- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄359756 > S29GL128P90FAIR10 (SPANSION LLC) 3.0 Volt-only Page Mode Flash Memory featuring 90 nm MirrorBit Process Technology PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | S29GL128P90FAIR10 |
| 廠商: | SPANSION LLC |
| 元件分類: | PROM |
| 英文描述: | 3.0 Volt-only Page Mode Flash Memory featuring 90 nm MirrorBit Process Technology |
| 中文描述: | 128M X 1 FLASH 3V PROM, 90 ns, PBGA64 |
| 封裝: | 13 X 11 MM, 1 MM PITCH, FBGA-64 |
| 文件頁數: | 26/77頁 |
| 文件大小: | 2121K |
| 代理商: | S29GL128P90FAIR10 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁當前第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁
26
S29GL-P MirrorBit
Flash Family
S29GL-P_00_A7 November 8, 2007
D a t a
S h e e t
( P r e l i m i n a r y )
Software Functions and Sample Code
Note
Base = Base Address.
The following is a C source code example of using the single word program function. Refer to the
Spansion
Low Level Driver User’s Guide
(available on
www.spansion.com
) for general information on Spansion Flash
memory software development guidelines.
/* Example: Program Command */
*( (UINT16 *)base_addr + 0x555 ) = 0x00AA; /* write unlock cycle 1 */
*( (UINT16 *)base_addr + 0x2AA ) = 0x0055; /* write unlock cycle 2 */
*( (UINT16 *)base_addr + 0x555 ) = 0x00A0; /* write program setup command */
*( (UINT16 *)pa ) = data; /* write data to be programmed */
/* Poll for program completion */
7.7.2
Write Buffer Programming
Write Buffer Programming allows the system to write a maximum of 32 words in one programming operation.
This results in a faster effective word programming time than the standard “word” programming algorithms.
The Write Buffer Programming command sequence is initiated by first writing two unlock cycles. This is
followed by a third write cycle containing the Write Buffer Load command written at the Sector Address in
which programming occurs. At this point, the system writes the number of “word locations minus 1” that are
loaded into the page buffer at the Sector Address in which programming occurs. This tells the device how
many write buffer addresses are loaded with data and therefore when to expect the “Program Buffer to Flash”
confirm command. The number of locations to program cannot exceed the size of the write buffer or the
operation aborts. (Number loaded = the number of locations to program minus 1. For example, if the system
programs 6 address locations, then 05h should be written to the device.)
The system then writes the starting address/data combination. This starting address is the first address/data
pair to be programmed, and selects the “write-buffer-page” address. All subsequent address/data pairs must
fall within the elected-write-buffer-page.
The “write-buffer-page” is selected by using the addresses A
MAX
–A5.
The “write-buffer-page” addresses must be the same for all address/data pairs loaded into the write buffer.
(This means Write Buffer Programming cannot be performed across multiple “write-buffer-pages.” This also
means that Write Buffer Programming cannot be performed across multiple sectors. If the system attempts to
load programming data outside of the selected “write-buffer-page”, the operation ABORTs.)
After writing the Starting Address/Data pair, the system then writes the remaining address/data pairs into the
write buffer.
Note that if a Write Buffer address location is loaded multiple times, the “address/data pair” counter is
decremented for every data load operation. Also, the last data loaded at a location before the “Program Buffer
to Flash” confirm command is the data programmed into the device. It is the software's responsibility to
comprehend ramifications of loading a write-buffer location more than once. The counter decrements for each
data load operation, NOT for each unique write-buffer-address location. Once the specified number of write
buffer locations have been loaded, the system must then write the “Program Buffer to Flash” command at the
Sector Address. Any other address/data write combinations abort the Write Buffer Programming operation.
The Write Operation Status bits should be used while monitoring the last address location loaded into the
write buffer. This eliminates the need to store an address in memory because the system can load the last
address location, issue the program confirm command at the last loaded address location, and then check
the write operation status at that same address. DQ7, DQ6, DQ5, DQ2, and DQ1 should be monitored to
determine the device status during Write Buffer Programming.
