- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄369509 > BT137B_SERIES Triacs PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | BT137B_SERIES |
| 英文描述: | Triacs |
| 中文描述: | 雙向可控硅 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 147/224頁 |
| 文件大小: | 2697K |
| 代理商: | BT137B_SERIES |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁當(dāng)前第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁第155頁第156頁第157頁第158頁第159頁第160頁第161頁第162頁第163頁第164頁第165頁第166頁第167頁第168頁第169頁第170頁第171頁第172頁第173頁第174頁第175頁第176頁第177頁第178頁第179頁第180頁第181頁第182頁第183頁第184頁第185頁第186頁第187頁第188頁第189頁第190頁第191頁第192頁第193頁第194頁第195頁第196頁第197頁第198頁第199頁第200頁第201頁第202頁第203頁第204頁第205頁第206頁第207頁第208頁第209頁第210頁第211頁第212頁第213頁第214頁第215頁第216頁第217頁第218頁第219頁第220頁第221頁第222頁第223頁第224頁
Application Notes
AN1004
2002 Teccor Electronics
Thyristor Product Catalog
AN1004 - 5
http://www.teccor.com
+1 972-580-7777
Soldering Of Leads
A prime consideration in soldering leads is the soldering of
device leads into PC boards, heat sinks, and so on. Significant
damage can be done to the device through improper soldering. In
any soldering process, do not exceed the data sheet lead solder
temperature of +230
°
C for 10 seconds, maximum,
≥
1/16" from
the case.
This application note presents details about the following three
types of soldering:
Hand soldering
Wave soldering
Dip soldering
Hand Soldering
This method is mostly used in prototype breadboarding applica-
tions and production of small modules. It has the greatest poten-
tial for misuse. The following recommendations apply to Teccor
TO-92, TO-202, TO-220, and TO-218 packages.
Select a small- to medium-duty electric soldering iron of 25 W to
45 W designed for electrical assembly application. Tip tempera-
ture should be rated from 600 °F to 800 °F (300 °C to 425 °C).
The iron should have sufficient heat capacity to heat the joint
quickly and efficiently in order to minimize contact time to the
part. Pencil tip probes work very well. Neither heavy-duty electri-
cal irons of greater than 45 W nor flame-heated irons and large
heavy tips are recommended, as the tip temperatures are far too
high and uncontrollable and can easily exceed the time-tempera-
ture limit of the part.
Teccor Fastpak devices require a different soldering technique.
Circuit connection can be done by either quick-connect terminals
or solder.
Since most quick-connect 0.250” female terminals have a maxi-
mum rating of 30 A, connection to terminals should be made by
soldering wires instead of quick-connects.
Recommended wire is 10 AWG stranded wire for use with MT1
and MT2 for load currents above 30 A. Soldering should be per-
formed with a 100-watt soldering iron. The iron should not remain
in contact with the wire and terminal longer than 40 seconds so
the Fastpak triac is not damaged.
For the Teccor TO-218X package, the basic rules for hand sol-
dering apply; however, a larger iron may be required to apply suf-
ficient heat to the larger leads to efficiently solder the joint.
Remember not to exceed the lead solder temperatures of
+230 °C for 10 seconds, maximum,
≥
1/16" (1.59mm) from the
case.
A 60/40 or 63/37 Sn/Pb solder is acceptable. This low melting-
point solder, used in conjunction with a mildly activated rosin flux,
is recommended.
Insert the device into the PC board and, if required, attach the
device to the heat sink before soldering. Each lead should be
individually heat sinked as it is soldered. Commercially available
heat sink clips are excellent for this use. Hemostats may also be
used if available. Needle-nose pliers are a good heat sink choice;
however, they are not as handy as stand-alone type clips.
In any case, the lead should be clipped or grasped between the
solder joint and the case, as near to the joint as possible. Avoid
straining or twisting the lead in any way.
Use a clean pre-tinned iron, and solder the joint as quickly as
possible. Avoid overheating the joint or bringing the iron or solder
into contact with other leads that are not heat sinked.
