- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄370425 > HAL710SF-E (Electronic Theatre Controls, Inc.) Chip-on-Glass (COG) Technology, 16 Characters x 2 Lines PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | HAL710SF-E |
| 廠商: | Electronic Theatre Controls, Inc. |
| 元件分類: | 霍爾效應(yīng)傳感器 |
| 英文描述: | Chip-on-Glass (COG) Technology, 16 Characters x 2 Lines |
| 中文描述: | 霍爾效應(yīng)的方向檢測傳感器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 5/12頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 165K |
| 代理商: | HAL710SF-E |
ADVANCE INFORMATION
HAL710
Micronas
5
2. Functional Description
The HAL 710 is a monolithic integrated circuit with two
independent subblocks consisting each of a Hall plate
and the corresponding comparator. Each subblock
independently switches the comparator output in
response to the magnetic field at the location of the
corresponding sensitive area. If a magnetic field with
flux lines perpendicular to the sensitive area is
present, the biased Hall plate generates a Hall voltage
proportional to this field. The Hall voltage is compared
with the actual threshold level in the comparator. The
subblocks are designed to have closely matched
switching points.
The temperature-dependent bias
–
common to both
subblocks
–
increases the supply voltage of the Hall
plates and adjusts the switching points to the decreas-
ing induction of magnets at higher temperatures. If the
magnetic field exceeds the threshold levels, the com-
parator switches to the appropriate state. The built-in
hysteresis prevents oscillations of the outputs.
In order to achieve good matching of the switching
points of both subblocks, the magnetic offset caused
by mechanical stress is compensated for by use of
“
switching offset compensation techniques
”
. Therefore,
an internal oscillator provides a two-phase clock to
both subblocks. For each subblock the Hall voltage is
sampled at the end of the first phase. At the end of the
second phase, both sampled and actual Hall voltages
are averaged and compared with the actual switching
point.
The output of comparator 1 (connected to S1) directly
controls the
‘
Count Output
’
. The outputs of both com-
parators enter the
‘
Direction Detection Block
’
control-
ling the state of the
‘
Direction Output
’
. The
‘
Direction
Output
’
is
’
high
’
if the edge at the output of
comparator 1 precedes that at comparator 2. In the
opposite case,
‘
Direction Output
’
is
’
low
’
. The previous
state of the
‘
Direction Output
’
is maintained between
edges of the
‘
Count Output
’
and in case the edges at
comparator 1 and comparator 2 occur in the same
clock period.
Shunt protection devices clamp voltage peaks at the
output pins and V
DD
-pin together with external series
resistors. Reverse current is limited at the V
DD
-pin by
an internal series resistor up to
15 V. No external
reverse protection diode is needed at the V
DD
-pin for
reverse voltages ranging from 0 V to
15 V.
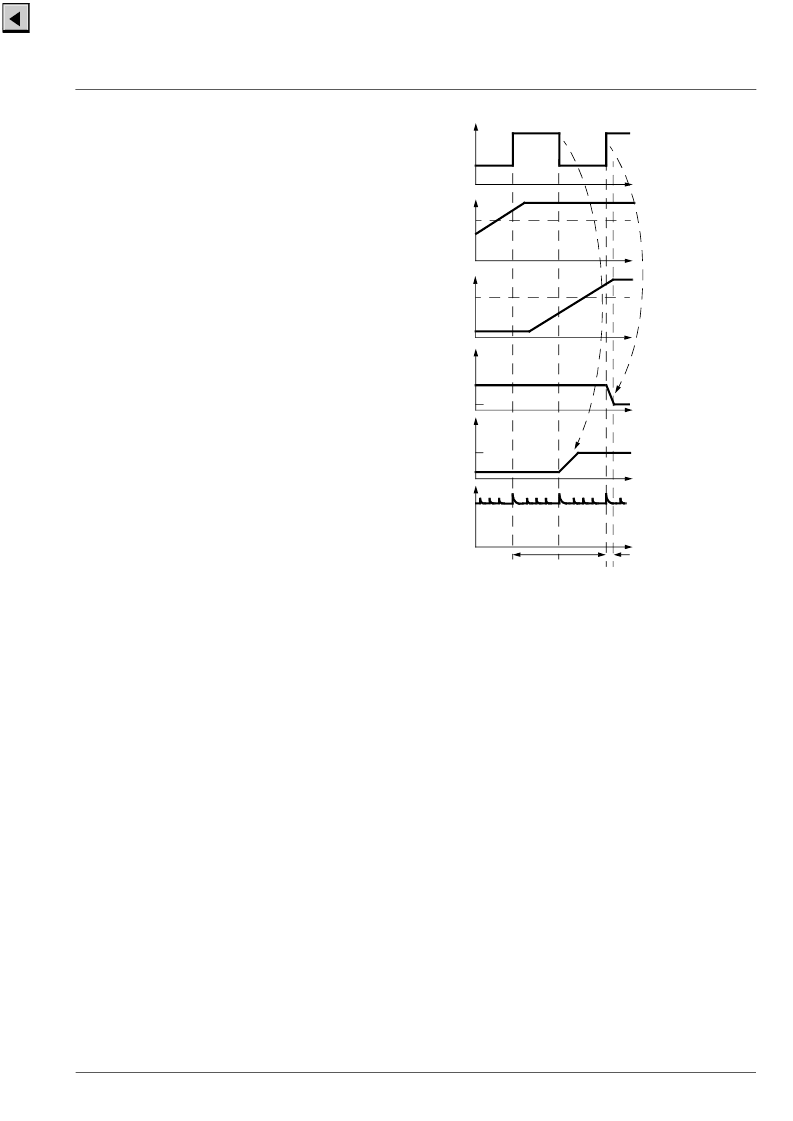
Fig. 2
–
1:
Timing diagram
I
dd
t
Direction
t
V
OH
V
OL
Count
t
V
OH
V
OL
B
S2
B
S2on
t
Clock
t
1/f
osc
t
f
B
S1
BS1
on
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| HAL710SF-K | Chip-on-Glass (COG) Technology, 16 Characters x 2 Lines |
| HAL710 | Hall-Effect Sensor with Direction Detection |
| HAL800 | Programmable Linear Hall Effect Sensor |
| HAL800UT-A | Programmable Linear Hall Effect Sensor |
| HAL800UT-C | Programmable Linear Hall Effect Sensor |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| HAL710SF-K | 制造商:MICRONAS 制造商全稱:MICRONAS 功能描述:Hall-Effect Sensors with Direction Detection |
| HAL730 | 制造商:MICRONAS 制造商全稱:MICRONAS 功能描述:Hall-Effect Sensors with Direction Detection |
| HAL730SF-E | 制造商:MICRONAS 制造商全稱:MICRONAS 功能描述:Hall-Effect Sensors with Direction Detection |
| HAL730SF-K | 制造商:MICRONAS 制造商全稱:MICRONAS 功能描述:Hall-Effect Sensors with Direction Detection |
| HAL740 | 制造商:MICRONAS 制造商全稱:MICRONAS 功能描述:Dual Hall-Effect Sensors with Independent Outputs |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。