- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄370837 > M32000D3FP (Mitsubishi Electric Corporation) SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | M32000D3FP |
| 廠商: | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation |
| 英文描述: | SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| 中文描述: | 單芯片32位CMOS微機 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 24/45頁 |
| 文件大小: | 565K |
| 代理商: | M32000D3FP |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁當前第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁
SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M32000D3FP
24
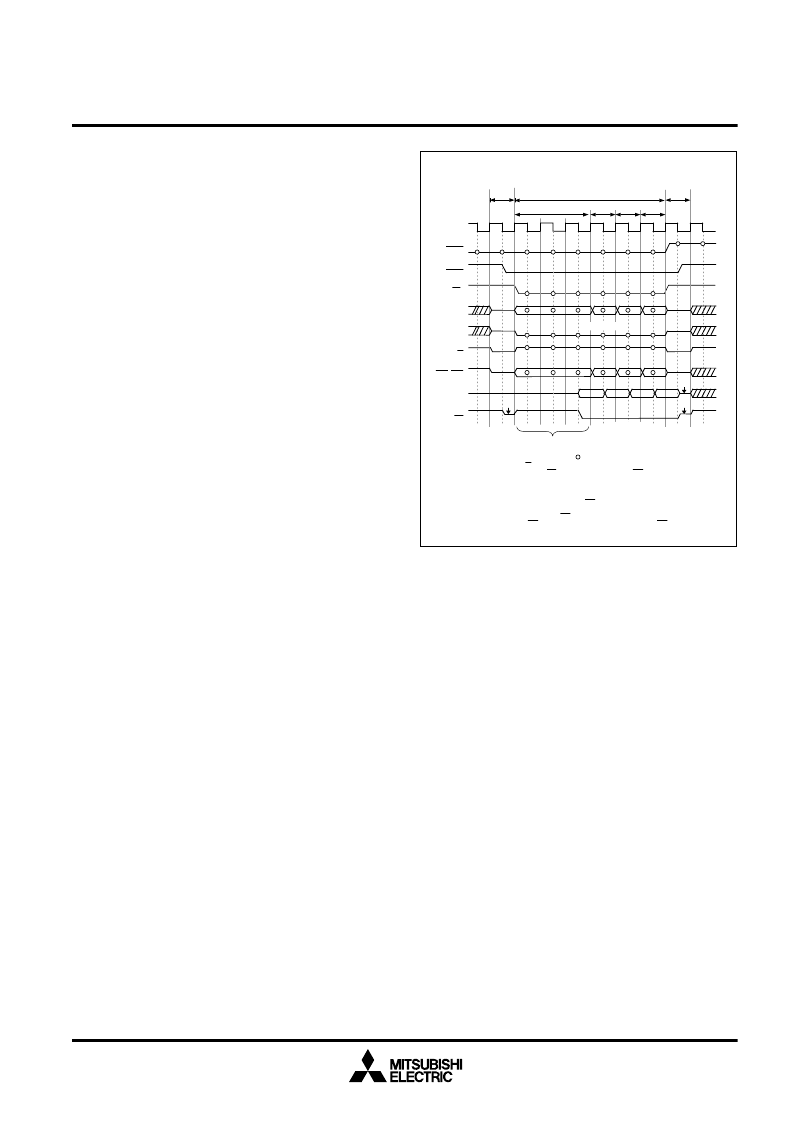
("L" output)
("L" input)
"Hi-z"
"Hi-z"
"Hi-z"
"Hi-z"
"Hi-z"
"Hi-z"
"Hi-z"
"Hi-z"
"Hi-z"
"Hi-z"
"Hi-z"
"Hi-z"
8
HREQ
BCH, BCL
D0 - D15
DC
R/W
hold shift
hold
return
HACK
A8 - A30
CS
read
read
read
read
SID
Note:
"Hi-z" means high impedance, and indicates sampling timing.
8
cannot be changed during CS="L", 3 to 7 CLKIN clock periods are necessary for
reading from the internal DRAM. Hold the input value of the address or other control
signals during these wait cycle periods (DC = "H"). Consecutive read operations
within an 128-bit boundary are completed in 1 CLKIN clock period.
During these wait cycle period, CS cannot be returned to an "H" level (the access
CLKIN
The value of the R/W signal that controls the data direction of the bus interface
When the M32000D3FP is in the hold state and an "L" level is input
to CS, the M32000D3FP interprets it as a bus access request to the
internal DRAM. In this case, when the R/W signal is an "H" level, the
memory controller drives a read cycle to the internal DRAM. In the
read cycle, the 16-bit data for the address specified with A8 to A30,
is output from D0 to D15 regardless of the BCH and BCL settings.
Also the DC signal is output.
The M32000D3FP reads 128 bits of data from the block on the 128-
bit boundary including the requested address into the 128-bit buffer
of the bus interface unit. 3 to 7 CLKIN clock periods are necessary
for the first bus access, however, when reading consecutive address
within the 128-bit boundary, the subsequent read bus cycles are com-
pleted in 1 CLKIN clock period because a read from the internal DRAM
does not take place. After DC outputs an "L" level (access complete),
return CS to the "H" level between the CLKIN falling edge corre-
sponding to the last read cycle and the following CLKIN falling edge.
Return HREQ to the "H" level to return the M32000D3FP to the nor-
mal operation mode from the hold state either at the same time as or
after CS is returned to the "H" level.
Fig. 23 Read bus cycle to internal DRAM
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| M32000D4 | SINGLE CHIP 32 BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M32000D4AFP | SINGLE CHIP 32 BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M32170F3VFP | SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M32174F3VFP | SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M32170F3VFG | 32-BIT RISC SINGLE-CHIP MICROCOMPUTER |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| M32000D4 | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE CHIP 32 BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M32000D4AFP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE CHIP 32 BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M32000D4BFP-80 | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 32-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M32002AGLJ | 制造商:MTRONPTI 制造商全稱:MTRONPTI 功能描述:9x14 mm, 3.3/2.5/1.8 Volt, PECL/LVDS/CML, VCXO |
| M32002AGMJ | 制造商:MTRONPTI 制造商全稱:MTRONPTI 功能描述:9x14 mm, 3.3/2.5/1.8 Volt, PECL/LVDS/CML, VCXO |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。