- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄385342 > GS881Z18T-66I (GSI TECHNOLOGY) 8Mb Pipelined and Flow Through Synchronous NBT SRAMs PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | GS881Z18T-66I |
| 廠商: | GSI TECHNOLOGY |
| 元件分類: | DRAM |
| 英文描述: | 8Mb Pipelined and Flow Through Synchronous NBT SRAMs |
| 中文描述: | 512K X 18 ZBT SRAM, 18 ns, PQFP100 |
| 封裝: | TQFP-100 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 13/34頁 |
| 文件大小: | 542K |
| 代理商: | GS881Z18T-66I |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁當(dāng)前第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁
Rev: 1.10 8/2000
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com
13/34
1998, Giga Semconductor, Inc.
Preliminary
.
GS881Z18/36T-11/100/80/66
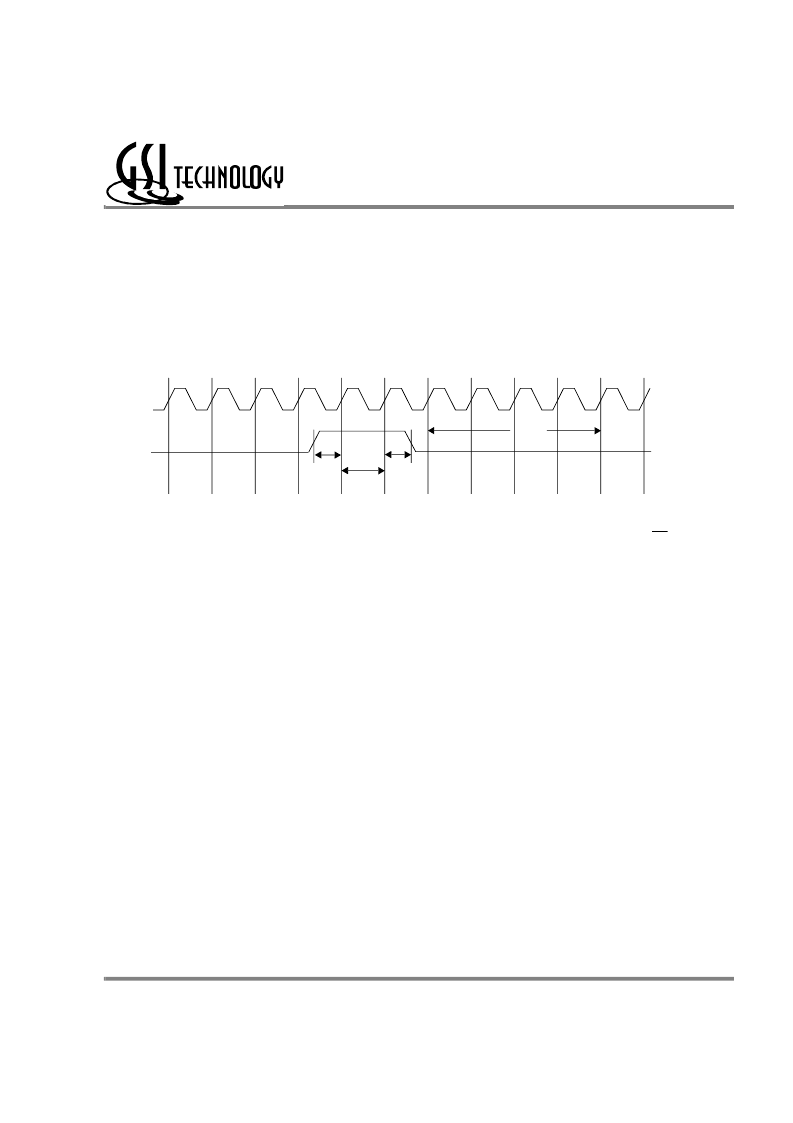
Sleep mode is a low current, power-down mode in which the device is deselected and current is reduced to I
SB
2. The duration of
Sleep mode is dictated by the length of time the ZZ is in a High state. After entering Sleep mode, all inputs except ZZ become
disabled and all outputs go to High-Z The ZZ pin is an asynchronous, active high input that causes the device to enter Sleep mode.
