- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄16911 > ISL28006FH-20EVAL1Z (Intersil)EVAL BOARD FOR ISL28006 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | ISL28006FH-20EVAL1Z |
| 廠商: | Intersil |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 15/26頁 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | EVAL BOARD FOR ISL28006 |
| 應(yīng)用說明: | ISL28005/06 Application Note |
| 產(chǎn)品培訓(xùn)模塊: | ISL28005-6 Overview Solutions for Test and Measurement Equipment Solutions for Industrial Control Applications |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 1 |
| 每 IC 通道數(shù): | 1 - 單 |
| 放大器類型: | 電流檢測 |
| 轉(zhuǎn)換速率: | 0.67 V/µs |
| 電流供應(yīng)(主 IC): | 50µA |
| 板類型: | 完全填充 |
| 已供物品: | 板 |
| 已用 IC / 零件: | ISL28006 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁當(dāng)前第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁
ISL28006
22
FN6548.6
November 22, 2013
Overall Accuracy (VOA %)
VOA is defined as the total output accuracy Referred-to-Output
(RTO). The output accuracy contains all offset and gain errors, at
a single output voltage. Equation 4 is used to calculate the %
total output accuracy.
where
VOUT Actual = VSENSE x GAIN
Example: Gain = 100, For 100mV VSENSE input we measure
Power Dissipation
It is possible to exceed the +150°C maximum junction
temperatures under certain load and power supply conditions. It
is therefore important to calculate the maximum junction
temperature (TJMAX) for all applications to determine if power
supply voltages, load conditions, or package type need to be
modified to remain in the safe operating area. These parameters
are related using Equation 6:
where:
PDMAXTOTAL is the sum of the maximum power dissipation of
each amplifier in the package (PDMAX)
where:
TMAX = Maximum ambient temperature
θJA = Thermal resistance of the package
PDMAX = Maximum power dissipation of 1 amplifier
VCC = Total supply voltage
IqMAX = Maximum quiescent supply current of 1 amplifier
VOUTMAX = Maximum output voltage swing of the application