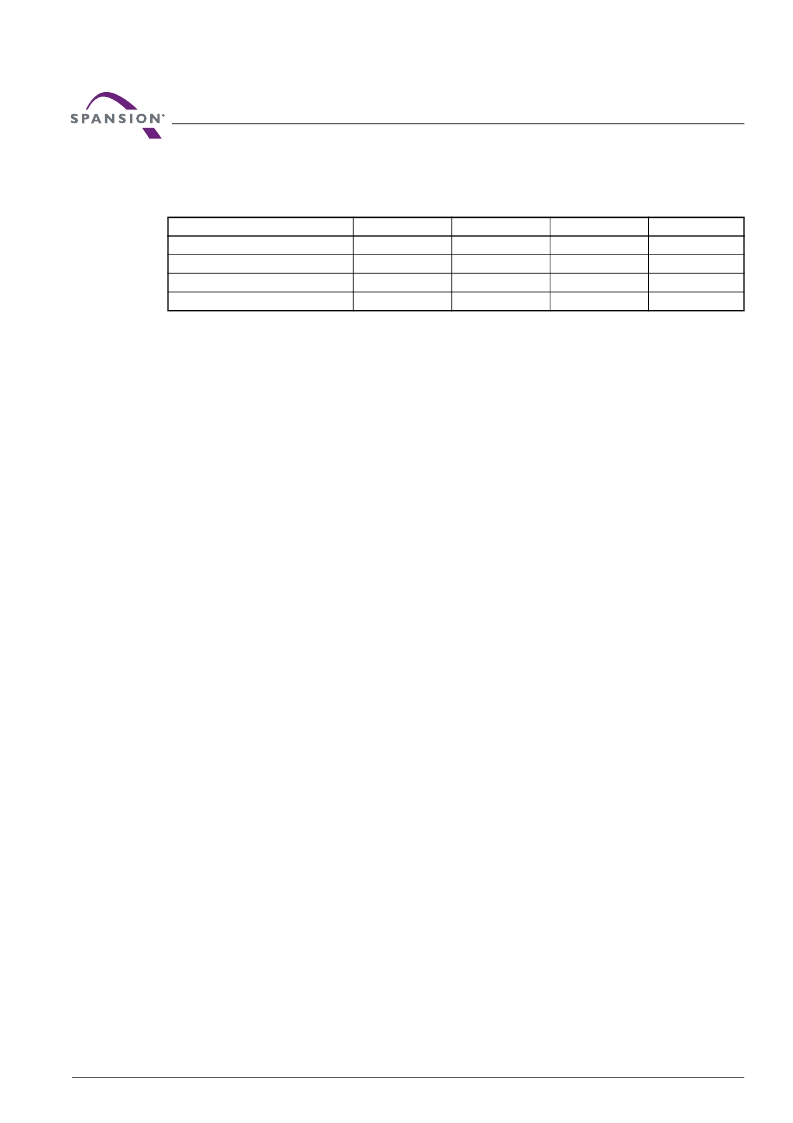
Table 7.6
Single Word/Byte Program
(LLD Function = lld_ProgramCmd)
Cycle
Operation
Byte Address
Word Address
Data
Unlock Cycle 1
Write
Base + AAAh
Base + 555h
00AAh
Unlock Cycle 2
Write
Base + 555h
Base + 2AAh
0055h
Program Setup
Write
Base + AAAh
Base + 555h
00A0h
Program
Write
Byte Address
Word Address
Data
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| S29GL128P90FAIR12 | 3.0 Volt-only Page Mode Flash Memory featuring 90 nm MirrorBit Process Technology |
| S29GL128P90FAIV10 | 3.0 Volt-only Page Mode Flash Memory featuring 90 nm MirrorBit Process Technology |
| S29GL128P90FAIV12 | 3.0 Volt-only Page Mode Flash Memory featuring 90 nm MirrorBit Process Technology |
| S29GL128P90FFI010 | 3.0 Volt-only Page Mode Flash Memory featuring 90 nm MirrorBit Process Technology |
| S29GL128P90FFI012 | 3.0 Volt-only Page Mode Flash Memory featuring 90 nm MirrorBit Process Technology |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| S29GL128P90FAIR20 | 制造商:Spansion 功能描述:FLASH PARALLEL 3V/3.3V 128MBIT 16MX8/8MX16 90NS 64BGA - Trays 制造商:Spansion 功能描述:SPZS29GL128P90FAIR20 IC 128M PAGE-MODE 制造商:Spansion 功能描述:NOR Flash Parallel 3V/3.3V 128Mbit 16M/8M x 8bit/16bit 90ns 64-Pin Fortified BGA Tray |
| S29GL128P90FFCR10 | 功能描述:閃存 128MB 3.0-3.6V 90ns Parallel NOR 閃存 RoHS:否 制造商:ON Semiconductor 數據總線寬度:1 bit 存儲類型:Flash 存儲容量:2 MB 結構:256 K x 8 定時類型: 接口類型:SPI 訪問時間: 電源電壓-最大:3.6 V 電源電壓-最小:2.3 V 最大工作電流:15 mA 工作溫度:- 40 C to + 85 C 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體: 封裝:Reel |
| S29GL128P90FFCR12 | 功能描述:閃存 128M 3.0V 90ns Parallel NOR 閃存 RoHS:否 制造商:ON Semiconductor 數據總線寬度:1 bit 存儲類型:Flash 存儲容量:2 MB 結構:256 K x 8 定時類型: 接口類型:SPI 訪問時間: 電源電壓-最大:3.6 V 電源電壓-最小:2.3 V 最大工作電流:15 mA 工作溫度:- 40 C to + 85 C 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體: 封裝:Reel |
| S29GL128P90FFCR20 | 功能描述:閃存 128MB 3.0-3.6V 90ns Parallel NOR 閃存 RoHS:否 制造商:ON Semiconductor 數據總線寬度:1 bit 存儲類型:Flash 存儲容量:2 MB 結構:256 K x 8 定時類型: 接口類型:SPI 訪問時間: 電源電壓-最大:3.6 V 電源電壓-最小:2.3 V 最大工作電流:15 mA 工作溫度:- 40 C to + 85 C 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體: 封裝:Reel |
| S29GL128P90FFCR23 | 功能描述:閃存 128M 3.0V 90ns Parallel NOR 閃存 RoHS:否 制造商:ON Semiconductor 數據總線寬度:1 bit 存儲類型:Flash 存儲容量:2 MB 結構:256 K x 8 定時類型: 接口類型:SPI 訪問時間: 電源電壓-最大:3.6 V 電源電壓-最小:2.3 V 最大工作電流:15 mA 工作溫度:- 40 C to + 85 C 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體: 封裝:Reel |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。