- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄382301 > MC33121P (MOTOROLA INC) LOW VOLTAGE SUBSCRIBER LOOP INTERFACE CIRCUIT PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MC33121P |
| 廠商: | MOTOROLA INC |
| 元件分類: | 模擬傳輸電路 |
| 英文描述: | LOW VOLTAGE SUBSCRIBER LOOP INTERFACE CIRCUIT |
| 中文描述: | TELECOM-SLIC, PDIP20 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, DIP-20 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 26/32頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 570K |
| 代理商: | MC33121P |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁當(dāng)前第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁
MC33121
26
MOTOROLA
Alternate Circuit Configurations
a) Loop Current Limit
Replacing the RRF resistor with the circuit in Figure 43 will
change the DC loop current characteristics in two ways from
the graphs of Figures 5 – 7; a) the maximum loop current on
a short line can be reduced while increasing the current on a
long line, and b) the temperature dependence of the maxi-
mum current is reduced to the TC of the external reference
diode.
Figure 43. Alternate Current Limit Circuit
VAG
RXI
RRF1
LM385–1.2
RFO
RRF2
The LM385–1.2 is a precision temperature stable zener
diode. As the load impedance at Tip and Ring is reduced, the
voltage at RFO goes increasingly negative. When the zener
diode is turned on, the current into RXI is then clamped at a
value determined by RRF1 and the zener diode. To calculate
the two resistors, use the following procedure:
RRF1 must be > 0.7
(RRF1 + RRF2);
Determine RRF1 to set the current limit on a short line by
using the following equation:
102
1.23 V
IL(max)– 3.0 mA
RRF1
(23)
Then using Equation 1 calculate RRF for the long line cur-
rent. RRF2 is then determined by;
RRF2 = RRF – RRF1
(24)
Figure 44 illustrates one example using the above circuit.
Comparing this graph to the 5100
curve of Figure 7 shows
a substantial decrease in the current limit (at RL = 0), result-
ing in reduced power consumption and dissipation. Use of
this circuit does not affect the hookswitch or fault thresholds.
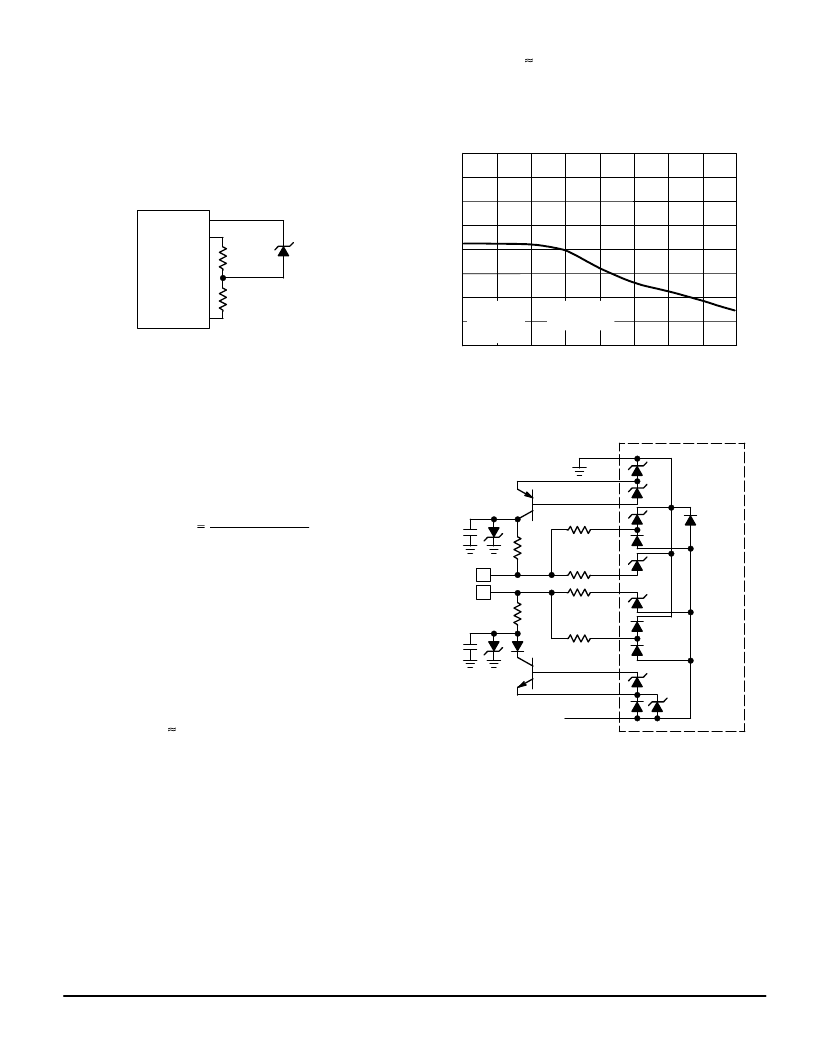
b) Protection Scheme
The protection circuit shown in Figure 45 has the advan-
tage of drawing
90% of the transient current from ground
(VCC) on a negative transient, rather than from the VEE line
as the circuit of Figure 4 does. The majority of the transient
current flows through the RP resistors and the Mosorbs while
a small amount (
and the CP, CN, RSI pins. On a positive transient, all the cur-
rent is directed to ground. The diode in the NPN’s collector
prevents reverse current through the base–collector junction
of the transistor during a negative transient.
10%) flows through the sense resistors
Figure 44. Loop Current versus Loop Resistance
Alternate Loop Current Limit Configuration
50
0
40
30
20
10
200
400
600
800
I
RL, LOOP RESISTANCE (
)
RRF1 = 4.3 k
RRF2 = 820
RS = 9.1 k
VEE = –24 V
TA = 25
°
C
Figure 45. Alternate Protection Scheme
VCC
EP
BP
CP
TSI
RSI
CN
BN
EN
VEE
14 V
MC33121
All zener diodes are 7.0 V except as noted.
14 V
1.5KE15
0.01
100 V
RP
TIP
RING
1.0 k
9100
1N4002
–24 V
0.01
100 V
RP
9100
1.0 k
1.5KE30
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MC33151 | High Speed Dual MOSFET Drivers |
| MC33151DR2 | High Speed Dual MOSFET Drivers |
| MC34151DR2 | High Speed Dual MOSFET Drivers |
| MC33151VDR2 | 0.022 UF 10% 50V X7R (0603) CAP TR |
| MC33151D | High Speed Dual MOSFET Drivers |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MC33128 | 制造商:MOTOROLA 制造商全稱:Motorola, Inc 功能描述:POWER MANAGEMENT CONTROLLER |
| MC33128D | 制造商:MOTOROLA 制造商全稱:Motorola, Inc 功能描述:POWER MANAGEMENT CONTROLLER |
| MC33129 | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:High Performance Current Mode Controllers |
| MC33129D | 制造商:Motorola Inc 功能描述: |
| MC33129DR2 | 制造商: 功能描述: 制造商:undefined 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。