- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄98229 > THS7368IPW (TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC) 6 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO20 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | THS7368IPW |
| 廠商: | TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC |
| 元件分類: | 音頻/視頻放大 |
| 英文描述: | 6 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO20 |
| 封裝: | GREEN, TSSOP-20 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 17/40頁 |
| 文件大小: | 1123K |
| 代理商: | THS7368IPW |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁當(dāng)前第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁
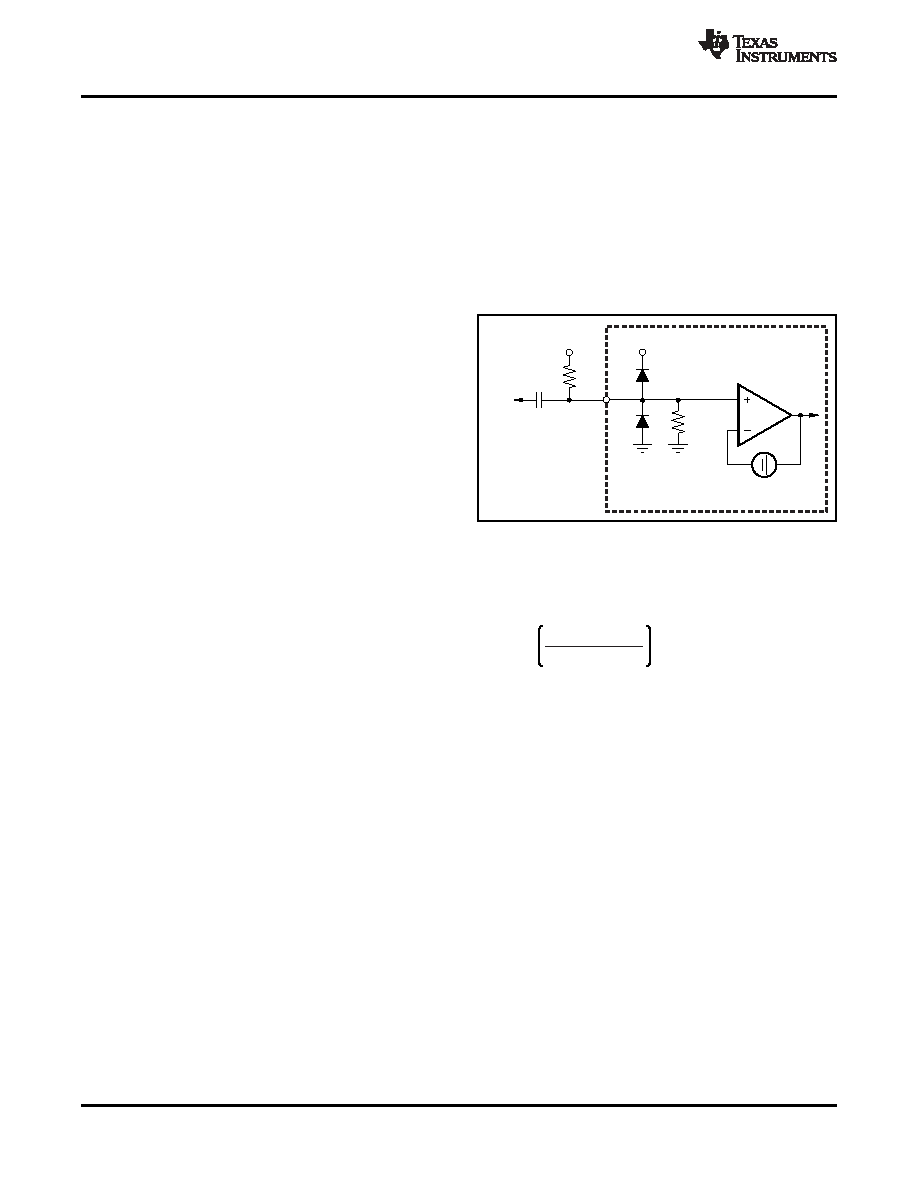
Level
Shift
Internal
Circuitry
+3.3V
800kW
R
PU
Input
Pin
Input
C
0.1 F
m
IN
V
=V
DC
S
800kW
800k
+R
W
PU
SBOS497 – DECEMBER 2009
www.ti.com
However, what happens if the input signal goes
INPUT MODE OF OPERATION: AC BIAS
above the 0-V input level? The problem is the video
Sync-tip clamps work very well for signals that have
signal is always above this level and must not be
horizontal and/or vertical syncs associated with them;
altered in any way. Thus, if the sync level of the input
however, some video signals do not have a sync
signal is above this 0-V level, then the internal
embedded within the signal. If ac-coupling of these
discharge (sink) current reduces the ac-coupled bias
signals is desired, then a dc bias is required to
signal to the proper 0-V level.
properly set the dc operating point within the
This discharge current must not be large enough to
THS7368. This function is easily accomplished with
alter the video signal appreciably or picture quality
the THS7368 by simply adding an external pull-up
issues may arise. This effect is often seen by looking
resistor to the positive power supply, as shown in
at the tilt (droop) of a constant luma signal being
applied and the resulting output level. The associated
change in luma level from the beginning and end of
the video line is the amount of line tilt (droop).
