- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄382378 > PCA9532 (NXP Semiconductors N.V.) 16-bit I2C LED dimmer PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | PCA9532 |
| 廠商: | NXP Semiconductors N.V. |
| 英文描述: | 16-bit I2C LED dimmer |
| 中文描述: | 16位I2C LED調(diào)光 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 5/20頁(yè) |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 154K |
| 代理商: | PCA9532 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)當(dāng)前第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)
Philips Semiconductors
Product data
PCA9532
16-bit I
2
C LED dimmer
2003 May 02
5
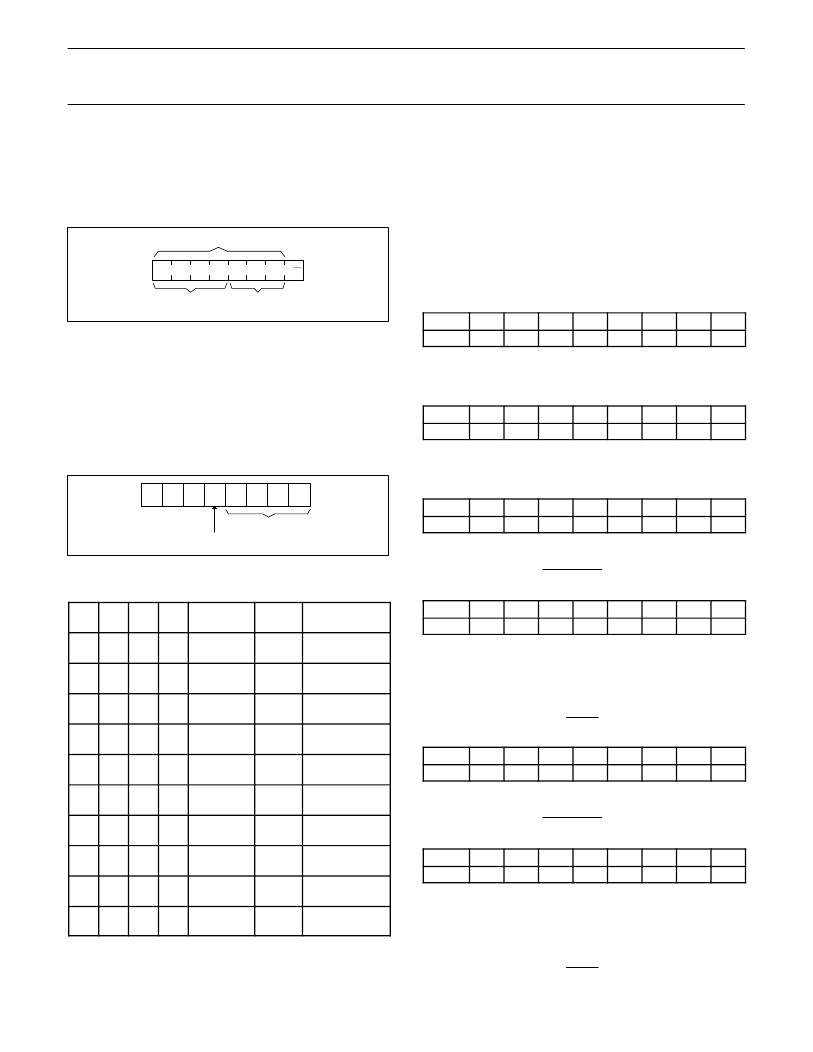
DEVICE ADDRESSING
Following a START condition the bus master must output the
address of the slave it is accessing. The address of the PCA9532 is
shown in Figure 4. To conserve power, no internal pull-up resistors
are incorporated on the hardware selectable address pins and they
must be pulled HIGH or LOW.
1
1
0
0
A2
A1
A0
SLAVE ADDRESS
su01420
FIXED
HARDWARE SELECTABLE
R/W
Figure 4. Slave address
The last bit of the address byte defines the operation to be
performed. When set to logic 1 a read is selected while a logic 0
selects a write operation.
CONTROL REGISTER
Following the successful acknowledgement of the slave address,
the bus master will send a byte to the PCA9532 which will be stored
in the Control Register. This register can be read and written via the
I
2
C-bus.
