- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄97995 > L6711 (STMICROELECTRONICS) 2 A SWITCHING CONTROLLER, 178 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PQFP48 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | L6711 |
| 廠商: | STMICROELECTRONICS |
| 元件分類: | 穩(wěn)壓器 |
| 英文描述: | 2 A SWITCHING CONTROLLER, 178 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PQFP48 |
| 封裝: | 7 X 7 MM, 1 MM HEIGHT, TQFP-48 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 39/50頁 |
| 文件大小: | 679K |
| 代理商: | L6711 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁當(dāng)前第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁
Obsolete
Product(s)
- Obsolete
Product(s)
Layout guidelines
L6711
44/50
18
Layout guidelines
Since the device manages control functions and high-current drivers, layout is one of the
most important things to consider when designing such high current applications.
A good layout solution can generate a benefit in lowering power dissipation on the power
paths, reducing radiation and a proper connection between signal and power ground can
optimize the performance of the control loops.
Integrated power drivers reduce components count and interconnections between control
functions and drivers, reducing the board space.
Here below are listed the main points to focus on when starting a new layout and rules are
suggested for a correct implementation.
18.1
Power connections.
These are the connections where switching and continuous current flows from the input
supply towards the load. The first priority when placing components has to be reserved to
this power section, minimizing the length of each connection and loop as much as possible.
To minimize noise and voltage spikes (EMI and losses) these interconnections must be a
part of a power plane and anyway realized by wide and thick copper traces: loop must be
anyway minimized. The critical components, i.e. the power transistors, must be located as
close as possible one to the other.
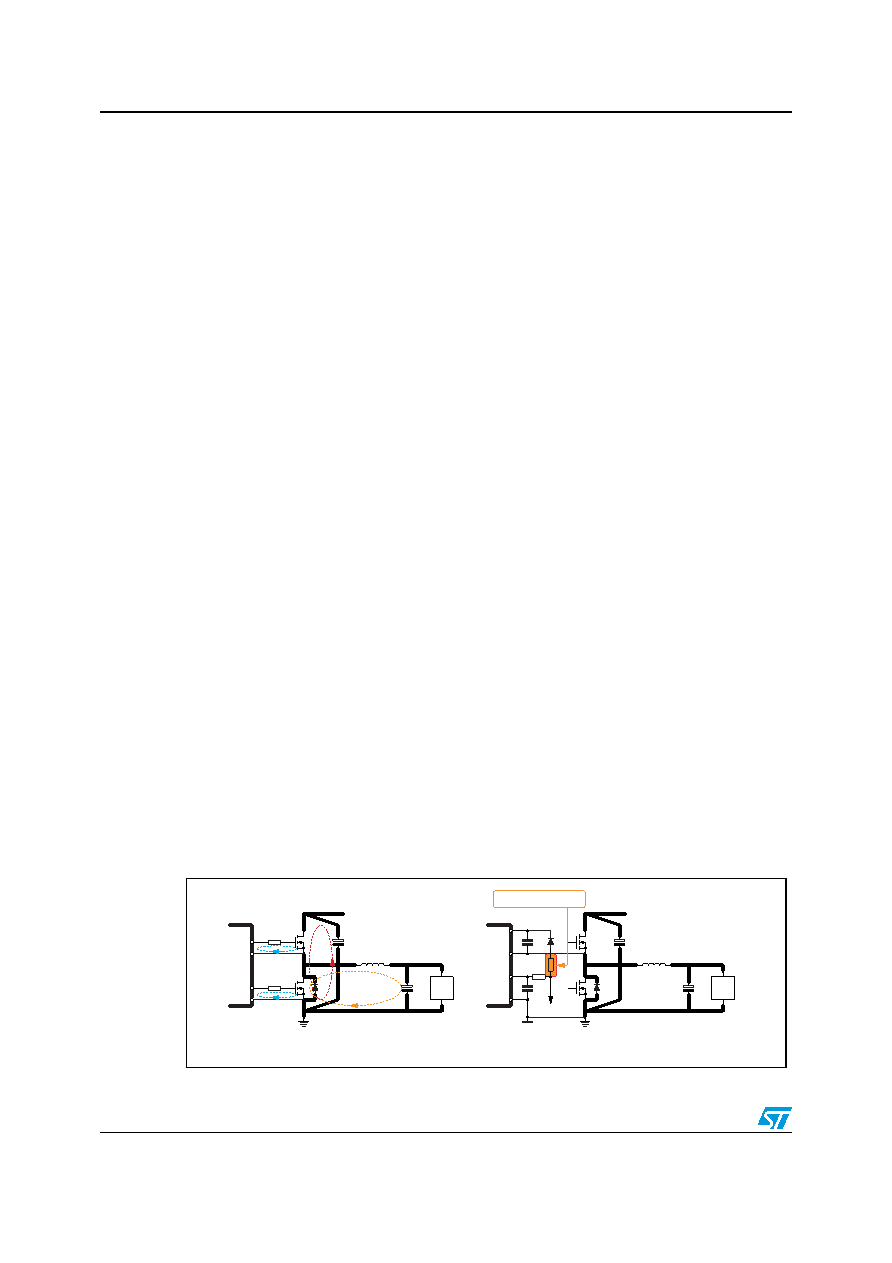
Figure 23 shows the details of the power connections involved and the current loops. The
input capacitance (CIN), or at least a portion of the total capacitance needed, has to be
placed close to the power section in order to eliminate the stray inductance generated by
