- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄385520 > MAX1031BETI-T (MAXIM INTEGRATED PRODUCTS INC) 10-Bit 300ksps ADCs with FIFO, Temp Sensor, Internal Reference PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MAX1031BETI-T |
| 廠商: | MAXIM INTEGRATED PRODUCTS INC |
| 元件分類: | ADC |
| 英文描述: | 10-Bit 300ksps ADCs with FIFO, Temp Sensor, Internal Reference |
| 中文描述: | 16-CH 10-BIT SUCCESSIVE APPROXIMATION ADC, SERIAL ACCESS, QCC28 |
| 封裝: | 5 X 5 MM, TQFN-28 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 11/23頁 |
| 文件大小: | 254K |
| 代理商: | MAX1031BETI-T |
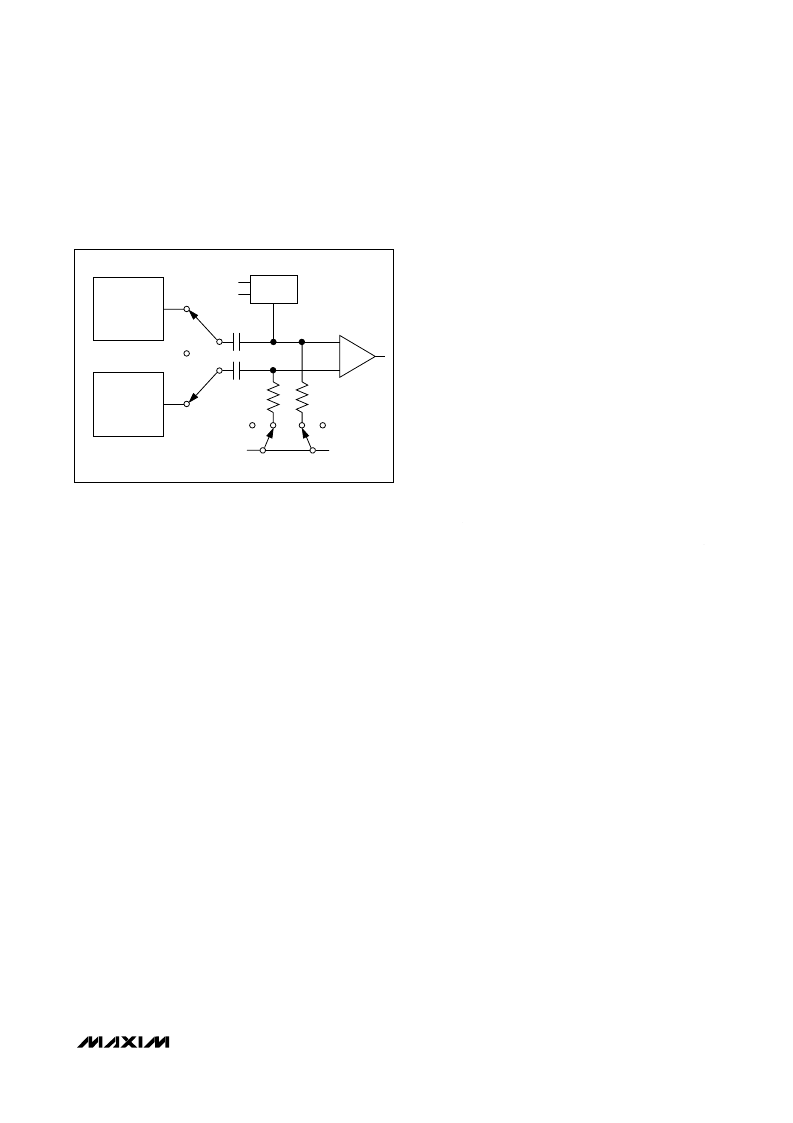
M
10-Bit 300ksps ADCs with FIFO,
Temp Sensor, Internal Reference
______________________________________________________________________________________
11
In differential mode, the T/H samples the difference
between two analog inputs, eliminating common-mode
DC offsets and noise. IN+ and IN- are selected from
the following pairs: AIN0/AIN1, AIN2/AIN3, AIN4/AIN5,
AIN6/AIN7, AIN8/AIN9, AIN10/AIN11, AIN12/AIN13,
and AIN14/AIN15. AIN0–AIN7 are available on the
MAX1027, MAX1029, and MAX1031. AIN8–AIN11 are
only available on the MAX1029 and MAX1031.
AIN12–AIN15 are only available on the MAX1031. See
Tables 2–5 for more details on configuring the inputs.
For the inputs that can be configured as
CNVST
or an
analog input, only one can be used at a time. For the
inputs that can be configured as REF- or an analog
input, the REF- configuration excludes the analog input.
Unipolar/Bipolar
Address the unipolar and bipolar registers through the
setup register (bits 1 and 0). Program a pair of analog
channels for differential operation by writing a 1 to the
appropriate bit of the bipolar or unipolar register.
Unipolar mode sets the differential input range from 0
to V
REF
. A negative differential analog input in unipolar
mode causes the digital output code to be zero.
Selecting bipolar mode sets the differential input range
to ±V
REF
/ 2. The digital output code is binary in unipo-
lar mode and two’s complement in bipolar mode (see
the transfer function graphs, Figures 8 and 9).