If the discharge current is very small, the amount of
tilt is very low, which is a generally a good thing.
However, the amount of time for the system to
capture the sync signal could be too long. This effect
is also termed hum rejection. Hum arises from the ac
line voltage frequency of 50 Hz or 60 Hz. The value
of the discharge current and the ac-coupling capacitor
combine to dictate the hum rejection and the amount
of line tilt.
To allow for both dc- and ac-coupling in the same
Figure 40. AC-Bias Input Mode Circuit
part, the THS7368 incorporates an 800-k
resistor to
Configuration
ground. Although a true constant current sink is
preferred over a resistor, there can be issues when
the voltage is near ground. This configuration can
The dc voltage appearing at the input pin is equal to
cause the current sink transistor to saturate and
cause potential problems with the signal. The 800-k
resistor is large enough to not impact a dc-coupled
DAC termination. For discharging an ac-coupled
(1)
source, Ohm’s Law is used. If the video signal is 1 V,
The THS7368 allowable input range is approximately
then there is 1 V/800 k
= 1.25-μA of discharge
0 V to (VS+ – 1.5 V), allowing for a very wide input
current. If more hum rejection is desired or there is a
voltage range. As such, the input dc bias point is very
loss of sync occurring, then simply decrease the
flexible, with the output dc bias point being the
0.1-
μF input coupling capacitor. A decrease from
primary factor. For example, if the output dc bias
0.1
μF to 0.047 μF increases the hum rejection by a
point is desired to be 1.6 V on a 3.3-V supply, then
factor of 2.1. Alternatively, an external pull-down
the input dc bias point should be (1.6 V – 300 mV)/2
resistor to ground may be added that decreases the
= 0.65 V. Thus, the pull-up resistor calculates to
overall
resistance
and
ultimately
increases
the
approximately 3.3 M
, resulting in 0.644 V. If the
discharge current.
output dc-bias point is desired to be 1.6 V with a 5-V
To ensure proper stability of the ac STC control loop,
power supply, then the pull-up resistor calculates to
the source impedance must be less than 1-k
with
approximately 5.36 M
.
the input capacitor in place. Otherwise, there is a
Keep in mind that the internal 800-k
resistor has
possibility of the control loop ringing, which may
approximately
a
±20%
variance.
As
such,
the
appear on the output of the THS7368. Because most
calculations should take this variance into account.
DACs or encoders use resistors to establish the
For the 0.644-V example above, using an ideal
voltage, which are typically less than 300-
, meeting
3.3-M
resistor,
the
input
dc
bias
voltage
is
the less than 1-k
requirement is easily done.
approximately 0.644 V ± 0.1 V.
However, if the source impedance looking from the
THS7368 input perspective is very high, then simply
The value of the output bias voltage is very flexible
adding a 1-k
resistor to GND ensures proper
and is left to each individual design. It is important to
operation of the THS7368.
ensure that the signal does not clip or saturate the
video signal. Thus, it is recommended to ensure the
output bias voltage is between 0.9 V and (VS+ – 1 V).
For 100% color saturated CVBS or signals with
24
Copyright 2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): THS7368
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| THS7372IPWR | 4 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO14 |
| THS7372IPW | 4 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO14 |
| THS7374IPWR | 4 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO14 |
| THS7374IPW | 4 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO14 |
| THS7374IPWG4 | 4 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO14 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| THS7368IPW | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:Video Amplifier IC 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:IC, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, HEX, 350MHZ TSSOP20 |
| THS7368IPWR | 功能描述:視頻放大器 6-Ch Video Amp RoHS:否 制造商:ON Semiconductor 通道數(shù)量:4 電源類型: 工作電源電壓:3.3 V, 5 V 電源電流: 最小工作溫度: 最大工作溫度: 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-14 封裝:Reel |
| THS7371IPW | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:VIDEO OPAM - Rail/Tube |
| THS7371IPWR | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:VIDEO OPAM - Tape and Reel |
| THS7372 | 制造商:TI 制造商全稱:Texas Instruments 功能描述:4-Channel Video Amplifier with One CVBS and Three Full-HD Filters with 6-dB Gain |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。