- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄4490 > A3P600-2FGG484 (Microsemi SoC)IC FPGA 1KB FLASH 600K 484-FBGA PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | A3P600-2FGG484 |
| 廠商: | Microsemi SoC |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 200/220頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 0K |
| 描述: | IC FPGA 1KB FLASH 600K 484-FBGA |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 40 |
| 系列: | ProASIC3 |
| RAM 位總計(jì): | 110592 |
| 輸入/輸出數(shù): | 235 |
| 門數(shù): | 600000 |
| 電源電壓: | 1.425 V ~ 1.575 V |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 工作溫度: | 0°C ~ 70°C |
| 封裝/外殼: | 484-BGA |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 484-FPBGA(23x23) |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁第155頁第156頁第157頁第158頁第159頁第160頁第161頁第162頁第163頁第164頁第165頁第166頁第167頁第168頁第169頁第170頁第171頁第172頁第173頁第174頁第175頁第176頁第177頁第178頁第179頁第180頁第181頁第182頁第183頁第184頁第185頁第186頁第187頁第188頁第189頁第190頁第191頁第192頁第193頁第194頁第195頁第196頁第197頁第198頁第199頁當(dāng)前第200頁第201頁第202頁第203頁第204頁第205頁第206頁第207頁第208頁第209頁第210頁第211頁第212頁第213頁第214頁第215頁第216頁第217頁第218頁第219頁第220頁
ProASIC3 DC and Switching Characteristics
2-66
Revision 13
B-LVDS/M-LVDS
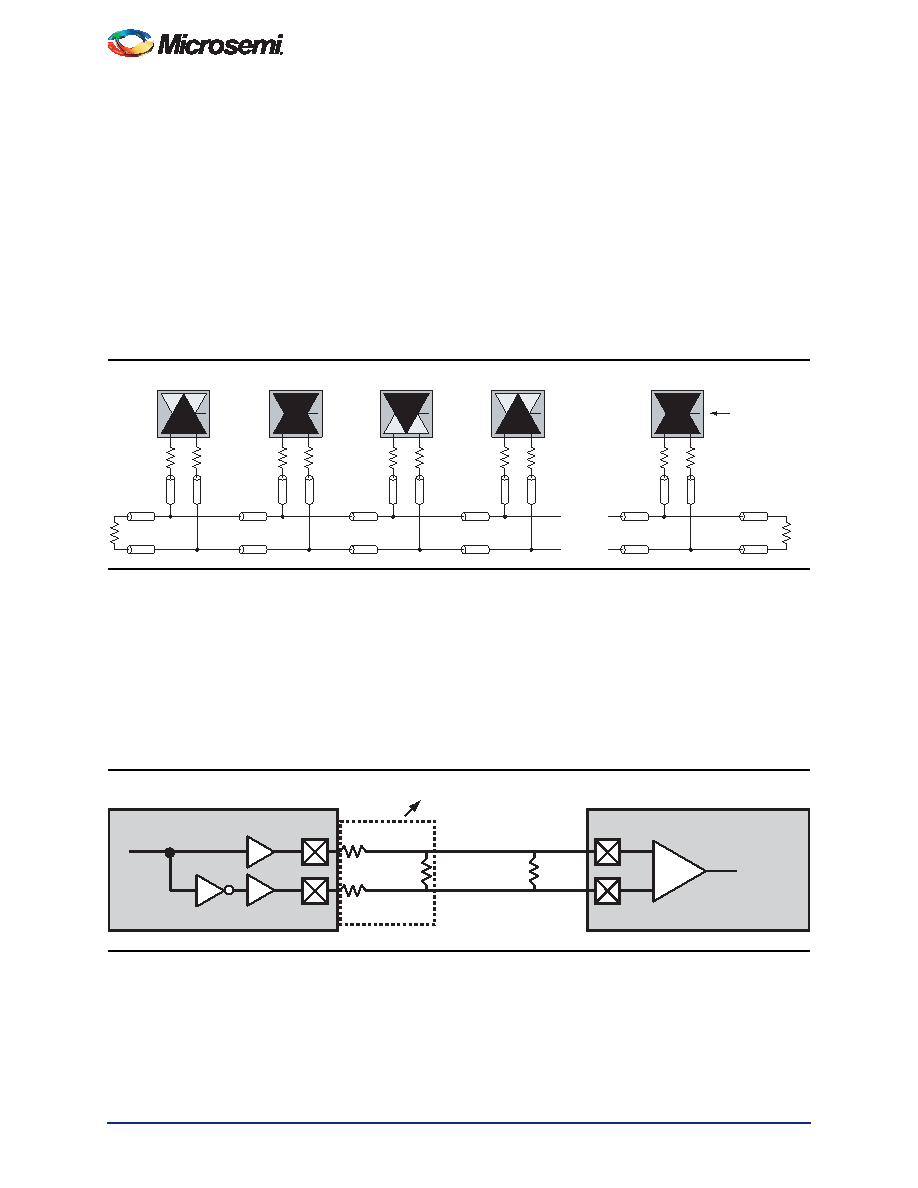
Bus LVDS (B-LVDS) and Multipoint LVDS (M-LVDS) specifications extend the existing LVDS standard to
high-performance multipoint bus applications. Multidrop and multipoint bus configurations may contain
any combination of drivers, receivers, and transceivers. Microsemi LVDS drivers provide the higher drive
current required by B-LVDS and M-LVDS to accommodate the loading. The drivers require series
terminations for better signal quality and to control voltage swing. Termination is also required at both
ends of the bus since the driver can be located anywhere on the bus. These configurations can be
implemented using the TRIBUF_LVDS and BIBUF_LVDS macros along with appropriate terminations.
