- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄358934 > LPC47M14I-NC (SMSC Corporation) 128 PIN ENGANCED SUPER I/O CONTROLLER WITH AN LPC INTERFACE AND USB HUB PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | LPC47M14I-NC |
| 廠商: | SMSC Corporation |
| 英文描述: | 128 PIN ENGANCED SUPER I/O CONTROLLER WITH AN LPC INTERFACE AND USB HUB |
| 中文描述: | 128引腳ENGANCED超級(jí)I / O與LPC接口和USB集線器控制器 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 34/205頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 1219K |
| 代理商: | LPC47M14I-NC |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)當(dāng)前第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)第77頁(yè)第78頁(yè)第79頁(yè)第80頁(yè)第81頁(yè)第82頁(yè)第83頁(yè)第84頁(yè)第85頁(yè)第86頁(yè)第87頁(yè)第88頁(yè)第89頁(yè)第90頁(yè)第91頁(yè)第92頁(yè)第93頁(yè)第94頁(yè)第95頁(yè)第96頁(yè)第97頁(yè)第98頁(yè)第99頁(yè)第100頁(yè)第101頁(yè)第102頁(yè)第103頁(yè)第104頁(yè)第105頁(yè)第106頁(yè)第107頁(yè)第108頁(yè)第109頁(yè)第110頁(yè)第111頁(yè)第112頁(yè)第113頁(yè)第114頁(yè)第115頁(yè)第116頁(yè)第117頁(yè)第118頁(yè)第119頁(yè)第120頁(yè)第121頁(yè)第122頁(yè)第123頁(yè)第124頁(yè)第125頁(yè)第126頁(yè)第127頁(yè)第128頁(yè)第129頁(yè)第130頁(yè)第131頁(yè)第132頁(yè)第133頁(yè)第134頁(yè)第135頁(yè)第136頁(yè)第137頁(yè)第138頁(yè)第139頁(yè)第140頁(yè)第141頁(yè)第142頁(yè)第143頁(yè)第144頁(yè)第145頁(yè)第146頁(yè)第147頁(yè)第148頁(yè)第149頁(yè)第150頁(yè)第151頁(yè)第152頁(yè)第153頁(yè)第154頁(yè)第155頁(yè)第156頁(yè)第157頁(yè)第158頁(yè)第159頁(yè)第160頁(yè)第161頁(yè)第162頁(yè)第163頁(yè)第164頁(yè)第165頁(yè)第166頁(yè)第167頁(yè)第168頁(yè)第169頁(yè)第170頁(yè)第171頁(yè)第172頁(yè)第173頁(yè)第174頁(yè)第175頁(yè)第176頁(yè)第177頁(yè)第178頁(yè)第179頁(yè)第180頁(yè)第181頁(yè)第182頁(yè)第183頁(yè)第184頁(yè)第185頁(yè)第186頁(yè)第187頁(yè)第188頁(yè)第189頁(yè)第190頁(yè)第191頁(yè)第192頁(yè)第193頁(yè)第194頁(yè)第195頁(yè)第196頁(yè)第197頁(yè)第198頁(yè)第199頁(yè)第200頁(yè)第201頁(yè)第202頁(yè)第203頁(yè)第204頁(yè)第205頁(yè)
SMSC DS – LPC47M14X
Page 34
Rev. 03/19/2001
MAIN STATUS REGISTER
Address 3F4 READ ONLY
The Main Status Register is a read-only register and indicates the status of the disk controller. The Main Status Register
can be read at any time. The MSR indicates when the disk controller is ready to receive data via the Data Register. It
should be read before each byte transferring to or from the data register except in DMA mode. No delay is required
when reading the MSR after a data transfer.
