- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄368266 > PSD835F1-12J (意法半導(dǎo)體) Configurable Memory System on a Chip for 8-Bit Microcontrollers PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | PSD835F1-12J |
| 廠商: | 意法半導(dǎo)體 |
| 英文描述: | Configurable Memory System on a Chip for 8-Bit Microcontrollers |
| 中文描述: | 在8片位微控制器可配置存儲系統(tǒng) |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 94/110頁 |
| 文件大小: | 570K |
| 代理商: | PSD835F1-12J |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁當(dāng)前第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁
PSD835G2
PSD8XX Family
93
-90
-12
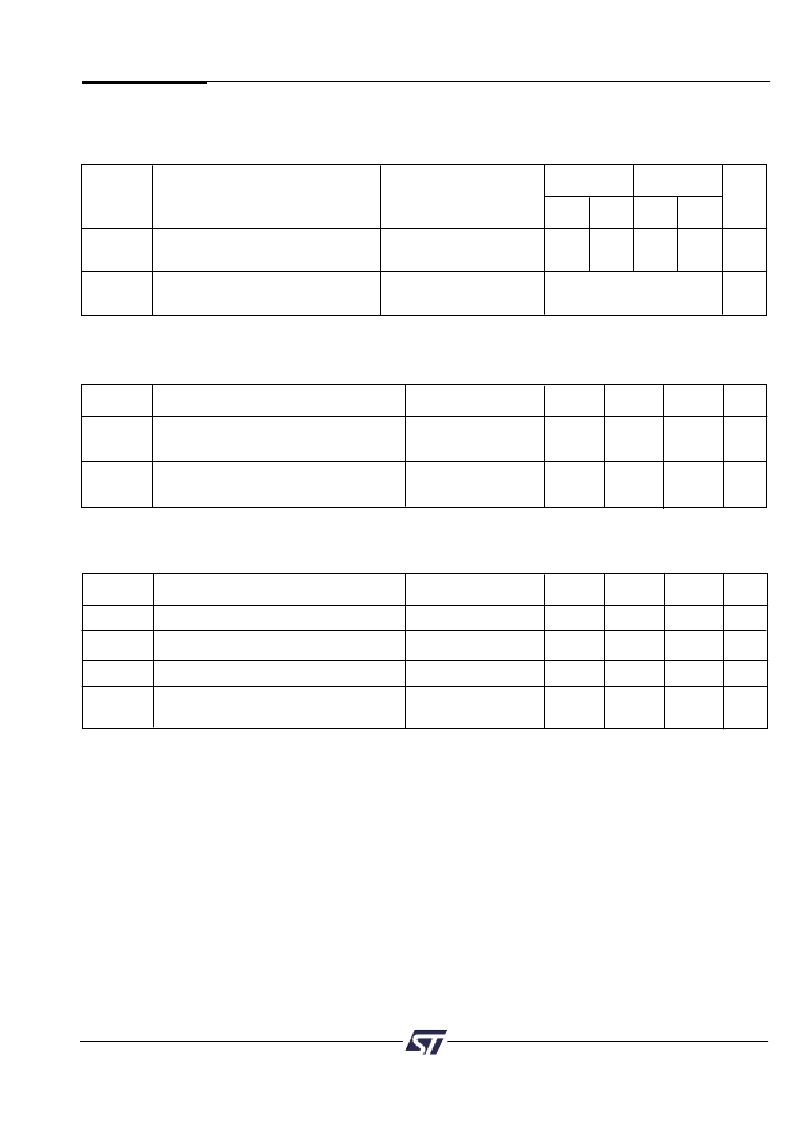
Symbol
Parameter
Conditions
Min
Max
Min
Max
Unit
t
LVDV
ALE Access Time from
Power Down
128
135
ns
Maximum Delay from APD Enable
to Internal PDN Valid Signal
t
CLWH
Using CLKIN Input
15
*
t
CLCL
(μs) (Note 1)
μs
Power Down Timing
(3.0 V to 3.6 V Versions)
Symbol
Parameter
Conditions
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
t
NLNH
Warm RESET Active Low Time (Note 1)
300
ns
t
OPR
RESET High to Operational Device
300
ns
t
NLNH-PO
Power On Reset Active Low Time
1
ms
Warm RESETActive Low Time
(Note 2)
t
NLNH-A
25
μs
Reset Pin Timing
(3.0 V to 3.6 V Versions)
NOTE:
1. t
CLCL
is the CLKIN clock period.
