.0 A H-Bridge with Load Current Feedback PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | MC33887 |
| 廠商: | Motorola, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | 5.0 A H-Bridge with Load Current Feedback |
| 中文描述: | 5.0的H -橋的負(fù)載電流反饋 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 10/28頁 |
| 文件大小: | 485K |
| 代理商: | MC33887 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁當(dāng)前第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁
33887
10
MOTOROLA ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DEVICE DATA
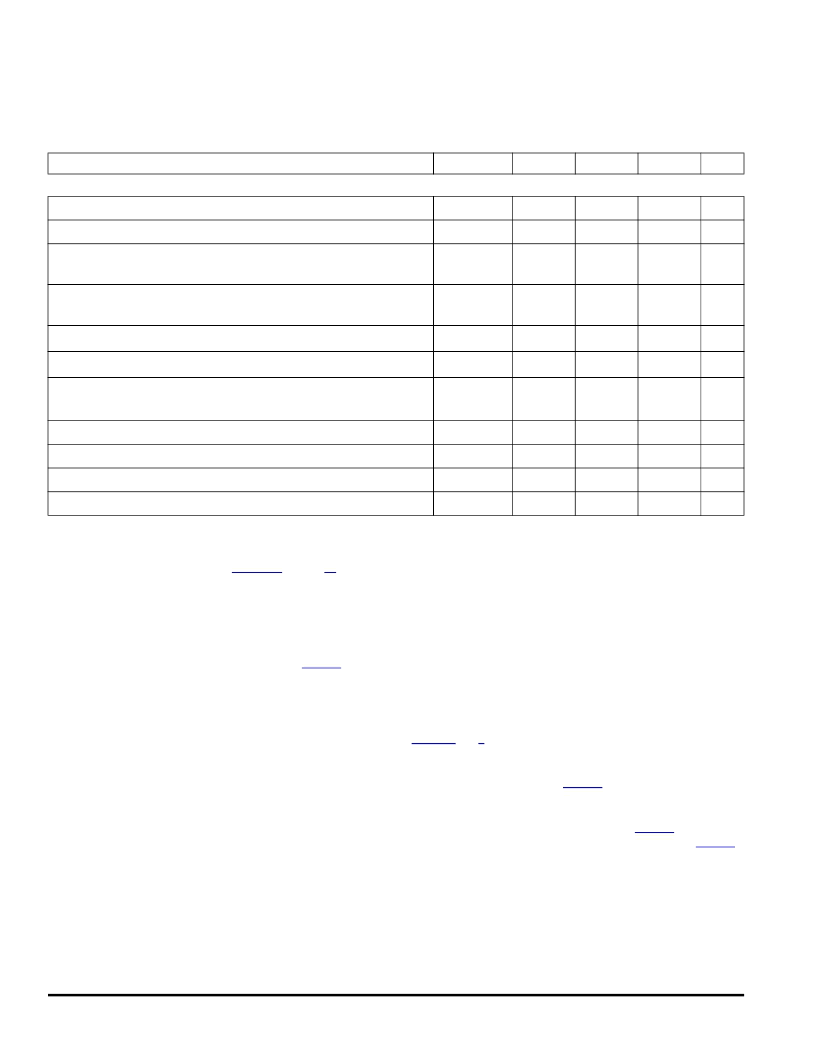
DYNAMIC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Characteristics noted under conditions 5.0 V
≤
V+
≤
28 V and -40
°
C
≤
T
A
≤
125
°
C unless otherwise noted. Typical values noted
reflect the approximate parameter mean at T
A
= 25
°
C under nominal conditions unless otherwise noted.
Characteristic
Symbol
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
PWM Frequency
(Note 23)
f
PWM
–
10
–
kHz
Maximum Switching Frequency During Active Current Limiting
(Note 24)
f
MAX
–
–
20
kHz
Output ON Delay
(Note 25)
V+ = 14 V
t
d
(ON)
–
–
18
μ
s
Output OFF Delay
(Note 25)
V+ = 14 V
t
d
(OFF)
–
–
18
μ
s
I
LIM
Output Constant-OFF Time for Low-Side MOSFETs
(Note 26), (Note 27)
t
a
15
20.5
26
μ
s
I
LIM
Blanking Time for Low-Side MOSFETs
(Note 28)
,
(Note 27)
t
b
12
16.5
21
μ
s
Output Rise and Fall Time
(Note 29)
V+ = 14 V, I
OUT
= 3.0 A
t
f
, t
r
2.0
5.0
8.0
μ
s
Disable Delay Time
(Note 30)
t
d(disable)
–
–
8.0
μ
s
Power-ON Delay Time
(Note 31)
t
pod
–
1.0
5.0
ms
Wake-Up Delay Time
(Note 31)
t
wud
–
1.0
5.0
ms
Output MOSFET Body Diode Reverse Recovery Time
(Note 32)
t
rr
100
–
–
ns
Notes
23.
