- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄374455 > MKT050104M500T (Sharma Electro Components Inc.) FILM CAPACITORS PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MKT050104M500T |
| 廠商: | Sharma Electro Components Inc. |
| 英文描述: | FILM CAPACITORS |
| 中文描述: | 薄膜電容器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 3/29頁 |
| 文件大小: | 1151K |
| 代理商: | MKT050104M500T |
第1頁第2頁當前第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁
ELECTRICAL - BASIC PARAMETERS
1.1 RATED CAPACITANCE
The nominal or rated value of capacitance is measured at 25 °C in an measuring bridge with 1K Hz
source, free of harmonics. Please refer to relevant series for the range of capacitance value covered.
Capacitance is frequency and temperature dependent. The variation pattern of capacitance with
temperature and frequency is explained in sections 2.1 and 2.2.
1.2 CAPACITANCE TOLERANCE
The permitted variation of actual value from the nominal value is termed the tolerance. The tolerance
is expressed in percentage. The standard tolerances for plastic film capacitors are ±5% (J), ±10% (K)
and ±20% (M).
1.3 RATED VOLTAGE
The voltage at which the capacitor can operate continuously up to a temperature of 85 °C (unless
otherwise specified) is the rated voltage. As this is a critical parameter for choosing a capacitor, the
case sizes are listed in a matrix of capacitance value and rated voltage.
1.4 CATEGORY VOLTAGE
The maximum voltage that may be applied continuously over the temperature range is termed the
category voltage. This is same as the rated voltage up to 85 °C unless otherwise specified in the
climactic category of the product. Above 85 °C a derating has to be applied depending upon the
dielectric.
1.5 OPERATING TEMPERATURE
This is the temperature range with in which the capacitor can function as specified in the climactic
category. Please refer to relevant sections for derating above the temperature at which the full rated
voltage can be applied.
1.6 DISSIPATION FACTOR
This is the measurement of tangent of loss angle (tan d) and is expressed as a percentage.
Measurement of dissipation factor is carried out at 1 K Hz. or 10 K Hz. as specified in the data sheet
of the relevant series at 25 °C. Dissipation factor is temperature and frequency dependent. The
nature of variation of dissipation factor with temperature and frequency for different dielectric are
explained in Figures 2.3A to 2.3C and 2.4A to 2.4C.
1.7 INSULATION RESISTANCE
Insulation Resistance is the electrical resistance offered by the capacitor. The Insulation Resistance
is measured directly in Mega Ohms where as for higher capacitance values it is expressed in seconds
as the product of M Ohm and μF.
