- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄97935 > EVB72031 EVB72031 EValuation Board TH72031 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | EVB72031 |
| 英文描述: | EVB72031 EValuation Board TH72031 |
| 中文描述: | EVB72031評估板TH72031 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 7/12頁 |
| 文件大小: | 307K |
| 代理商: | EVB72031 |
EVB72001
315MHz FSK Transmitter
Evaluation Board Description
390127200101
Page 4 of 12
EVB Description
Rev. 002
Oct/02
PR
EL
IM
INA
RY
2 Functional Description
2.1
Crystal Oscillator
A Colpitts crystal oscillator with integrated functional capacitors is used as the reference oscillator for the PLL
synthesizer. The equivalent input capacitance CRO offered by the crystal oscillator input pin ROI is about
18pF. The crystal oscillator is provided with an amplitude control loop in order to have a very stable
frequency over the specified supply voltage and temperature range in combination with a short start-up time.
2.2
FSK Modulation
FSK modulation can be achieved by pulling the
crystal
oscillator
frequency.
A
CMOS-
compatible data stream applied at the pin
FSKDTA digitally modulates the XOSC via an
integrated NMOS switch. Two external pulling
capacitors CX1
and
CX2
allow
the
FSK
deviation
f and the center frequency f
c to be
adjusted independently. At FSKDTA = 0, CX2 is
connected in parallel to CX1 leading to the low-
frequency component of the FSK spectrum
(fmin); while at FSKDTA = 1, CX2 is deactivated
and the XOSC is set to its high frequency fmax.
An external reference signal can be directly AC-
coupled to the reference oscillator input pin
ROI. Then the transmitter is used without a
crystal. Now the reference signal sets the
carrier frequency and may also contain the FSK
(or FM) modulation.
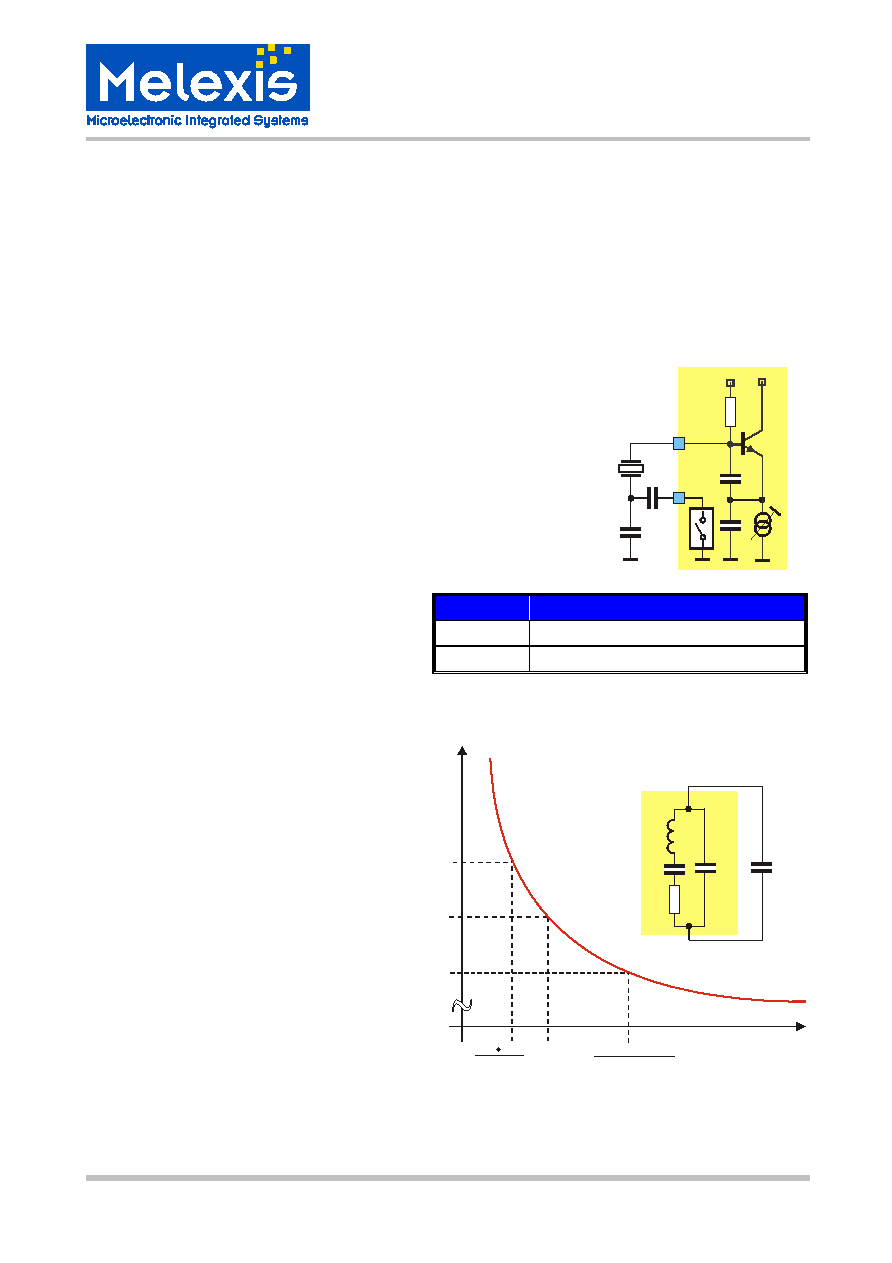
Fig. 2: Crystal pulling circuitry
FSKDTA
Description
0
fmin= fc -
f (FSK switch is closed)
1
fmax= fc +
f (FSK switch is open)
2.3
Crystal Pulling
A crystal is tuned by the manufacturer to the
required oscillation frequency f0 at a given load
capacitance
