- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄384755 > MT48LC16M8A2 (Micron Technology, Inc.) SYNCHRONOUS DRAM PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MT48LC16M8A2 |
| 廠商: | Micron Technology, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | SYNCHRONOUS DRAM |
| 中文描述: | 同步DRAM |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 11/59頁 |
| 文件大小: | 1844K |
| 代理商: | MT48LC16M8A2 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁當(dāng)前第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁
11
128Mb: x4, x8, x16 SDRAM
128MSDRAM_E.p65
–
Rev. E; Pub. 1/02
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
2001, Micron Technology, Inc.
128Mb: x4, x8, x16
SDRAM
Operating Mode
The normal operating mode is selected by setting M7
and M8 to zero; the other combinations of values for M7
and M8 are reserved for future use and/or test modes.
The programmed burst length applies to both READ and
WRITE bursts.
Test modes and reserved states should not be used
because unknown operation or incompatibility with fu-
ture versions may result.
Write Burst Mode
When M9 = 0, the burst length programmed via
M0-M2 applies to both READ and WRITE bursts; when
M9 = 1, the programmed burst length applies to
READ bursts, but write accesses are single-location
(nonburst) accesses.
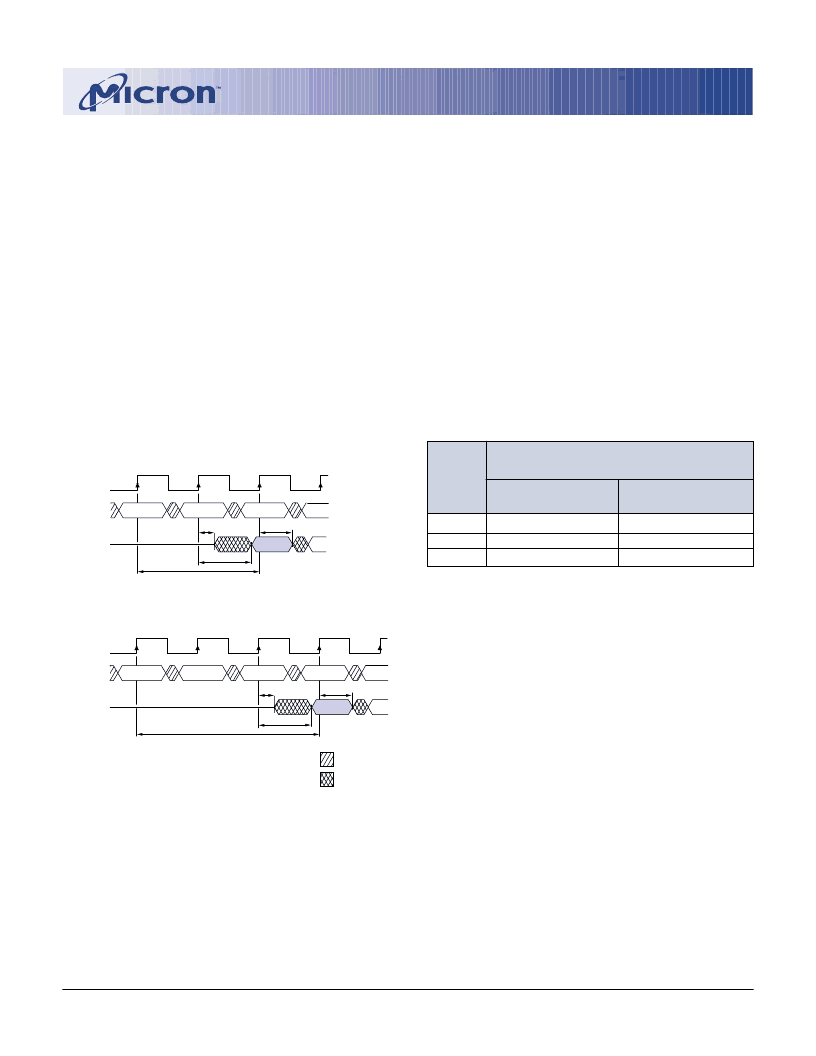
CAS Latency
The CAS latency is the delay, in clock cycles, between
the registration of a READ command and the availability
of the first piece of output data. The latency can be set to
two or three clocks.
If a READ command is registered at clock edge
n
, and
the latency is
m
clocks, the data will be available by clock
edge
n + m
. The DQs will start driving as a result of the
clock edge one cycle earlier (
n + m
- 1), and provided that
the relevant access times are met, the data will be valid by
clock edge
n + m
. For example, assuming that the clock
cycle time is such that all relevant access times are met,
if a READ command is registered at T0 and the latency is
programmed to two clocks, the DQs will start driving
after T1 and the data will be valid by T2, as shown in
Figure 2. Table 2 below indicates the operating frequen-
cies at which each CAS latency setting can be used.
Reserved states should not be used as unknown op-
eration or incompatibility with future versions
may result.
Figure 2
CAS Latency
CLK
DQ
T2
T1
T3
T0
CAS Latency = 3
LZ
t
D
OUT
tOH
COMMAND
NOP
READ
tAC
NOP
T4
NOP
DON
’
T CARE
UNDEFINED
CLK
DQ
T2
T1
T3
T0
CAS Latency = 2
LZ
t
D
OUT
tOH
COMMAND
NOP
READ
tAC
NOP
Table 2
CAS Latency
ALLOWABLE OPERATING
FREQUENCY (MHz)
CAS
LATENCY = 2
≤
133
≤
100
≤
100
CAS
SPEED
-7E
-75
-8E
LATENCY = 3
≤
143
≤
133
≤
125
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MT48LC2M32B2 | SYNCHRONOUS DRAM |
| MT48LC32M8A2 | SYNCHRONOUS DRAM |
| MT48LC16M16A2 | SYNCHRONOUS DRAM |
| MT48LC64M4A2 | SYNCHRONOUS DRAM |
| MT48LC4M32B2 | SYNCHRONOUS DRAM |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。