Wave Solder
Wave soldering is one of the most efficient methods of soldering
large numbers of PC boards quickly and effectively. Guidelines
for soldering by this method are supplied by equipment manufac-
turers. The boards should be pre-heated to avoid thermal shock
to semiconductor components, and the time-temperature cycle in
the solder wave should be regulated to avoid heating the device
beyond the recommended temperature rating. A mildly activated
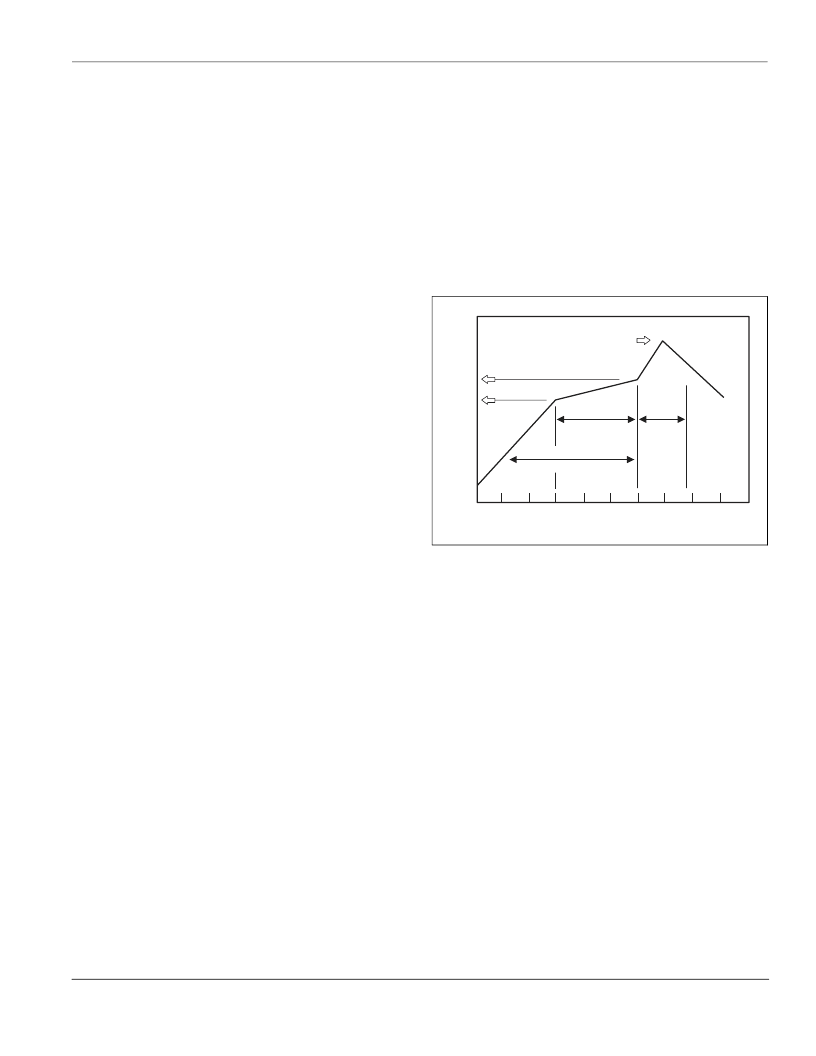
resin flux is recommended. Figure AN1004.12 shows typical heat
and time conditions.
Figure AN1004.12
Reflow Soldering with Pre-heating
Dip Soldering
Dip soldering is very similar to wave soldering, but it is a hand
operation. Follow the same considerations as for wave soldering,
particularly the time-temperature cycle which may become oper-
ator dependent because of the wide process variations that may
occur. This method is not recommended.
Board or device clean-up is left to the discretion of the customer.
Teccor devices are tolerant of a wide variety of solvents, and they
conform to MIL-STD 202E method 215 “Resistance to Solvents.”
Time (Seconds)
0
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
200
220
240
30
60
90
120
150
180
210
240
270
300
T
Pre-heat
Soak
Reflow
Cool
Down
0.5 - 0.6
C/s
1.3 - 1.6
C/s
<2.5
C/s
<2.5
C/s
Peak Temperature
220
C - 245
C
Soaking Zone
Reflow Zone
Pre-heating Zone
( 2-4 min MAX )
( 2 min. MAX )
60 - 90 s typical
( 2 min. MAX )
30 - 60 s typical
260
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| BT137B_SERIES_E | Triacs sensitive gate |
| BT137M_SERIES_E | Transient Voltage Suppressor Diodes |
| BT137S_SERIES | Transient Voltage Suppressor Diodes |
| BT137S_SERIES_E | Transient Voltage Suppressor Diodes |
| BT137SERIES | Transient Voltage Suppressor Diodes |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| BT137BSERIESD | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:Triacs logic level |
| BT137BSERIESE | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:Triacs sensitive gate |
| BT137F | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全稱:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:Triacs |
| BT137F-500 | 制造商:TECCOR 制造商全稱:TECCOR 功能描述:Thyristor Product Catalog |
| BT137F-500D | 制造商:TECCOR 制造商全稱:TECCOR 功能描述:Thyristor Product Catalog |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。