- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄98006 > M37702S1ABFP 16-BIT, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP80 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | M37702S1ABFP |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 16-BIT, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP80 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, QFP-80 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 57/59頁 |
| 文件大小: | 811K |
| 代理商: | M37702S1ABFP |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁當(dāng)前第57頁第58頁第59頁
7
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37702M2AXXXFP, M37702M2BXXXFP
M37702S1AFP, M37702S1BFP
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU)
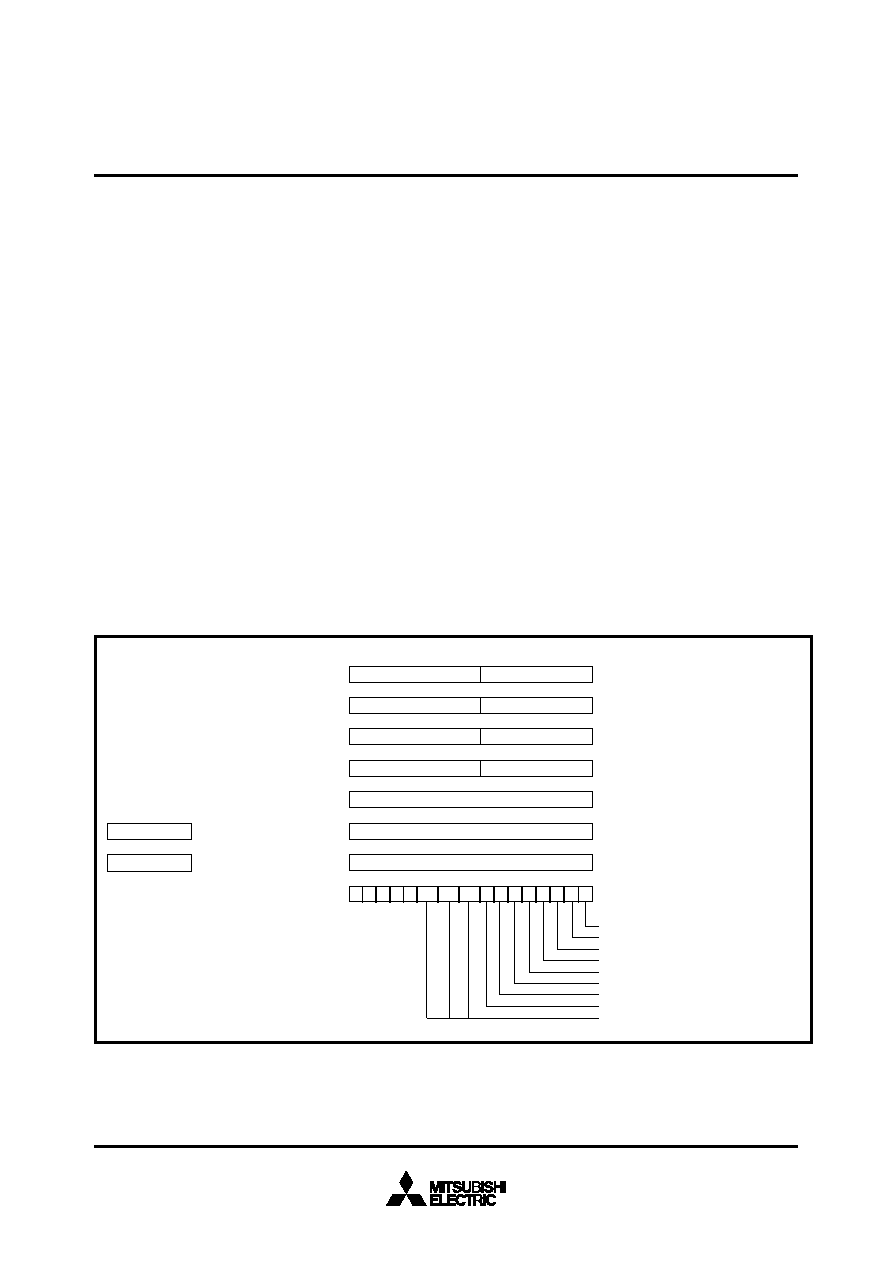
The CPU has ten registers and is shown in Figure 3. Each of
these registers is described below.
ACCUMULATOR A (A)
Accumulator A is the main register of the microcomputer. It con-
sists of 16 bits and the lower 8 bits can be used separately. The
data length flag m determines whether the register is used as 16-
bit register or as 8-bit register. It is used as a 16-bit register when
flag m is “0” and as an 8-bit register when flag m is “1”. Flag m is
a part of the processor status register (PS) which is described
later.
Data operations such as calculations, data transfer, input/output,
etc., is executed mainly through the accumulator.
ACCUMULATOR B (B)
Accumulator B has the same functions as accumulator A, but the
use of accumulator B requires more instruction bytes and execu-
tion cycles than accumulator A.
INDEX REGISTER X (X)
Index register X consists of 16 bits and the lower 8 bits can be
used separately. The index register length flag x determines
whether the register is used as 16-bit register or as 8-bit register.
It is used as a 16-bit register when flag x is “0” and as an 8-bit reg-
ister when flag x is “1”. Flag x is a part of the processor status reg-
ister (PS) which is described later.
In index addressing mode, register X is used as the index register
and the contents of this address is added to obtain the real ad-
dress.
Also, when executing a block transfer instruction MVP or MVN, the
contents of index register X indicate the low-order 16 bits of the
source data address. The third byte of the MVP and MVN is the
high-order 8 bits of the source data address.
INDEX REGISTER Y (Y)
Index register Y consists of 16 bits and the lower 8 bits can be
used separately. The index register length flag x determines
whether the register is used as 16-bit register or as 8-bit register.
It is used as a 16-bit register when flag x is “0” and as an 8-bit reg-
ister when flag x is “1”. Flag x is a part of the processor status
register (PS) which is described later.
In index addressing mode, register Y is used as the index register
and the contents of this address is added to obtain the real ad-
dress.
Also, when executing a block transfer instruction MVP or MVN, the
contents of index register Y indicate the low-order 16 bits of the
destination address. The second byte of the MVP and MVN is the
high-order 8 bits of the destination data address.
Fig. 3 Register structure
70
PG
Program bank register PG
70
DT
Data bank register DT
Carry flag
Zero flag
Interrupt disable flag
Decimal mode flag
Index register length flag
Data length flag
Negative flag
Overflow flag
Processor interrupt priority level IPL
Accumulator A
Accumulator B
Index register X
Index register Y
Stack pointer S
Program counter PC
Direct page register DPR
Processor status register PS
0
AH
AL
15
0
7
BH
BL
15
0
7
XH
XL
15
0
7
YH
YL
15
0
7
15
0
PC
15
0
15
0
DPR
7
15
0
N
IPL2
IPL0
IPL1
C
Z
I
D
x
m
V
00 00
S
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| M37703E2BSP | 16-BIT, OTPROM, 25 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP64 |
| M37703E4BSP | 16-BIT, OTPROM, 25 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP64 |
| M37703E4ESP | 16-BIT, OTPROM, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP64 |
| M37703M4AXXXSP | 16-BIT, MROM, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP64 |
| M37703M4BSP | 16-BIT, MROM, 25 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP64 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| M37702S1AFP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M37702S1BFP | 制造商:Renesas Electronics Corporation 功能描述: |
| M37702S1LGP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M37702S1LHP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M37702S4AFP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。