1.8 PULSE RISE TIME
The pulse rise time or dv/dt rating is the capability of the capacitor to handle rapid changes in voltage
or pulse. This is expressed in terms of Volts per μseconds. The dv/ dt rating of a capacitor depends
upon the dielectric as well as the design and construction of the capacitors. The dv/dt values of
different types of capacitors are listed in the corresponding data sheets of the capacitors.
ELECTRICAL - EFFECTS AND RELATIONS
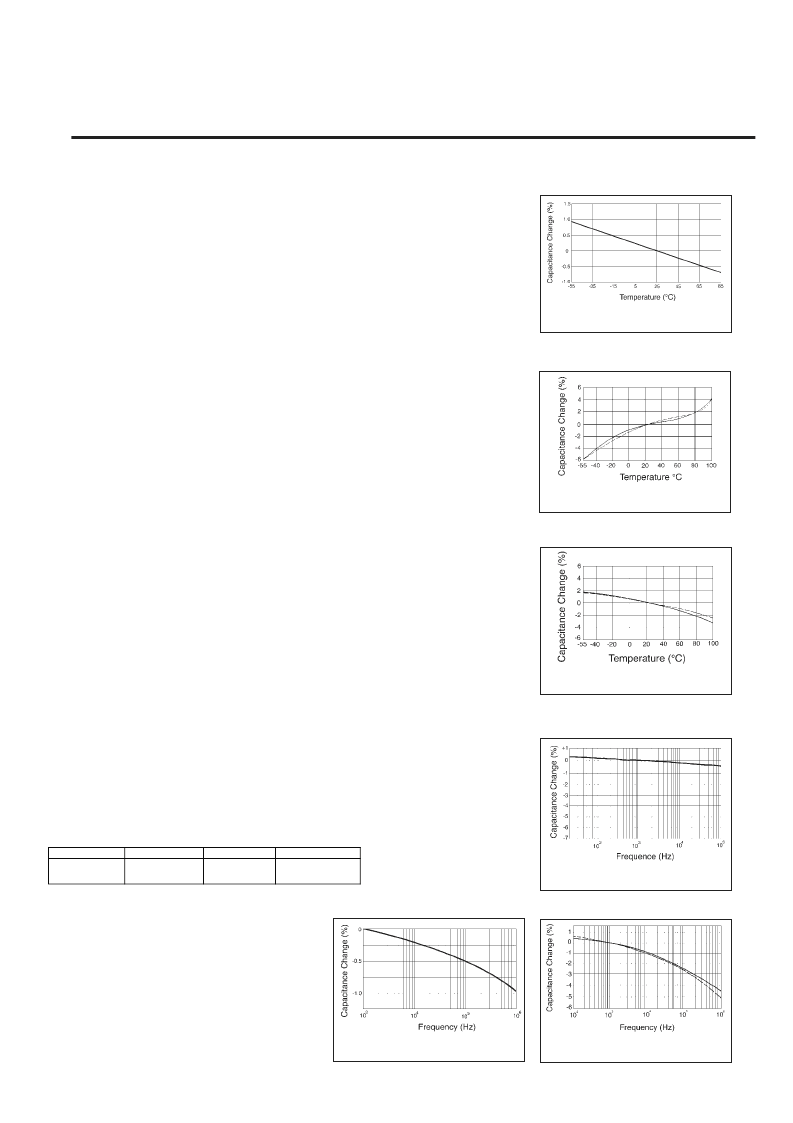
2.1 TEMPERATURE DEPENDENCE OF CAPACITANCE
Capacitance of plastic film capacitors vary with temperature. However the pattern of variation is
different for different plastic film dielectrics such as Polystyrene, Polyester and Polypropylene. The
The variation patterns for these dielectrics are shown in figure 2.1A, 2.1B and 2.1C. The rate of
change of capacitance with temperature is termed the Temperature Coefficient. The nominal values
of temperature coefficient for different dielectrics are shown below.
2.2 FREQUENCY DEPENDENCE OF CAPACITANCE
Capacitance reduces with increase in frequency. The
variation pattern for different dielectrics are shown in
figure 2.2A, 2.2B and 2.2C.
2.3 TEMPERATURE DEPENDENCE OF
DISSIPATION FACTOR
The dissipation factor varies with temperature. Each
dielectric follows a unique variation pattern. The variation
pattern for different dielectrics are shown in figure 2.3A,
2.3B and 2.3C.
PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 2.1B
Figure 2.1C
Figure 2.2A
Figure 2.2C
Figure 2.2B
Polyester
Capacitance Change Vs. Temperature
Polypropylene
Capacitance Change Vs. Temperature
Polystyrene
Capacitance Change Vs. Frequency
Polyester
Capacitance Change Vs. Frequency
Polypropylene
Capacitance Change Vs. Frequency
DIELECTRICS
POLYSTYRENE
POLYESTER
POLYPROPYLENE
TEMPERATURE
COEFFICIENT
-150 ppm
+400 ppm
-200 ppm
Figure 2.1A
Polystyrene
Capacitance Change Vs. Temperature
Sharma Film Capacitors
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MKT075102A101 | FILM CAPACITORS |
| MKT075102A101A | FILM CAPACITORS |
| MKT075102A101T | FILM CAPACITORS |
| MKT075102A251 | FILM CAPACITORS |
| MKT075102A251A | FILM CAPACITORS |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MKT075 | 制造商:SHARMA 制造商全稱:Sharma Electro Components,Inc 功能描述:Sharma Film Capacitors |
| MKT075_1 | 制造商:SHARMA 制造商全稱:Sharma Electro Components,Inc 功能描述:Sharma Film Capacitors |
| MKT075102A101 | 制造商:SHARMA 制造商全稱:Sharma Electro Components,Inc 功能描述:FILM CAPACITORS |
| MKT075102A101A | 制造商:SHARMA 制造商全稱:Sharma Electro Components,Inc 功能描述:FILM CAPACITORS |
| MKT075102A101T | 制造商:SHARMA 制造商全稱:Sharma Electro Components,Inc 功能描述:FILM CAPACITORS |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。