Multipoint designs using Microsemi LVDS macros can achieve up to 200 MHz with a maximum of 20
loads. A sample application is given in Figure 2-12. The input and output buffer delays are available in
the LVDS section in Table 2-92.
Example: For a bus consisting of 20 equidistant loads, the following terminations provide the required
differential voltage, in worst-case Industrial operating conditions, at the farthest receiver: RS =60 and
RT =70 , given Z0 =50 (2") and Zstub =50 (~1.5").
LVPECL
Low-Voltage Positive Emitter-Coupled Logic (LVPECL) is another differential I/O standard. It requires
that one data bit be carried through two signal lines. Like LVDS, two pins are needed. It also requires
external resistor termination.
The full implementation of the LVDS transmitter and receiver is shown in an example in Figure 2-13. The
building blocks of the LVPECL transmitter-receiver are one transmitter macro, one receiver macro, three
board resistors at the transmitter end, and one resistor at the receiver end. The values for the three driver
resistors are different from those used in the LVDS implementation because the output standard
specifications are different.
Figure 2-12 B-LVDS/M-LVDS Multipoint Application Using LVDS I/O Buffers
...
RT
BIBUF_LVDS
R
+
-
T
+
-
R
+
-
T
+
-
D
+
-
EN
Receiver
Transceiver
Receiver
Transceiver
Driver
RS RS
Zstub
Z0
Figure 2-13 LVPECL Circuit Diagram and Board-Level Implementation
187 W
100
Z0 = 50
100
100
+
–
P
N
P
N
INBUF_LVPECL
OUTBUF_LVPECL
FPGA
Bourns Part Number: CAT16-PC4F12
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| RMM44DRKH-S13 | CONN EDGECARD 88POS .156 EXTEND |
| RSM44DRYS | CONN EDGECARD 88POS DIP .156 SLD |
| RMM44DRYS | CONN EDGECARD 88POS DIP .156 SLD |
| ASM36DRYN | CONN EDGECARD 72POS DIP .156 SLD |
| ASM36DRYH | CONN EDGECARD 72POS DIP .156 SLD |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| A3P600-2FGG484I | 功能描述:IC FPGA 1KB FLASH 600K 484-FBGA RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 嵌入式 - FPGA(現(xiàn)場可編程門陣列) 系列:ProASIC3 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝:40 系列:SX-A LAB/CLB數(shù):6036 邏輯元件/單元數(shù):- RAM 位總計(jì):- 輸入/輸出數(shù):360 門數(shù):108000 電源電壓:2.25 V ~ 5.25 V 安裝類型:表面貼裝 工作溫度:0°C ~ 70°C 封裝/外殼:484-BGA 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝:484-FPBGA(27X27) |
| A3P600-2PQ144 | 制造商:ACTEL 制造商全稱:Actel Corporation 功能描述:ProASIC3 Flash Family FPGAs |
| A3P600-2PQ144ES | 制造商:ACTEL 制造商全稱:Actel Corporation 功能描述:ProASIC3 Flash Family FPGAs |
| A3P600-2PQ144I | 制造商:ACTEL 制造商全稱:Actel Corporation 功能描述:ProASIC3 Flash Family FPGAs |
| A3P600-2PQ144PP | 制造商:ACTEL 制造商全稱:Actel Corporation 功能描述:ProASIC3 Flash Family FPGAs |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。