The outputs can be PWM-controlled from an external source. This is typically done by holding one input high while applying a PWM pulse
train to the other input. The maximum PWM frequency obtainable is a compromise between switching losses and switching frequency. See
Typical Switching Waveforms,
Figures 11
through
18
, pp. 15–16.
The Maximum Switching Frequency during active current limiting is internally implemented. The internal current limit circuitry produces a
constant-OFF-time pulse-width modulation of the output current. The output load’s inductance, capacitance, and resistance characteristics
affect the total switching period (OFF-time + ON-time) and thus the PWM frequency during current limit.
Output Delay is the time duration from the midpoint of the IN1 or IN2 input signal to the 10% or 90% point (dependent on the transition
direction) of the OUT1 or OUT2 signal. If the output is transitioning HIGH-to-LOW, the delay is from the midpoint of the input signal to the
90% point of the output response signal. If the output is transitioning LOW-to-HIGH, the delay is from the midpoint of the input signal to the
10% point of the output response signal. See
Figure 2
, page 11.
I
LIM
Output Constant-OFF Time is the time during which the internal constant-OFF time PWM current regulation circuit has tri-stated the
output bridge.
Load currents ramping up to the current regulation threshold become limited at the I
LIM
value. The short circuit currents possess a di/dt that
ramps up to the I
SCH
or I
SCL
threshold during the I
LIM
blanking time, registering as a short circuit event detection and causing the shutdown
circuitry to force the output into an immediate tri-state latch-OFF. See
Figures 6
and
7
, page 12. Operation in
Current Limit mode
may cause
junction temperatures to rise. Junction temperatures above ~160
°
C will cause the output current limit threshold to progressively “fold back”,
or decrease with temperature, until ~175
°
C is reached, after which the T
LIM
thermal latch-OFF will occur. Permissible operation within this
foldback region is limited to nonrepetitive transient events of duration not to exceed 30 seconds. See
Figure 5
, page 11.
I
LIM
Blanking Time is the time during which the current regulation threshold is ignored so that the short-circuit detection threshold
comparators my have time to act.
Rise Time is from the 10% to the 90% level and Fall Time is from the 90% to the 10% level of the output signal. See
Figure 4
, page 11.
Disable Delay Time is the time duration from the midpoint of the D (disable) input signal to 10% of the output tri-state response. See
Figure 3
,
page 11.
Parameter has been characterized but not production tested.
Parameter is guaranteed by design but not production tested.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
F
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
n
.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MC33887DH | 5.0 A H-Bridge with Load Current Feedback |
| MC33887DHR2 | 5.0 A H-Bridge with Load Current Feedback |
| MC33887DWB | 5.0 A H-Bridge with Load Current Feedback |
| MC33887DWBR2 | 5.0 A H-Bridge with Load Current Feedback |
| MC33887PNB | 5.0 A H-Bridge with Load Current Feedback |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MC33887APVW | 功能描述:馬達(dá)/運(yùn)動(dòng)/點(diǎn)火控制器和驅(qū)動(dòng)器 H-BRIDGE W/LD CURNT FDBK RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 產(chǎn)品:Stepper Motor Controllers / Drivers 類型:2 Phase Stepper Motor Driver 工作電源電壓:8 V to 45 V 電源電流:0.5 mA 工作溫度:- 25 C to + 125 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:HTSSOP-28 封裝:Tube |
| MC33887APVW-PB | 制造商:Freescale Semiconductor 功能描述: |
| MC33887APVWR2 | 功能描述:馬達(dá)/運(yùn)動(dòng)/點(diǎn)火控制器和驅(qū)動(dòng)器 H-BRIDGE W/LD CURNT FDBK RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 產(chǎn)品:Stepper Motor Controllers / Drivers 類型:2 Phase Stepper Motor Driver 工作電源電壓:8 V to 45 V 電源電流:0.5 mA 工作溫度:- 25 C to + 125 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:HTSSOP-28 封裝:Tube |
| MC33887AVW | 功能描述:開關(guān) IC - 各種 H-BRIDGE W/LD CURNT FDBK RoHS:否 制造商:Fairchild Semiconductor 開啟電阻(最大值): 電源電壓-最大:4.4 V 電源電壓-最小:2.5 V 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 封裝 / 箱體:WLCSP-9 封裝:Reel |
| MC33887AVWR2 | 功能描述:馬達(dá)/運(yùn)動(dòng)/點(diǎn)火控制器和驅(qū)動(dòng)器 H-BRIDGE W/LD CURNT FDBK RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 產(chǎn)品:Stepper Motor Controllers / Drivers 類型:2 Phase Stepper Motor Driver 工作電源電壓:8 V to 45 V 電源電流:0.5 mA 工作溫度:- 25 C to + 125 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:HTSSOP-28 封裝:Tube |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。