the copper traces. Low ESR and ESL capacitors are preferred.
Use as much VIAs as possible when power traces have to move between different planes
on the PCB: this reduces both parasitic resistance and inductance. Moreover, reproducing
the same high-current trace on more than one PCB layer will reduce the parasitic resistance
associated to that connection.
Connect output bulk capacitor as near as possible to the load, minimizing parasitic
inductance and resistance associated to the copper trace also adding extra decoupling
capacitors along the way to the load when this results in being far from the bulk capacitor
bank.
Figure 23.
Power connections and related connections layout guidelines (same for
all phases).
L
CIN
VIN
UGATEx
PHASEx
LGATEx
PGNDx
LOAD
BOOTx
PHASEx
VCC
SGND
+Vcc
C
BOOT
L
CIN
VIN
LOAD
To limit C
BOOT
Extra-Charge
a. PCB power and ground planes areas
b. PCB small signal components placement
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| L6714TR | SWITCHING CONTROLLER, 170 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PQFP64 |
| L6714 | SWITCHING CONTROLLER, 170 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PQFP64 |
| L6725TR | 20 A SWITCHING CONTROLLER, 500 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PDSO16 |
| L6728ATR | SWITCHING CONTROLLER, 660 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PDSO10 |
| L6728A | SWITCHING CONTROLLER, 660 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PDSO10 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| L6711_06 | 制造商:STMICROELECTRONICS 制造商全稱:STMicroelectronics 功能描述:3 Phase controller with dynamic VID and selectable DACs |
| L6711TR | 功能描述:DC/DC 開關(guān)控制器 3 PHASE CONTROLLER RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 輸入電壓:6 V to 100 V 開關(guān)頻率: 輸出電壓:1.215 V to 80 V 輸出電流:3.5 A 輸出端數(shù)量:1 最大工作溫度:+ 125 C 安裝風(fēng)格: 封裝 / 箱體:CPAK |
| L6712 | 制造商:STMICROELECTRONICS 制造商全稱:STMicroelectronics 功能描述:TWO-PHASE INTERLEAVED DC/DC CONTROLLER |
| L6712_05 | 制造商:STMICROELECTRONICS 制造商全稱:STMicroelectronics 功能描述:TWO-PHASE INTERLEAVED DC/DC CONTROLLER |
| L6712A | 制造商:STMICROELECTRONICS 制造商全稱:STMicroelectronics 功能描述:TWO-PHASE INTERLEAVED DC/DC CONTROLLER |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。