- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄97995 > L6238SQT (STMICROELECTRONICS) BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR CONTROLLER, 5 A, PQFP64 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | L6238SQT |
| 廠商: | STMICROELECTRONICS |
| 元件分類: | 運動控制電子 |
| 英文描述: | BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR CONTROLLER, 5 A, PQFP64 |
| 封裝: | TQFP-64 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 13/31頁 |
| 文件大小: | 3465K |
| 代理商: | L6238SQT |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁當(dāng)前第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁
given application is too slow. Figure 4-9 is an os-
cillograph taken on a device that had a fairly large
value for Rslew and failed to spin up and phase
lock a motor.
The problem manifests itself as the motor begins
to spin up. At lower RPMs, the Bemf of the motor
is relatively small resulting in higher amounts of
commutation current. In figure 4-9, the upper
waveform is the voltage appearing at OUTPUT
relative to the CENTER TAP input. The lower
waveform is the actual output of the Bemf ampli-
fier available on special engineering prototypes.
The oscillograph was taken just as the problem
occured. The period between zero crossings was
~800
s resulting in a mask time period of 200s.
As can be seen, the excessively long slew rate
actually exceeded the mask period and was de-
tected as a zero crossing.
This resulted in improper sequencing of the out-
puts relative to the proper phases and caused the
motor to spin down.
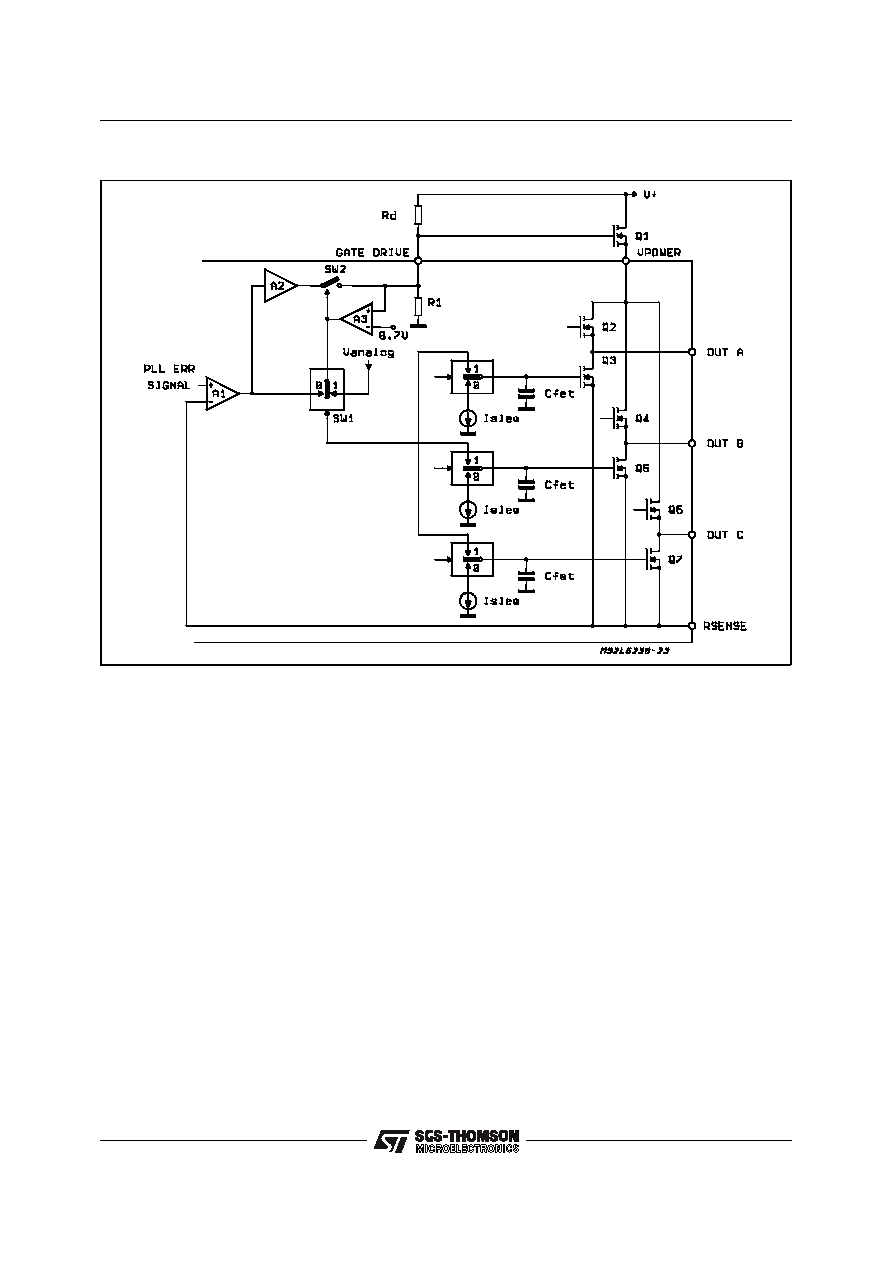
4.7 Ext PFET Driver
The power handling capabilities of the 3 phase
output stage can be extended with the addition of
a single P-Channel FET.
Figure 4-10 shows the Ext FET connection and
demonstrates how the L6238S automatically
senses the FETs presence. When the voltage at
the Gate Drive pin is
≥ 0.7V, the output of com-
parator A3 goes high, removing the variable drive
A1 from the internal FETs and connects them in-
stead to Vanalog via the commutation switches to
facilitate full conduction.
The upper FETs drive paths are not shown for
clarity. A3 also closes SW2 allowing A1 to linearly
drive the external P-Channel FET Q1 via inverter
A2.
4.8 Bemf Ampolifier
Since no Hall Effect Sensors are required, the
commutation information is derived from the Bemf
voltage zero-crossings of the undriven phase with
respect to the center tap. The Bemf comparator
and associated signal levels are depicted in figure
4-11. For reliable operation, the Bemf signal am-
plitude should be a minimum of
± 60 mV to be
properly detected. In order to provide for noise
immunity, internal hysteresis is incorporated in
the detection circuitry to prevent false zero cross-
ing detection.
For laboratory evaluation purposes, a simple re-
Figure 4-10: External P-Fet.
L6238S
20/31
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| L6238S013TR | BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR CONTROLLER, 5 A, PQCC44 |
| L6246 | VOICE COIL MOTOR CONTROLLER, 3 A, PQFP44 |
| L6258EA | STEPPER MOTOR CONTROLLER, 2 A, PDSO36 |
| L6268 | VOICE COIL MOTOR CONTROLLER, 2.1 A, PQFP44 |
| L6269 | VOICE COIL MOTOR CONTROLLER, 2.1 A, PQFP44 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| L6239 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述: |
| L623C | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:THYRISTOR MODULE|BRIDGE|HALF-CNTLD|CA|280V V(RRM)|46A I(T) |
| L623F | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:THYRISTOR MODULE|BRIDGE|HALF-CNTLD|CA|280V V(RRM)|46A I(T) |
| L624 | 制造商:CRYDOM 制造商全稱:Crydom Inc., 功能描述:Power Modules |
| L6242 | 制造商:STMICROELECTRONICS 制造商全稱:STMicroelectronics 功能描述:VOICE COIL MOTOR DRIVER |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。