0
0
AI
B2
B1 B0
0
SW00898
B3
AUTO-INCREMENT FLAG
REGISTER ADDRESS
RESET STATE: 00h
Figure 5. Control register
CONTROL REGISTER DEFINITION
B3
B2
B1
B0
REGISTER
NAME
TYPE
REGISTER
FUNCTION
0
0
0
0
INPUT0
READ
INPUT
REGISTER 0
0
0
0
1
INPUT1
READ
INPUT
REGISTER 1
0
0
1
0
PSC0
READ/
WRITE
FREQUENCY
PRESCALER 0
0
0
1
1
PWM0
READ/
WRITE
PWM
REGISTER 0
0
1
0
0
PSC1
READ/
WRITE
FREQUENCY
PRESCALER 1
0
1
0
1
PWM1
READ/
WRITE
PWM
REGISTER 1
0
1
1
0
LS0
READ/
WRITE
LED 0-3
SELECTOR
0
1
1
1
LS1
READ/
WRITE
LED 4-7
SELECTOR
1
0
0
0
LS2
READ/
WRITE
LED 8-11
SELECTOR
1
0
0
1
LS3
READ/
WRITE
LED 12-15
SELECTOR
REGISTER DESCRIPTION
The lowest 3 bits are used as a pointer to determine which register
will be accessed.
If the auto-increment flag (AI) is set, the four low order bits of the
Control Register are automatically incremented after a read or write.
This allows the user to program the registers sequentially. The
contents of these bits will rollover to ‘0000’ after the last register is
accessed.
When auto-increment flag is set (AI = 1) and a read sequence is
initiated, the sequence must start by reading a register different from
‘0’ (B3 B2 B1 B0
0 0 0 0)
Only the 4 least significant bits are affected by the AI flag.
Unused bits must be programmed with zeroes.
INPUT0
—
INPUT REGISTER 1
bit
I7
I6
default
0
0
The INPUT register 1 reflects the state of the device pins (inputs 0
to 7). Writes to this register will be acknowledged but will have no
effect.
INPUT1
—
INPUT REGISTER 2
bit
I15
I14
I13
default
0
0
0
The INPUT register 1 reflects the state of the device pins (inputs 8
to 15). Writes to this register will be acknowledged but will have no
effect.
PSC0
—
FREQUENCY PRESCALER 0
bit
7
6
5
default
0
0
0
PSC0 is used to program the period of the PWM output.
I5
0
I4
0
I3
0
I2
0
I1
0
I0
0
I12
0
I11
0
I10
0
I9
0
I8
0
4
0
3
0
2
0
1
0
0
0
The period of BLINK0
(PSC0
1)
152
PWM0
—
PWM REGISTER 0
bit
7
default
1
The PWM0 register determines the duty cycle of BLINK0. The
outputs are LOW (LED on) when the count is less than the value in
PWM0 and HIGH (LED off) when it is greater. If PWM0 is
programmed with 00h, then the PWM0 output is always HIGH
(LED off).
6
0
5
0
4
0
3
0
2
0
1
0
0
0
The duty cycle of BLINK0 is: P256
PSC1
—
FREQUENCY PRESCALER 1
bit
7
6
default
0
0
PSC1 is used to program the period of PWM output.
5
0
4
0
3
0
2
0
1
0
0
0
The period of BLINK1
(PSC1
1)
152
PWM1
—
PWM REGISTER 1
bit
7
default
1
The PWM1 register determines the duty cycle of BLINK1. The
outputs are LOW (LED on) when the count is less than the value in
PWM1 and HIGH (LED off) when it is greater. If PWM1 is
programmed with 00h, then the PWM1 output is always HIGH
(LED off).
6
0
5
0
4
0
3
0
2
0
1
0
0
0
The duty cycle of BLINK1 is: P256
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PCA9533 | 4-bit I2C LED dimmer |
| PCA9533D01 | 4-bit I2C LED dimmer |
| PCA9533D02 | 4-bit I2C LED dimmer |
| PCA9533DP01 | 4-bit I2C LED dimmer |
| PCA9533DP02 | 4-bit I2C LED dimmer |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| PCA9532BS | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:16-bit I2C-bus LED dimmer |
| PCA9532BS,118 | 功能描述:LED照明驅(qū)動(dòng)器 I2C LED DIMMER 16BIT RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 輸入電壓:11.5 V to 23 V 工作頻率: 最大電源電流:1.7 mA 輸出電流: 最大工作溫度: 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:SO-16N |
| PCA9532BS-T | 功能描述:LED照明驅(qū)動(dòng)器 I2C LED DIMMER 16BIT RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 輸入電壓:11.5 V to 23 V 工作頻率: 最大電源電流:1.7 mA 輸出電流: 最大工作溫度: 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:SO-16N |
| PCA9532D | 功能描述:LED照明驅(qū)動(dòng)器 I2C LED DIMMER 16BIT RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 輸入電壓:11.5 V to 23 V 工作頻率: 最大電源電流:1.7 mA 輸出電流: 最大工作溫度: 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:SO-16N |
| PCA9532D,112 | 功能描述:LED照明驅(qū)動(dòng)器 I2C LED DIMMER 16BIT RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 輸入電壓:11.5 V to 23 V 工作頻率: 最大電源電流:1.7 mA 輸出電流: 最大工作溫度: 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:SO-16N |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。