- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄385404 > HT82K68 (Holtek Semiconductor Inc.) Multimedia Keyboard Encoder OTP PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | HT82K68 |
| 廠商: | Holtek Semiconductor Inc. |
| 英文描述: | Multimedia Keyboard Encoder OTP |
| 中文描述: | 多媒體鍵盤編碼器檢察官辦公室 |
| 文件頁數: | 7/40頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 260K |
| 代理商: | HT82K68 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁當前第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁
HT82K68E
7
August 8, 2000
Preliminary
2
,
2
,
2
,
8
$ &
& 5
6
9& & 5 : 6
8
$ &
& 5
; 6
9& & 5 6
8
$ &
& 5
; 6
9& & 5 ; 6
;
;
" & . <
& 5 & " 6
5
& &
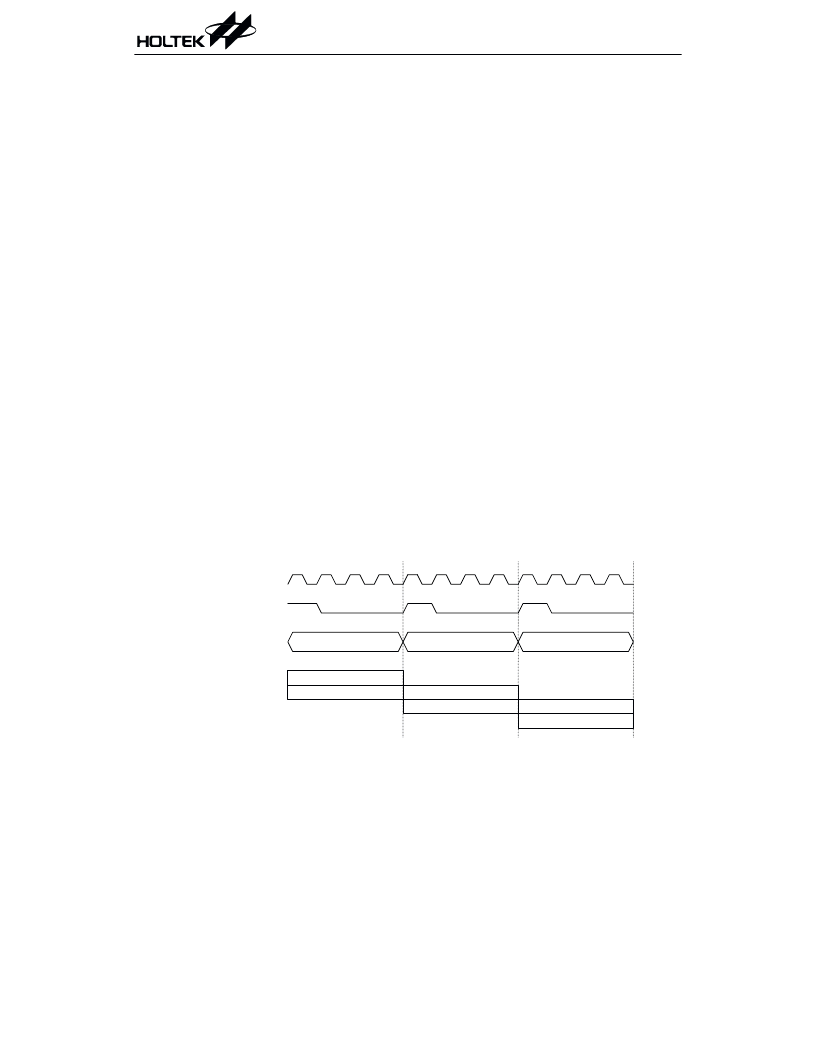
Execution flow
Functional Description
Execution flow
The HT82K68E system clock is derived from ei-
ther a crystal or an RC oscillator. The system
clock is internally divided into four
non-overlapping clocks. One instruction cycle
consists of four system clock cycles.
Instruction fetching and execution are
pipelined in such a way that a fetch takes one
instruction cycle while decoding and execution
takes the next instruction cycle. However, the
pipelining scheme causes each instruction to
effectively execute within one cycle. If an in-
struction changes the program counter, two cy-
cles are required to complete the instruction.
Program counter
PC
The 12-bit program counter (PC) controls the
sequenceinwhichtheinstructionsstoredinthe
program ROM are executed and its contents
specify a maximum of 4096 addresses.
After accessing a program memory word to
fetch an instruction code, the contents of the
program counter are incremented by one. The
program counter then points to the memory
word containing the next instruction code.
When executing a jump instruction, conditional
skip execution, loading PCL register, subrou-
tine call, initial reset, internal interrupt, exter-
nal interrupt or return from subroutine, the PC
manipulates the program transfer by loading
the address corresponding to each instruction.
The conditional skip is activated by instruction.
Once the condition is met, the next instruction,
fetched during the current instruction execu-
tion, is discarded and a dummy cycle replaces it
to get the proper instruction. Otherwise pro-
ceed with the next instruction.
The lower byte of the program counter (PCL) is
areadableandwriteableregister(06H).Moving
data into the PCL performs a short jump. The
destinationwillbewithin256locations.
Once a control transfer takes place, an addi-
tional dummy cycle is required.
Program memory
PROM
The program memory is used to store the pro-
gram instructions which are to be executed. It
also contains data, table, and interrupt entries,
and is organized with 3072
by the program counter and table pointer.
16 bits, addressed
Certain locations in the program memory are
reserved for special usage:
Location 000
This area is reserved for the initialization
program. After chip reset, the program al-
ways begins execution at location 000H.
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| HT82K94A | USB Multimedia Keyboard Encoder 8-Bit MCU |
| HT82K94E | USB Multimedia Keyboard Encoder 8-Bit MCU |
| HT82K94E_07 | USB Multimedia Keyboard Encoder 8-Bit MCU |
| HT82K95AE | USB Multimedia Keyboard Encoder 8-Bit MCU |
| HT82K95EE | USB Multimedia Keyboard Encoder 8-Bit MCU |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| HT82K68A | 制造商:HOLTEK 制造商全稱:Holtek Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:Multimedia Keyboard Encoder Body |
| HT82K68A_01 | 制造商:HOLTEK 制造商全稱:Holtek Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:8-Bit Multimedia Keyboard Encoder Mask MCU |
| HT82K68A-L | 制造商:HOLTEK 制造商全稱:Holtek Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:Multimedia Keyboard Encoder 8-Bit MCU |
| HT82K68E | 制造商:HOLTEK 制造商全稱:Holtek Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:Multimedia Keyboard Encoder OTP |
| HT82K68E_07 | 制造商:HOLTEK 制造商全稱:Holtek Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:Multimedia Keyboard Encoder 8-Bit OTP MCU |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。