RL = Load resistance
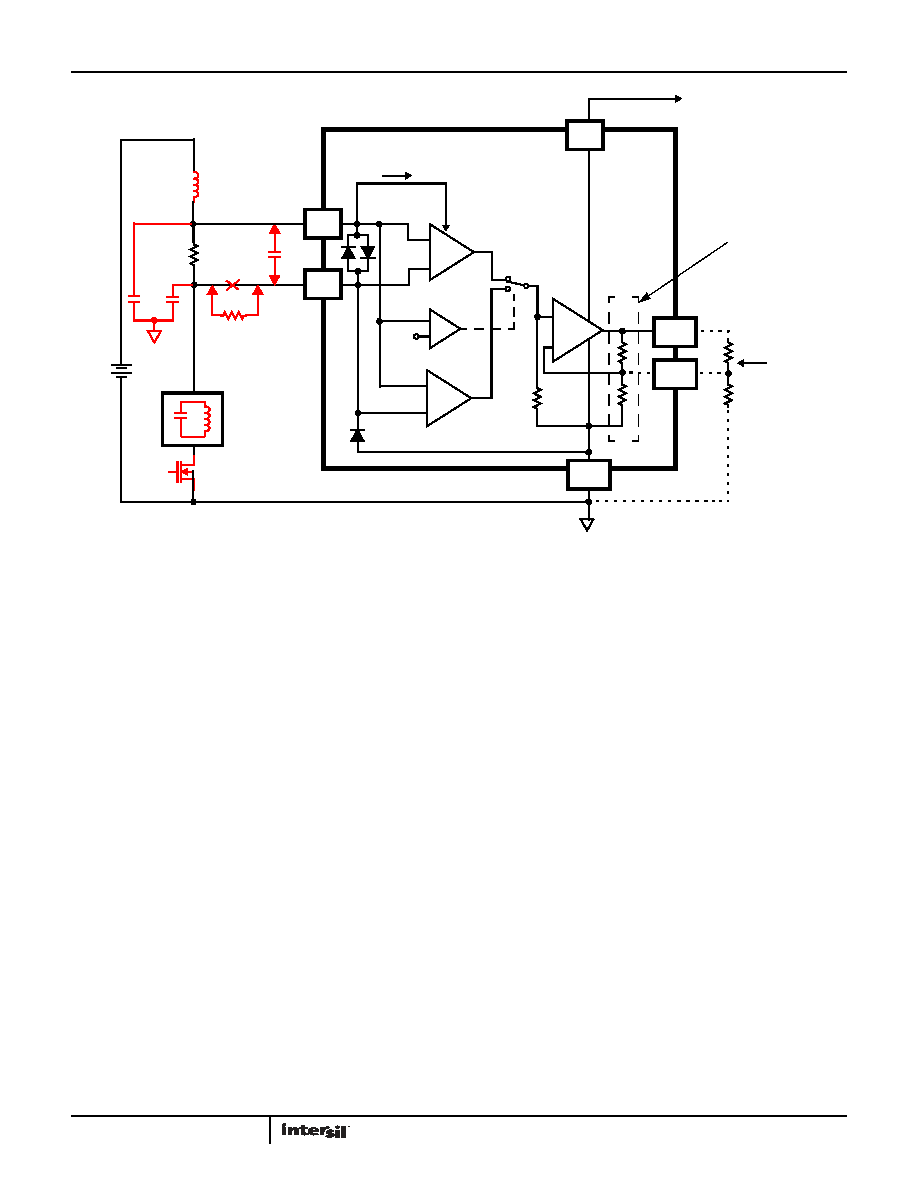
FIGURE 80. TYPICAL APPLICATION CIRCUIT
gmHI
gmLO
1.35V
+
-
VCC
ADJ
OPTION
ONLY
I = 2.86A
GND
RS
RS-
RP
(1m
TO
0.1)
0.1VDC
TO
28VDC
+
-
CD
LOAD
CM
2.7VDC
TO
28VDC
RS+
FB
OUT
FIXED GAIN
OPTION
ONLY
VOA
100
VOUTactual VOUT
ected
exp
–
VOUT
ected
exp
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
×
=
(EQ. 4)
(EQ. 5)
VOA
100
10.1 10
–
10
-------------------------
×
1%
==
TJMAX
TMAX θJAxPDMAXTOTAL
+
=
(EQ. 6)
PDMAX
VS IqMAX VS
(
- VOUTMAX)
VOUTMAX
RL
------------------------
×
+
×
=
(EQ. 7)
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| 36182C | INDUCTOR 1.8UH 7A SMD FLAT |
| 380LX101M500H452 | CAP ALUM 100UF 500V 20% SNAP |
| 843031-000 | BOOT MOLDED |
| 1-1589475-0 | CONN PLUG 65POS DUAL 30AWG |
| 202D953-4/42-0 | BOOT MOLDED |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| ISL28006FH20Z-T7 | 功能描述:放大器 IC 開發(fā)工具 ISL28006FH20Z MICRO PWR CUR SENSE AMP W/ RoHS:否 制造商:International Rectifier 產(chǎn)品:Demonstration Boards 類型:Power Amplifiers 工具用于評(píng)估:IR4302 工作電源電壓:13 V to 23 V |
| ISL28006FH20Z-T7A | 功能描述:放大器 IC 開發(fā)工具 ISL28006FH20Z MICRO PWR CUR SENSE AMP W/ RoHS:否 制造商:International Rectifier 產(chǎn)品:Demonstration Boards 類型:Power Amplifiers 工具用于評(píng)估:IR4302 工作電源電壓:13 V to 23 V |
| ISL28006FH-50EVAL1Z | 功能描述:放大器 IC 開發(fā)工具 ISL28006FH EVALRD 1 5LD GAIN OF 50 - RoHS:否 制造商:International Rectifier 產(chǎn)品:Demonstration Boards 類型:Power Amplifiers 工具用于評(píng)估:IR4302 工作電源電壓:13 V to 23 V |
| ISL28006FH50Z-T7 | 功能描述:放大器 IC 開發(fā)工具 ISL28006FH50Z MICRO PWR CUR SENSE AMP W/ RoHS:否 制造商:International Rectifier 產(chǎn)品:Demonstration Boards 類型:Power Amplifiers 工具用于評(píng)估:IR4302 工作電源電壓:13 V to 23 V |
| ISL28006FH50Z-T7A | 功能描述:放大器 IC 開發(fā)工具 ISL28006FH50Z MICRO PWR CUR SENSE AMP W/ RoHS:否 制造商:International Rectifier 產(chǎn)品:Demonstration Boards 類型:Power Amplifiers 工具用于評(píng)估:IR4302 工作電源電壓:13 V to 23 V |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。