When the ZZ pin is driven high, I
SB
2 is guaranteed after the time tZZI is met. Because ZZ is an asynchronous input, pending
operations or operations in progress may not be properly completed if ZZ is asserted. Therefore, Sleep mode must not be initiated
until valid pending operations are completed. Similarly, when exiting Sleep mode during tZZR, only a Deselect or Read commands
may be applied while the SRAM is recovering from Sleep mode.
Sleep Mode Timing Diagram
Designing for Compatibility
The GSI NBT SRAMs offer users a configurable selection between Flow Through mode and Pipeline mode via the FT signal found
on Pin 14. Not all vendors offer this option, however most mark Pin 14 as V
DD
or V
DDQ
on pipelined parts and V
SS
on flow
through parts. GSI NBT SRAMs are fully compatible with these sockets.
Pin 66, a No Connect (NC) on GSI’s GS880Z18/36 NBT SRAM, the Parity Error open drain output on GSI’s GS881Z18/36 NBT
SRAM, is often marked as a power pin on other vendor’s NBT-compatible SRAMs. Specifically, it is marked V
DD
or V
DDQ
on
pipelined parts and V
SS
on flow through parts. Users of GSI NBT devices who are not actually using the ByteSafe parity feature
may want to design the board site for the RAM with Pin 66 tied high through a 1k ohm resistor in Pipeline mode applications or
tied low in Flow Through mode applications in order to keep the option to use non-configurable devices open. By using the pull-up
resistor, rather than tying the pin to one of the power rails, users interested in upgrading to GSI’s ByteSafe NBT SRAMs
(GS881Z18/36), featuring Parity Error detection and JTAG Boundary Scan, will be ready for connection to the active low, open
drain Parity Error output driver at Pin 66 on GSI’s TQFP ByteSafe RAMs.
ByteSafe
Parity Functions
This SRAM includes a write data parity check that checks the validity of data coming into the RAM on write cycles. In Flow
Through mode, write data errors are reported in the cycle following the data input cycle. In Pipeline mode, write data errors are
reported one clock cycle later. (See
Write Parity Error Output Timing Diagram
.) The Data Parity Mode (DP) pin must be tied
high to set the RAM to check for even parity or low to check for odd parity. Read data parity is not checked by the RAM as data.
Validity is best established at the data’s destination. The Parity Error Output is an open drain output and drives low to indicate a
parity error. Multiple Parity Error Output pins may share a common pull-up resistor.
CK
ZZ
tZZR
tZZH
tZZS
~
~
Sleep
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| GS881Z18T-80 | 8Mb Pipelined and Flow Through Synchronous NBT SRAMs |
| GS881Z18T-80I | 8Mb Pipelined and Flow Through Synchronous NBT SRAMs |
| GS881Z36T-100 | 8Mb Pipelined and Flow Through Synchronous NBT SRAMs |
| GS881Z36T-100I | 8Mb Pipelined and Flow Through Synchronous NBT SRAMs |
| GS881Z36T-11 | 8Mb Pipelined and Flow Through Synchronous NBT SRAMs |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| GS881Z18T-80 | 制造商:GSI 制造商全稱:GSI Technology 功能描述:8Mb Pipelined and Flow Through Synchronous NBT SRAMs |
| GS881Z18T-80I | 制造商:GSI 制造商全稱:GSI Technology 功能描述:8Mb Pipelined and Flow Through Synchronous NBT SRAMs |
| GS881Z32BD-150 | 制造商:GSI 制造商全稱:GSI Technology 功能描述:9Mb Pipelined and Flow Through Synchronous NBT SRAM |
| GS881Z32BD-150I | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:9Mb Pipelined and Flow Through Synchronous NBT SRAM |
| GS881Z32BD-150IT | 制造商:GSI 制造商全稱:GSI Technology 功能描述:9Mb Pipelined and Flow Through Synchronous NBT SRAM |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。