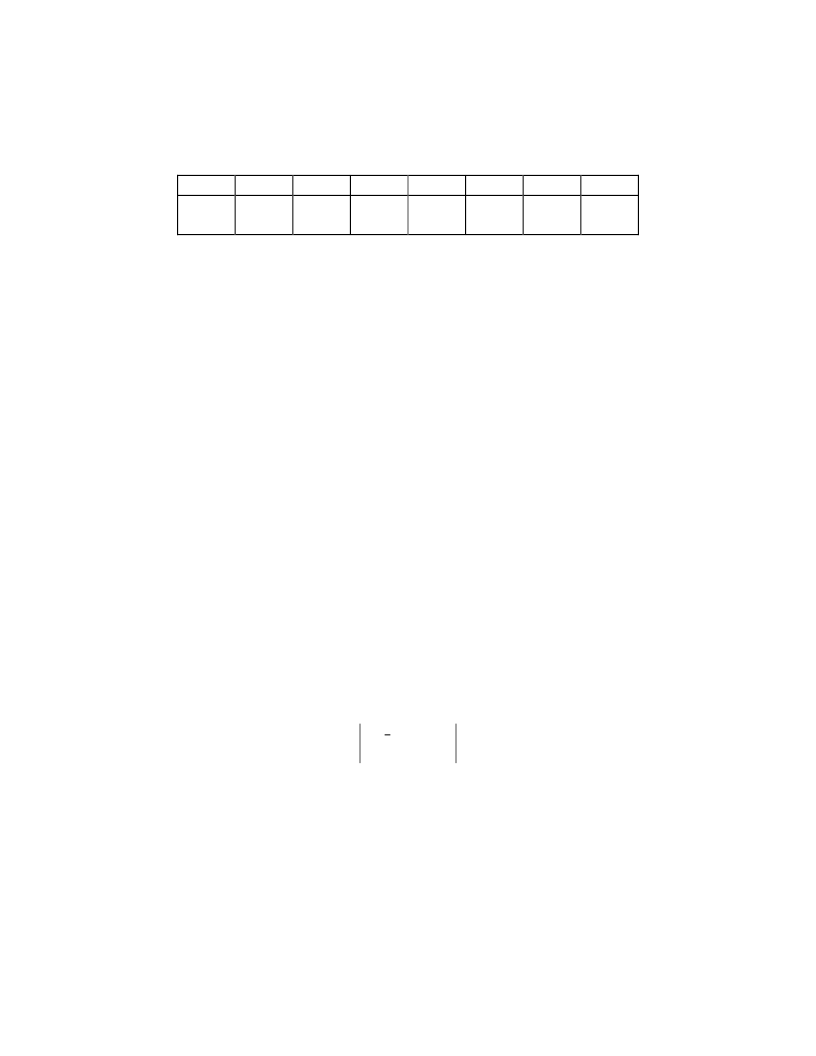
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
RQM
DIO
NON
DMA
CMD
BUSY
Reserved
Reserved
DRV1
BUSY
DRV0
BUSY
BIT 0 - 1 DRV x BUSY
These bits are set to 1s when a drive is in the seek portion of a command, including implied and overlapped seeks and
recalibrates.
BIT 4 COMMAND BUSY
This bit is set to a 1 when a command is in progress. This bit will go active after the command byte has been accepted
and goes inactive at the end of the results phase. If there is no result phase (Seek, Recalibrate commands), this bit is
returned to a 0 after the last command byte.
BIT 5 NON-DMA
Reserved, read ‘0’. This part does not support non-DMA mode.
BIT 6 DIO
Indicates the direction of a data transfer once a RQM is set. A 1 indicates a read and a 0 indicates a write is required.
BIT 7 RQM
Indicates that the host can transfer data if set to a 1. No access is permitted if set to a 0.
DATA REGISTER (FIFO)
Address 3F5 READ/WRITE
All command parameter information, disk data and result status are transferred between the host processor and the
floppy disk controller through the Data Register.
Data transfers are governed by the RQM and DIO bits in the Main Status Register.
The Data Register defaults to FIFO disabled mode after any form of reset. This maintains PC/AT hardware
compatibility. The default values can be changed through the Configure command (enable full FIFO operation with
threshold control). The advantage of the FIFO is that it allows the system a larger DMA latency without causing a disk
error. Table 12 gives several examples of the delays with a FIFO.
The data is based upon the following formula:
Threshold # x
1
DATA
RATE
At the start of a command, the FIFO action is always disabled and command parameters must be sent based upon the
RQM and DIO bit settings. As the command execution phase is entered, the FIFO is cleared of any data to ensure that
invalid data is not transferred.
x 8
- 1.5
μ
s =
DELAY
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| LPC47M14K-NC | RESTR 1.50K 1 TOL 1/8W MF |
| LPC47M14P-NC | 128 PIN ENGANCED SUPER I/O CONTROLLER WITH AN LPC INTERFACE AND USB HUB |
| LPC47M14X | 128 PIN ENGANCED SUPER I/O CONTROLLER WITH AN LPC INTERFACE AND USB HUB |
| LPC47M14B-NC | GE KIT:CAT5 VGA VIDEO 4CHSPLITTER & 3 LR REMOTES |
| LPC47M14D-NC | POS LASER SCANNER CABLE B |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| LPC47M14J-NC | 制造商:SMSC 制造商全稱:SMSC 功能描述:128 PIN ENGANCED SUPER I/O CONTROLLER WITH AN LPC INTERFACE AND USB HUB |
| LPC47M14K-NC | 制造商:SMSC 制造商全稱:SMSC 功能描述:128 PIN ENGANCED SUPER I/O CONTROLLER WITH AN LPC INTERFACE AND USB HUB |
| LPC47M14L-NC | 制造商:SMSC 制造商全稱:SMSC 功能描述:128 PIN ENGANCED SUPER I/O CONTROLLER WITH AN LPC INTERFACE AND USB HUB |
| LPC47M14M-NC | 制造商:SMSC 制造商全稱:SMSC 功能描述:128 PIN ENGANCED SUPER I/O CONTROLLER WITH AN LPC INTERFACE AND USB HUB |
| LPC47M14N-NC | 制造商:SMSC 制造商全稱:SMSC 功能描述:128 PIN ENGANCED SUPER I/O CONTROLLER WITH AN LPC INTERFACE AND USB HUB |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。