- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄359243 > MVTX2802 (Zarlink Semiconductor Inc.) Managed 4-Port 1000 Mbps Ethernet Switch PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MVTX2802 |
| 廠商: | Zarlink Semiconductor Inc. |
| 英文描述: | Managed 4-Port 1000 Mbps Ethernet Switch |
| 中文描述: | 管理4端口1000 Mbps以太網(wǎng)交換機 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 21/154頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 1936K |
| 代理商: | MVTX2802 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁當(dāng)前第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁
MVTX2802
Data Sheet
21
Zarlink Semiconductor Inc.
3.2 Multicast Data Frame Forwarding
After receiving the switch response, the TxQ manager has to make the dropping decision. A global decision to
drop can be made, based on global FDB utilization and reservations. If so, then the FCB is released and the
frame is dropped. In addition, a selective decision to drop can be made, based on the TxQ occupancy at some
subset of the multicast packet’s destinations. If so, then the frame is dropped at some destinations but not
others, and the FCB is not released.
If the frame is not dropped at a particular destination port, then the TxQ manager formats an entry in the
multicast queue for that port and class. Multicast queues are physical queues (unlike the linked lists for unicast
frames). There are 4 multicast queues for each of the 4 Gigabit ports. During scheduling, the TxQ manager
treats the unicast queue and the multicast queue of the same class as one logical queue.
The port control requests a FCB release only after the EOF for the multicast frame has been read by all ports to
which the frame is destined.
3.3 Frame Forwarding To and From CPU
Frame forwarding
from
the CPU port to a regular transmission port is nearly the same as forwarding between
transmission ports. The only difference is that the physical destination port must be indicated in addition to the
destination MAC address. If an invalid port is indicated the frame is forwarded accordingly to the destination
MAC address.
Frame forwarding
to
the CPU port is nearly the same as forwarding to a regular transmission port. The only
difference is in frame scheduling. Instead of using the patent-pending scheduling algorithms, scheduling for
the CPU port is simply based on strict priority. That is, a frame in a high priority queue will always be transmitted
before a frame in a lower priority queue. There are four output queues to the CPU and one received queue.
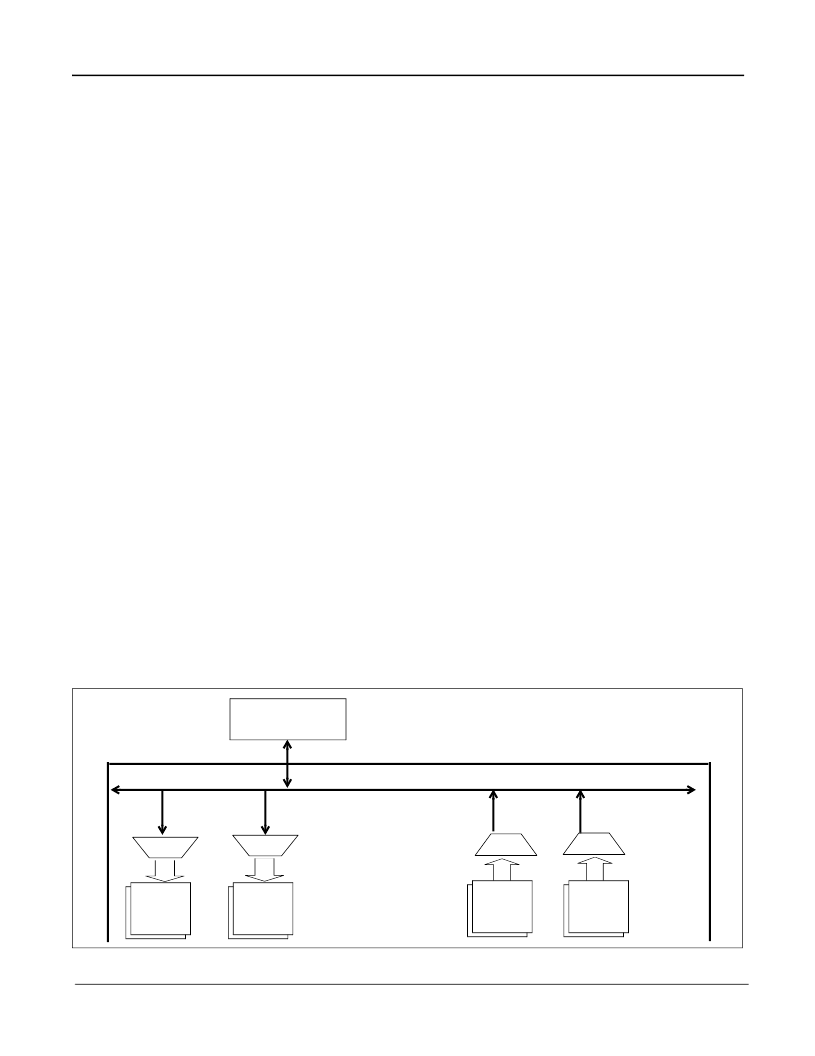
4.0 Memory Interface
4.1 Overview
The figure below illustrates the first part of the ZBT-SRAM interface for the MVTX2802AG. As shown, a 64 bit
bus ZBT-SRAM bank A is used for Tx/RxDMA access. Because the clock frequency is 133 MHz, the total
memory bandwidth is 64 bits
×
133 MHz = 8.5 Gbps, for frame data buffer (FDB) access.
Not shown in the figure are the CPU port RxDMA’s and TxDMA’s, each separately connected to its own bank
selector.
Figure 4 - MVTX2802AG SRAM Interface Block Diagram (DMAs for Gigabit Ports)
ZBT-SRAM Bank A
TX DMA
0-1
RX DMA
0-1
RX DMA
2-3
TX DMA
2-3
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MVTX2802AG | Managed 4-Port 1000 Mbps Ethernet Switch |
| MVTX2803 | Unmanaged 8-Port 1000 Mbps Ethernet Switch |
| MVTX2803AG | Unmanaged 8-Port 1000 Mbps Ethernet Switch |
| MVTX2804 | 8-Port 1000 Mbps Ethernet Distributed Switch |
| MVTX2804AG | 8-Port 1000 Mbps Ethernet Distributed Switch |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MVTX2802A | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Managed 4 port Gigabit Ethernet switch |
| MVTX2802AG | 制造商:ZARLINK 制造商全稱:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:Managed 4-Port 1000 Mbps Ethernet Switch |
| MVTX2803 | 制造商:ZARLINK 制造商全稱:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:Unmanaged 8-Port 1000 Mbps Ethernet Switch |
| MVTX2803A | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Unmanaged 8 port Gigabit Ethernet switch |
| MVTX2803AG | 制造商:ZARLINK 制造商全稱:Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 功能描述:Unmanaged 8-Port 1000 Mbps Ethernet Switch |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。