In single-ended mode, the MAX1027/MAX1029/
MAX1031 always operate in unipolar mode. The analog
inputs are internally referenced to GND with a full-scale
input range from 0 to V
REF
.
True Differential Analog Input T/H
The equivalent circuit of Figure 3 shows the
MAX1027/MAX1029/MAX1031s’ input architecture. In
track mode, a positive input capacitor is connected to
AIN0–AIN15 in single-ended mode (and AIN0, AIN2,
AIN4…AIN14 in differential mode). A negative input
capacitor is connected to GND in single-ended mode
(or AIN1, AIN3, AIN5…AIN15 in differential mode). For
external track-and-hold timing, use clock mode 01.
After the T/H enters hold mode, the difference between
the sampled positive and negative input voltages is
converted. The time required for the T/H to acquire an
input signal is determined by how quickly its input
capacitance is charged. If the input signal’s source
impedance is high, the required acquisition time
lengthens. The acquisition time, t
ACQ
, is the maximum
time needed for a signal to be acquired, plus the power-
up time. It is calculated by the following equation:
where R
IN
= 1.5k
, R
S
is the source impedance of the
input signal, and t
PWR
= 1μs, the power-up time of the
device. The varying power-up times are detailed in the
explanation of the clock mode conversions.
t
ACQ
is never less than 1.4μs, and any source imped-
ance below 300
does not significantly affect the
ADC’s AC performance. A high-impedance source can
be accommodated either by lengthening t
ACQ
or by
placing a 1μF capacitor between the positive and neg-
ative analog inputs.
Internal FIFO
The MAX1027/MAX1029/MAX1031 contain a FIFO
buffer that can hold up to 16 ADC results plus one tem-
perature result. This allows the ADC to handle multiple
internally clocked conversions and a temperature mea-
surement, without tying up the serial bus.
If the FIFO is filled and further conversions are request-
ed without reading from the FIFO, the oldest ADC
results are overwritten by the new ADC results. Each
result contains 2 bytes, with the MSB preceded by four
leading zeros and the LSB followed by two sub-bits.
After each falling edge of
CS
, the oldest available byte
of data is available at DOUT, MSB first. When the FIFO
is empty, DOUT is zero.
The first 2 bytes of data read out after a temperature
measurement always contain the temperature result
preceded by four leading zeros, MSB first. If another
t
x R
R
x
pF
t
AQC
S
IN
PWR
9
+
=
)
+
24
+
-
HOLD
CIN+
REF
GND
DAC
CIN-
V
DD
/2
COMPARATOR
AIN0-AIN15
(SINGLE ENDED);
AIN0, AIN2,
AIN4…AIN14
(DIFFERENTIAL)
GND
(SINGLE ENDED);
AIN1, AIN3,
AIN5…AIN15
(DIFFERENTIAL)
HOLD
HOLD
Figure 3. Equivalent Input Circuit
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MAX104 | 【5V, 1Gsps, 8-Bit ADC with On-Chip 2.2GHz Track/Hold Amplifier |
| MAX104CHC | 【5V, 1Gsps, 8-Bit ADC with On-Chip 2.2GHz Track/Hold Amplifier |
| MAX105 | Dual, 6-Bit, 800Msps ADC with On-Chip, Wideband Input Amplifier |
| MAX105ECS | Dual, 6-Bit, 800Msps ADC with On-Chip, Wideband Input Amplifier |
| MAX1067ACEE | Multichannel, 14-Bit, 200ksps Analog-to-Digital Converters |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MAX1032 | 制造商:MAXIM 制造商全稱:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:8-/4-Channel, 【12V Multirange Inputs, Serial 14-Bit ADCs |
| MAX1032_11 | 制造商:MAXIM 制造商全稱:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:8- and 4-Channel, ±3 x VREF Multirange Inputs, Serial 14-Bit ADCs |
| MAX1032_1112 | 制造商:MAXIM 制造商全稱:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:8- and 4-Channel, 3 x VREF Multirange Inputs, Serial 14-Bit ADCs |
| MAX1032BEUG+ | 功能描述:模數(shù)轉(zhuǎn)換器 - ADC 14Bit 8Ch 12V Serial ADC RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 通道數(shù)量:2 結(jié)構(gòu):Sigma-Delta 轉(zhuǎn)換速率:125 SPs to 8 KSPs 分辨率:24 bit 輸入類型:Differential 信噪比:107 dB 接口類型:SPI 工作電源電壓:1.7 V to 3.6 V, 2.7 V to 5.25 V 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:VQFN-32 |
| MAX1032BEUG+T | 功能描述:模數(shù)轉(zhuǎn)換器 - ADC 14Bit 8Ch 12V Serial ADC RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 通道數(shù)量:2 結(jié)構(gòu):Sigma-Delta 轉(zhuǎn)換速率:125 SPs to 8 KSPs 分辨率:24 bit 輸入類型:Differential 信噪比:107 dB 接口類型:SPI 工作電源電壓:1.7 V to 3.6 V, 2.7 V to 5.25 V 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:VQFN-32 |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。