CL
and
within
the
specified
calibration tolerance. The only way to pull the
oscillation frequency is to vary the effective load
capacitance CLeff seen by the crystal.
Figure 3 shows the oscillation frequency of a
crystal as a function of the effective load
capacitance.
This
capacitance
changes
in
accordance with the logic level of FSKDTA
around the specified load capacitance. The
figure illustrates the relationship between the
external pulling capacitors and the frequency
deviation.
It can also be seen that the pulling sensitivity
increases with the reduction of CL. Therefore,
applications with a high frequency deviation
require a low load capacitance. For narrow
band
FSK
applications,
a
higher
load
capacitance could be chosen in order to reduce
the frequency drift caused by the tolerances of
the chip and the external pulling capacitors.
Fig. 3: Crystal pulling characteristic
CX2
VCC
XTAL
CX1
ROI
FSKSW
VEE
f min
fo
f
fmax
eff
CL
eff
CL
R1
C1
C0
L1
XTAL
CL
CX1 CRO
CX1+CRO
(CX1+CX2) CRO
CX1+CX2+CRO
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| EVB72032 | EVB72032 EValuation Board for TH72032 |
| EVKIT | 3.3V Palmtop Computer and Flash Memory Power Supply Regulator |
| EVM-1702 | EVM-1702 - EVALUATION MODULE |
| EW32F00BCW | SED1335 |
| EWSCASQXX | Buletooth Module |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| EVB72032 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:EVB72032 EValuation Board for TH72032 |
| EVB72035 | 制造商:MELEXIS 制造商全稱:Melexis Microelectronic Systems 功能描述:868/915MHz FSK/ASK Transmitter Evaluation Board Description |
| EVB72035-315-ASK-A | 制造商:MELEXIS 制造商全稱:Melexis Microelectronic Systems 功能描述:868/915MHz FSK/ASK Transmitter Evaluation Board Description |
| EVB72035-315-ASK-C | 制造商:MELEXIS 制造商全稱:Melexis Microelectronic Systems 功能描述:868/915MHz FSK/ASK Transmitter Evaluation Board Description |
| EVB72035-315-FM-A | 制造商:MELEXIS 制造商全稱:Melexis Microelectronic Systems 功能描述:868/915MHz FSK/ASK Transmitter Evaluation Board Description |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。