Microcontroller Interface – PSD835G2 AC/DC Parameters
(3.0 V to 3.6 V Versions)
Symbol
Parameter
Conditions
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
t
BVBH
VstbyDetection to VstbyonOutput
High
(Note 1)
20
μs
t
BXBL
VstbyOff Detection to Vstbyon
Output Low
(Note 1)
20
μs
V
stbyon
Timing
(3.0 V to 3.6 V Versions)
NOTE:
1. RESET will not abort Flash programming/erase cycles.
2. RESET will abort Flash programming or erase cycle.
NOTE:
1. Vstbyon is measured at V
CC
ramp rate of 2 ms.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PSD835F1-12JI | Configurable Memory System on a Chip for 8-Bit Microcontrollers |
| PSD835F3-A-12B81 | DIODE ZENER SINGLE 200mW 8.2Vz 20mA-Izt 0.05 3uA-Ir 6.5 SOD-323 3K/REEL |
| PSD835G3-A-12B81I | DIODE ZENER SINGLE 200mW 11Vz 20mA-Izt 0.05 2uA-Ir 8.4 SOD-323 3K/REEL |
| PSD835F3-A-12B81I | DIODE, ZENER, 12V, 5%, 1/2W, SOD-123 |
| PSD835G3-B-12B81 | DIODE SCHOTTKY SINGLE 40V 200mW 0.4V-vf 15mA-IFM 1mA-IF 0.2uA-IR SOD-323 3K/REEL |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| PSD835G2-70U | 功能描述:靜態(tài)隨機存取存儲器 5.0V 4M 70ns RoHS:否 制造商:Cypress Semiconductor 存儲容量:16 Mbit 組織:1 M x 16 訪問時間:55 ns 電源電壓-最大:3.6 V 電源電壓-最小:2.2 V 最大工作電流:22 uA 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TSOP-48 封裝:Tray |
| PSD835G2-90U | 功能描述:靜態(tài)隨機存取存儲器 5.0V 4M 90ns RoHS:否 制造商:Cypress Semiconductor 存儲容量:16 Mbit 組織:1 M x 16 訪問時間:55 ns 電源電壓-最大:3.6 V 電源電壓-最小:2.2 V 最大工作電流:22 uA 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TSOP-48 封裝:Tray |
| PSD835G2-90UI | 功能描述:靜態(tài)隨機存取存儲器 5.0V 4M 90ns RoHS:否 制造商:Cypress Semiconductor 存儲容量:16 Mbit 組織:1 M x 16 訪問時間:55 ns 電源電壓-最大:3.6 V 電源電壓-最小:2.2 V 最大工作電流:22 uA 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TSOP-48 封裝:Tray |
| PSD835G2V-12UI | 功能描述:靜態(tài)隨機存取存儲器 3.0V 4M 120ns RoHS:否 制造商:Cypress Semiconductor 存儲容量:16 Mbit 組織:1 M x 16 訪問時間:55 ns 電源電壓-最大:3.6 V 電源電壓-最小:2.2 V 最大工作電流:22 uA 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TSOP-48 封裝:Tray |
| PSD835G2V-90U | 功能描述:靜態(tài)隨機存取存儲器 3.0V 4M 90ns RoHS:否 制造商:Cypress Semiconductor 存儲容量:16 Mbit 組織:1 M x 16 訪問時間:55 ns 電源電壓-最大:3.6 V 電源電壓-最小:2.2 V 最大工作電流:22 uA 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TSOP-48 封裝:Tray |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。